5385
Effects of tCDS to vmPFC functional connectivity after 36 hours total sleep deprivation: a resting-state fMRI study1CT and MRI, The General Hospital of The Air Force People's Liberation Army, Beijing, People's Republic of China, 2Cognitive and Mental Health Research Center, Beijing Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
There are fifteen health indibiduals recruited in order To explore the changes of functional connectivity in vmPFC with tDCS stimuli after 36 hours sleep deprivation. Colleceting resting-state fMRI data under the tDCS stimuli and sham stimuli conditions. Using the vmPFC as the seed region,and then the time courses of all brain voxels were correlated separately with the mean time course generated from the ROI by Pearson cross-correlation. Finally, we found that tDCS can effectively mediate the dysfunction of brain connectivity.
Introduction
Sleep deprivation (SD) is defined as a state of sleep loss and accompanied with a series of psychological and physiological dysfunction, especially decision making. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a new treatment for resisting the negative effect by SD, but the neural mechanism of tDCS treatment is still remain unclear. The ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) was reported as an important region with decision making.We used functional MRI to explore the changes of functional connectivity in vmPFC with tDCS stimuli after 36 hours sleep deprivation, which may provide the experiment mechanism for tDCS effect on SD.Method
Fifteen right-hand healthy individuals with mean age of 20.94 were recruited in this study. According to a self-controlled design, subjects were examined twice with resting-state fMRI scanning under the tDCS stimuli and sham stimuli conditions. The tDCS stimuli was supported by CNC-3 II type treatment instrument produced by Luoyang Kangbei Biological Engineering Co., ltd. We placed thecathode(electrode sizes 3 x 3cm) over the rightmastoid and the anode over the left mPFC. The stimulation intensity is 1mA and the duration of tDCS stimuli is 20 minutes. For sham stimulation, we turned the device off after 20 seconds[1]. All MRI data were acquired through a 3.0-Tesla discovery MRI scanner (GE). The data were firstly preprocessed with spm8 software. The ROI of vmPFC was defined as a 10-mm-radius spheres centered on MNI coordinates(x = 0, y = 51, z = -10) from left and right mPFC[2]. Finally the mean time series of all voxels were extracted within ROI. The time courses of all brain voxels were correlated separately with the mean time course generated from the ROI by Pearson cross-correlation.Results
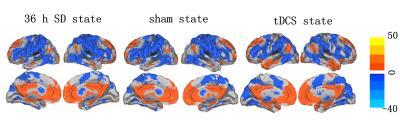
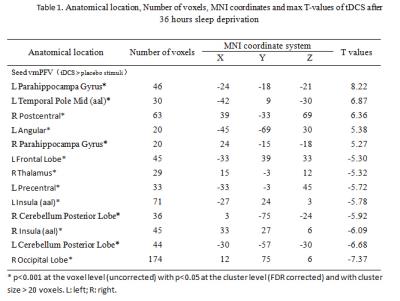
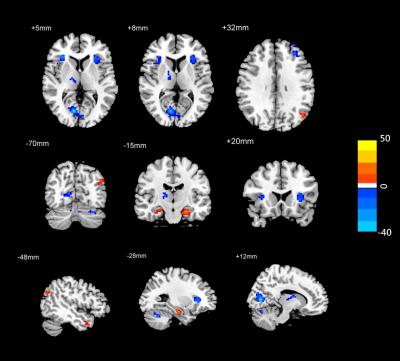
Compared with sham conditing after 36 hours TSD, subjects with tDCS stimuli exhibited significantly increased functional connectivity in the bilateral parahippocampa gyrus, right poster central, left temporal pole middle and angular; and showed significant deceased functional connectivity in the right occipital lobe, bilateral insula, right thalamus, left precentral and bilateral cerebellum posterior lobe.Conclusion
These results suggests that tDCS can effectively mediate the dysfunction of brain function by adjust the communication of different brain areas after 36 hours TSD.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Marilyne Joyal, Shirley Fecteau. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Effects on Semantic Processing in Healthy Individuals [J]. Brain Stimulation, 2016, 9(2016): 682-691.
[2] Liu, x., Hairston, J., Schrier, M., et al. Common and distinct networks underlying reward valence and processing stages: A meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 2011, 35(5): 1219-1236.
Figures