5533
A Vendor-Agnostic MRSI Acquisition and Reconstruction XML Descriptor Format1Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, UCSF, San Francisco, CA, United States
Synopsis
The evaluation of MRSI data is complex because data files are encoded with vendor specific file formats and there is a lack of standardized tools for reconstruction. A standard way to describe raw MRSI data is necessary for the reconstruction of sequences utilizing parallel and non-Cartesian sampling strategies. In this work we are developing a vendor neutral data format to define MRSI sequences with arbitrary k-space trajectories that can be used by reconstruction software to understand the data acquisition scheme. This file format is XML-based and uses the ISMRMRD header as a basis for its scheme.
Purpose
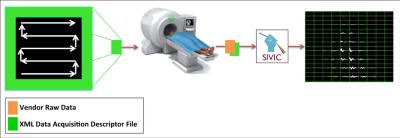
The purpose of this study is to develop a vendor neutral data format to define MRSI sequences with arbitrary k-space trajectories that can be used by reconstruction software to understand the data acquisition scheme. The evaluation of MRSI data is complex because data files are encoded with vendor specific formats and there is a lack of standardized tools for reconstruction. Many of these data formats do not contain a full description of the acquisition methods and therefore a priori knowledge of the specific pulse sequence is required to interpret the raw data and to implement the reconstruction and analysis. This problem is further exacerbated by the use of parallel and non-Cartesian sampling patterns, which are becoming more common and render raw data unintelligible without a complete description of the methods applied. The ISMRMRD1 group has already made great progress towards developing a data format capable of describing 3D MRI sequences. The present work extends the ISMRMD concepts to MRSI acquisitions in the form of a Data Acquisition Descriptor (DAD) file format. The purpose of this file format is to clearly document all acquisition parameters for an arbitrary MRSI acquisition such that when combined with the raw data enough information will be available to fully reconstruct the acquisition. This file is to be installed on scanners and used to acquire the data, as well as being transmitted with the raw data for reconstruction. Additionally using a standard XML format has the added benefit of being portable to multiple scanner platforms. This will facilitate the use of advanced acquisition techniques in multi-center trials. We have implemented tools for reading and writing DAD files as well as developing reconstruction tools for GE-Pfiles acquired with a DAD file using the SIVIC2,3 framework. This workflow is diagrammed in figure 1.Implementation
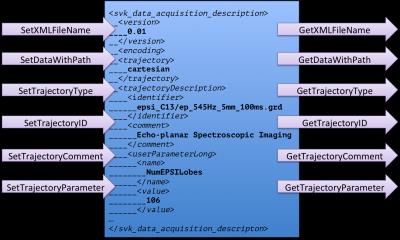
The ISMRMRD format contains an XML header that has many parameters in common with those required for the MRSI acquisition. While developing our format we have conformed to the scheme of the ISMRMRD wherever possible. Once properly vetted we hope to propose additions to the ISMRMRD to enable support for MRSI data. An API for reading and writing DAD files has been implemented in the SIVIC open-source framework. This API is accessed through the svkDataAcquisitionDescriptor class, which is diagrammed in figure 2. The API provides C/C++ interfaces for standard fields in the schema as well as a basic XPath implementation for arbitrary XML elements. This simultaneously provides an extensible interface for setting custom variables as well as a standard interface for parameters defined in the schema.Results
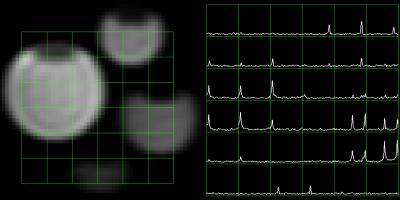
A DAD file was generated using the SIVIC API for the acquisition of a symmetric EPSI sequence. This DAD file was used to acquire both 1H and 13C data on phantoms on a GE 3T scanner. These DAD files were installed on the scanner along with a custom EPIC sequence that parses the DAD file using the SIVIC API. During the acquisition the DAD file is loaded into memory, the parameters necessary to drive the acquisition are extracted, and then the DAD file is modified with additional any parameters specific to that particular acquisition such as the FOV, resolution, position, etc. Once the acquisition is complete the scanner outputs the modified DAD file along with the raw data. These files were then copied off the scanner and the data were reconstructed on a research workstation using the SIVIC GUI. Results are shown in figure 3.Discussion
With the advent of more advanced sampling techniques current vendor data formats do not provide sufficient information to fully reconstruct raw MRSI data. This means that research groups are required to develop custom reconstruction routines for each sequence. The DAD file provides an extensible, standard-based format that can be used to sufficiently describe a raw data acquisition for reconstruction. It permits a single processing routine to be used to reconstruct data acquired using different methodologies. In addition using DAD files simplifies porting sequences between vendors, as a single sequence that can interpret the DAD file format is able to support data acquisition on multiple platforms. This will also speed up sequence development, as the modification of a DAD file is significantly easier then developing a vendor-specific sequence.Conclusion
The DAD file facilitates the acquisition, dissemination, and reconstruction of MRSI data for cutting-edge acquisition techniques. It also helps to promote the use of a standard lexicon that was develop for imaging data through the ISMRMRD. Using this scheme makes these new sequences easier to develop and more portable, facilitating their use in multi-center studies.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant P41 EB013598.References
1. ISMRMRD. Available at: http://ismrmrd.github.io/.
2. SIVIC. Available at: http://sivic.sourceforge.net.
3. Crane, J. C., Olson, M. P. & Nelson, S. J. SIVIC: Open-source, standards-based software for DICOM MR spectroscopy workflows. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2013, (2013).
Figures