5276
Topologically Reorganized Functional Connectivity in Children with Abacus Training1Bio-X Laboratory, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
Cognitive training is an interesting topic in Neuroscience. Abacus-mental based calculation (AMC) training improves math ability that indicates it might affect functional connectivity architecture. Modularity analysis showed between-group differences in visual network and cingulo-opercular network (CON). Compared to the controls, increased local efficient observed in visual network, while decreased in CON in AMC experts. An alternative reason is that visual-spatial strategy involving in AMC training rather than languish strategy, leading to different trend to networks related to different function. Our findings shed light on topological reorganization of functional connectivity induced by AMC training.
Introduction
Training can cause structural and functional reorganization of brain network1. Abacus-based mental calculation (AMC) is the method to manipulate numbers by imagining an abacus in mind. Long-term AMC training can improve remarkable capabilities of human cognition, accompanied by inducing brain functional and structural plasticity2. However, very little is known about whether brain functional connectivity would be altered by AMC training. Here, we employed graph theory and modularity analysis to identify relevant subnetworks that subserve specific functions. Also we provided a framework to test whether and how AMC training affects the topological architecture of brain functional connectivity.Method
One hundred sixty-two children participated in our study, including ninety children accepting one to five years (average = 2.68) AMC training as the abacus group (aged , 39 males) and seventy-two children without any abacus knowledge as the control group (aged , 32 males).
All data were collected using a 1.5T Philips scanner with a standard head coil. The resting state images were collected using a T2*-weighted EPI sequence with the following parameters: TR/TE=2000/50ms, flip angle=90°, FOV=230mm×230mm, matrix =64×64, slice thickness/ gap = 5 mm/0.8 mm, and 22 slices in 180 scans. High resolution anatomical scan was also acquired (TR/TE = 25/4.6 ms, flip angle = 15°, FOV=256mm×256mm, acquisition matrix=256×256, reconstruction voxel size=1×1×1mm3 , 150 slices in the sagittal plane).
The first 5 images were discarded, followed by slice-timing correction, realign, normalization by DARTEL, smoothing, filter, detrend and nuisance regression as image processing by using SPM12. We extracted time courses from 251 nodes and computed the nodal-wise Pearson correlation matrix. We used a set of thresholds beginning from 2% network density to remove weak correlations and get binary network matrix. ‘Modularity fine-tune algorithm’ was employed to identify modules as subnetworks. Network properties were computed respectively for each subnetwork and compared between two groups by two sample t-test.
Result
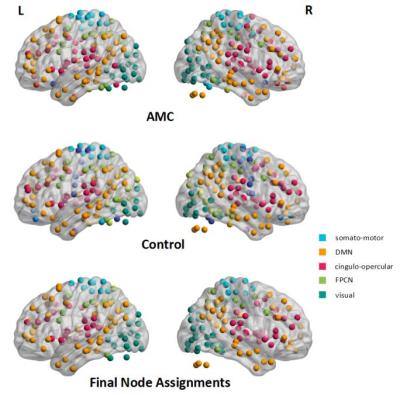
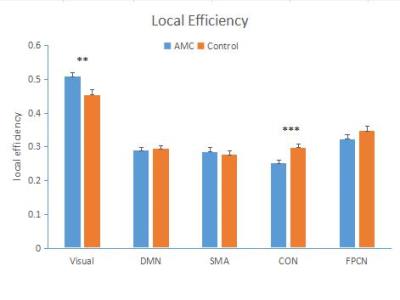
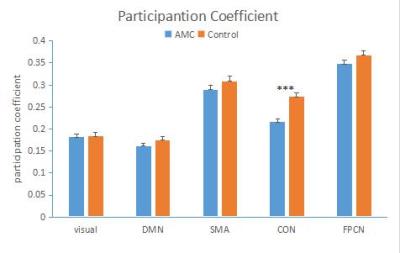
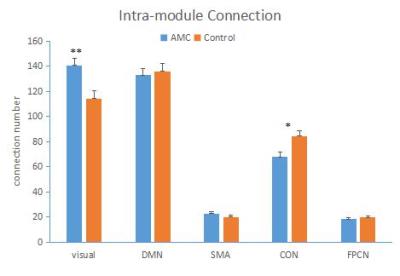
The modules we identified were similar in two groups and previous literatures3, including 5 subnetworks: visual network, default mode network (DMN), somato-motor (SMA), cingulo-opercular network (CON) and fronto-partietal control network (FPCN) (Fig. 1). Separate analysis in each functional network showed AMC training mainly induced significant differences in two networks. Higher local efficiency and intra-connections were found in AMC group in visual network than the controls (Fig. 2 and Fig. 4). While increased local efficiency, intra-connections and participation coefficient were observed in the cingulo-opercular network in the control group, comparing with the AMC group(Fig. 2, Fig. 3, and Fig. 4).Discussion
In line with previous studies, our results showed human brain is topologically organized into a set of functionally specific and spatial distributed networks (Fig. 1). We also observed increased local efficiency and intra-module connections of visual network in AMC group, and decreased local efficiency and participation coefficient in CON (Fig. 2, Fig. 3,Fig. 4). We hypothesize that individuals with AMC expertise employ visual-spatial strategy rather than languish strategy4. Long-term training might lead to more information transferred and processed through visual network, and in turn, languish-related network (CON)5 might decrease its importance in the human functional network.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the NSFC (No. 030900389 and No. 31270026)References
1.Ma L, Shalini Narayana, Donald A. Robin, Peter T. Fox, Xiong J. 2011. Changes occur in resting state network of motor system during 4 weeks of motor skill learning. NeuroImage 58:226_233.
2.Hu Y, Geng F, Tao L, Hu N, Du F, Fu K, Chen F. 2011. Enhanced white matter tracts integrity in children with abacus training. Human Brain Mappig 32:10-21.
3.Power JD, Cohen A, Nelson S, Wig G, Barnes K, Church J, Vogel A, Laumann T, Miezin F, Schlaggar B et al. 2011. Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron. 72(4):665–678.
4.Dehaene S, Spelke E, Pinel P, Stanescu R, Tsivkin S .1999. Sources of mathematical thinking: Behavioral and brain-imaging evidence. Science 284 (5416):970-974.
5. Vaden K I, Kuchinsky S E, Cute S L, et al. The cingulo-opercular network provides word-recognition benefit[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2013, 33(48): 18979-18986.
Figures