5495
Inter and intra-subject repeatability study of GABA Editing using MEGA-PRESS and ImSpecial Sequence1Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Menlo Park, CA, United States, 3Center for Cognitive and Neurobiological Imaging, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Synopsis
GABA editing with frequency-insensitive macromolecule suppression using improved MEGA-SPECIAL sequence (ImSpecial) has been developed. By using a very frequency-selective editing pulse with a pulse width of 30 ms, macromolecule was suppressed without applying a lysine-symmetric editing. An inter and intra-subject repeatability studies were conducted to evaluate GABA editing with MEGA-PRESS and ImSpecial. Compared with GABA+/Cre levels using MEGA-PRESS, GABA/Cre levels using ImSpecial is about 40% less with lower variations for both inter and intra-subject repeatability studies, demonstrating significant MM suppression achieved using ImSpecial.
Purpose
In-vivo measurement of Gamma-aminobutyric-acid (GABA) using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) offers valuable information for understanding brain function. Based on J-difference editing, the most widely used sequence for MRS GABA detection is MEGA-PRESS, where the editing pulse is applied to GABA C3 resonance at 1.9 ppm for the "ON" case to flip the outer peaks of its C4 triplet resonance at 3 ppm.1 For the "OFF" case, the editing pulse is generally applied at 7.5 ppm, which is symmetrical to the water resonance at 4.7 ppm. The major problem with this editing scheme is the coediting of the lysine-containing macromolecules due to the wide transition band of the editing pulses. At 68 ms, MM typically contribute 40% to 60% to the 3 ppm resonance in the edited spectrum, complicating the quantification of GABA. As a result, the 3 ppm resonance in the non-MM-suppressed edited spectrum is often labeled as GABA+.
Recently, B0-inhomogeneity-insensitive GABA editing with MM suppression has been developed using improved MEGA-SPECIAL (ImSpecial) sequence.2,3 Based on 1D ISIS spatial localization and single spin echo, this editing technique allows much longer and more selective editing pulses than used in MEGA-PRESS. To reduce susceptibility and motion artifacts in the ISIS direction, out-of-voxel suppression was achieved using a 1D echo planar (EP) version of spectroscopic imaging mode (SIAM).4 Because of the selectivity of the editing pulses, significant MM suppression is achieved without compromise of GABA editing. Here we compare GABA editing with MEGA-PRESS and ImSpecial in an inter and intra-subject repeatability study to demonstrate reduced variation in GABA measurement with MM suppression using ImSpecial.
Methods
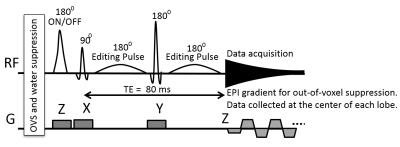
ImSpecial sequence incorporating a 1D echo-planar readout for out-of-voxel artifact suppression is shown in Figure 1. In vivo MRS data were acquired on a GE 750 3T scanner using a Nova 32 channel coil [3]. The editing pulses for MEGA-PRESS were 14 ms 180º Gaussian pulses and were applied at 1.9/7.5ppm with TE/TR=68ms/2s. For ImSpecial, the editing pulse were 30ms Gaussian pulse and applied at 1.9/7.5ppm with TE/TR=80ms/2s. GABA editing was performed on a 30x30x30mm voxel in occipital lobe. For inter-subject study, data were collected from five healthy subjects while for intra-subject study, data were collected from the same healthy subject in five sessions. For both MEGA-PRESS and ImSpecial, 256 transients were acquired with an 8:40 minute scan time. GABA levels were estimated by integrating the edited peak from 2.9 to 3.1ppm and referenced to Cre for quantification.Results
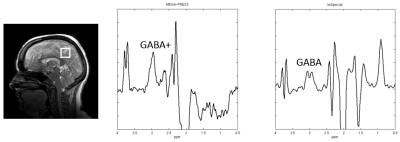
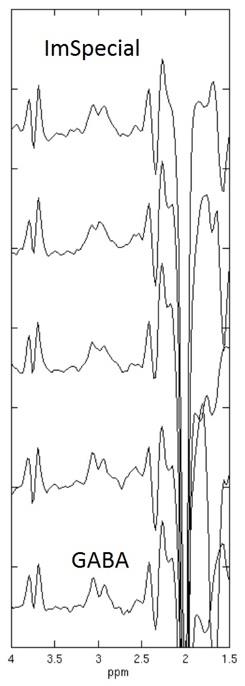
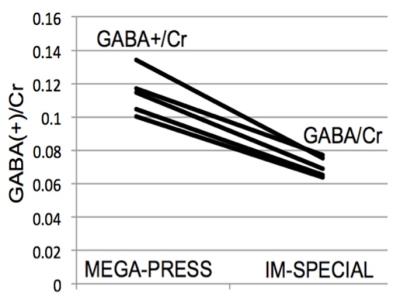
Representative edited spectra using MEGA-PRESS and ImSpecial are shown in Figure 2. All five edited spectra using ImSpecial for the intra-subject repeatability study are shown in Figure 3. For MEGA-PRESS, the edited spectra at 3ppm showed a broad singlet while for ImSpecial they showed a pseudo-triplet consistently at 3ppm. Shown in Figure 4 are the GABA(+)/Cre values for the inter-subject study using MEGA-PRESS and ImSpecial. The mean and standard deviation of GABA+/Cre is 0.114 and 0.013 using MEGA-PRESS while the mean and standard deviation of GABA/Cre is 0.07 and 0.006 using ImSpecial. For the intra-subject repeatability study, the mean and standard deviation of GABA+/Cre is 0.1134 and 0.0068 using MEGA-PRESS while the mean and standard deviation of GABA/Cre is 0.06578 and 0.00387 using ImSpecial.Conclusion
Compared with GABA+/Cre levels using MEGA-PRESS, GABA/Cre levels using ImSpecial is about 40% less with lower variations for both inter and intra-subject repeatability studies, demonstrating significant MM suppression achieved using ImSpecial.Acknowledgements
Lucas foundation, GE Health Care, NIH EB 015891, Stanford Center for Cognitive and Neurobiological ImagingReferences
[1] Mescher M, Merkle H, Kirsch J, Garwood M, Gruetter R. Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression. NMR Biomed. 1998;11(6):266-72.
[2] Near J, Simpson R, Cowen P, Jezzard P. Efficient gamma-aminobutyric acid editing at 3T without macromolecule contamination: MEGA-SPECIAL. NMR Biomed. 2011;24(10):1277-85.
[3] Gu M, Hurd R, Noeske R, Rokem A, Baltusis L, Spielman D. Macromolecule Suppressed GABA Editing with Single Spin-Echo and Out-Of-Voxel Artifact Suppression. Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance and Medicine, Toronto, Canada. 2015:4692.
[4] Hurd R, Sailasuta N. Elimination of artifacts in short echo proton spectroscopy. Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance and Medicine, Vancouver, Canada. 1997:1453.
Figures