5508
J-difference semi-LASER for GABA editing1GE Healthcare, Berlin, Germany
Synopsis
The performance of a J-difference spectral editing technique based on the across vendor implementation of semi-LASER with high bandwidth GOIA-WURST adiabatic gradient modulated refocusing pulses for a GABA+ and macromolecule-suppressed GABA protocol was investigated. Phantom measurements show a TE dependence of the edited 3ppm GABA signal that allows using the longer TE of 80ms to implement a macromolecular-suppressed protocol with higher signal compared to a PRESS based implementation.
Purpose
There is significant attention within the neuroscience community in the detection and quantification of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by J-difference spectral editing [1]. There exist various implementations based on BASING [2] or MEGA [3] combined with PRESS localization. The high bandwidth of the refocusing pulses in the semi-LASER sequence [4-6] reduces the Chemical Shift Displacement (CSD) error compared to other implementations like MEGA-PRESS.
This study will investigate the performance of a J-difference spectral editing technique [7] based on the across vendor implementation of semi-LASER [8] with high bandwidth GOIA-WURST adiabatic gradient modulated refocusing pulses for a GABA+ and macromolecule-suppressed (MM) GABA protocol [9].
Methods
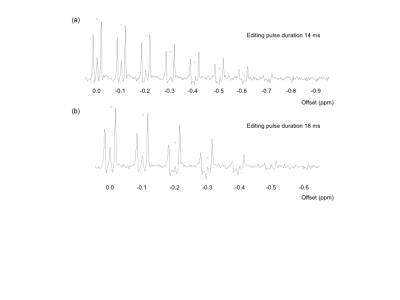
A semi-LASER sequence with crusher scheme described in [4] including two J-difference editing pulses with TE/2 time separation (for TE ≥ 72ms) and additional crushers [10] (Figure 1) was implemented on a clinical 3T scanner (MR750w, GE Healthcare). A 4.2ms asymmetric excitation pulse (FWHM 3.7kHz) and 4.5ms adiabatic gradient modulated GOIA-WURST refocusing pulses (FWHM 10kHz) [11] were used. The editing pulse was either a 14ms Gaussian (1% truncation, FWHM 109Hz = 0.85ppm) or a 18ms Gaussian (10% truncation, FWHM 63Hz = 0.5ppm). Spectra (20 × 20 ×20 mm3, TR = 2s, 64 averages/scheme) were acquired using a GABA phantom (10mM GABA, flask diameter = 8cm) using the GEM Head coil.
Transmit gain (TG) was set using a voxel based Bloch-Siegert STEAM technique [12] followed by additional calibration of the VAPOR suppression pulses. Edited spectra with TE between 68ms (editing pulse separation of 37ms) and 96ms were acquired as well as with different editing ON frequencies both for the GABA+ (TE = 72ms, ON = 1.9ppm to 1.0ppm in steps of 0.1ppm) and MM-suppressed protocol (TE = 80ms, ON = 1.9ppm to 1.3ppm in steps of 0.1ppm). The editing OFF frequency was always set to 7.5ppm. The MM-suppressed protocol was also acquired with ON = 1.9ppm and OFF = 1.5ppm and GABA+ protocol with a J-difference editing PRESS protocol (ON = 1.9ppm and OFF=7.5ppm) and reduced flip-angle SLR refocusing pulses [13]. Data processing was implemented in MATLAB (coil combination, frequency and phase correction).
Results and Discussion
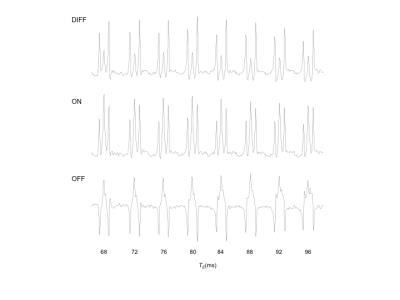
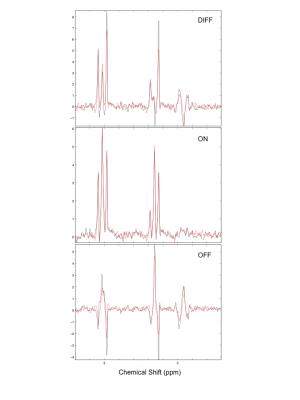
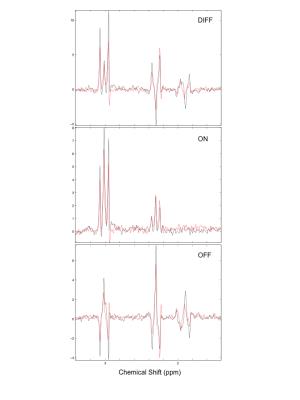
The GABA signal at 1.9ppm is fully suppressed in the ON scheme (Figure 4) and the editing signal at 3.0ppm shows a dependency on TE in the range of 68ms to 96ms, especially the center peak (Figure 2). The frequency dependence of the editing signal for the two protocols is shown in Figure 3. Due to the lower FWHM the 18ms Gaussian shows a smaller signal at 0.4ppm offset with an integral close to 0. Nevertheless this still results in a slightly different result for the 3ppm signal with GABA+ and MM-suppressed editing scheme (Figure 4). The semi-LASER implementation shows higher 3ppm signal compared to the PRESS based due to the higher bandwidth of the pulses but also due to the use of reduced flip-angle SLR refocusing pulses [13] in the PRESS implementation as shown in [14].Conclusion
With the separation of the two editing pulses of TE/2 the minimum TE for the implemented J-difference semi-LASER sequence is slightly longer compared to a PRESS based implementation. Due to the small changes in signal amplitude of the edited 3ppm GABA signal with increasing TE the proposed TE for MEGA-PRESS in [9] of 80ms also shows good results. Even though the integral over the 3ppm signal for 0.4ppm frequency offset is close to 0 there is still an effect of the GABA signal that needs to be taken into account for real model fitting like LCModel compared to fitting a Gaussian line-shape like GANNET [15].Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Mullins et al. Neuroimage 2014; 86: 43–52
2. Star-Lack et al. Magn Reson Med 1997; 38: 311–321
3. Mescher et al. NMR Biomed 1998; 11: 266-272
4. Öz et al. Magn Reson Med 2011; 65: 901–910
5. Boer et al. NMR Biomed 2011; 24: 1038–1046
6. Scheenen et al. Magn Reson Med 2008; 59: 1–6
7. Noeske et al. ISMRM Workshop on Spectroscopy 2016; 5
8. Deelchand et al. ISMRM Workshop on Spectroscopy 2016
9. Edden et al. Magn Reson Med 2012; 68, 657–661
10. Wijnen et al. NMR Biomed 2015; 28: 514–522
11. Andronesi et al, J Magn Reson 2010; 203: 283–293
12. Toncelli et al. ISMRM 2015; 4695
13. Raidy et al. ISMRM 1995; 1020
14. Near et al. Magn Reson Med 2013; 70: 1183–1191.
15. Edden et al. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014; 40: 1445–1452
Figures