5241
SCITH Approach Reveals Stable Functional Connectivity1Biophysics, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States
Synopsis
Current Multi-Echo fMRI approach can only acquire up to three echoes due to the fast T2* decay. We hypothesized that more echo will improve the capability of increasing the BOLD CNR and denoise accuracy, and we managed to acquire up to six echoes using our within TR keyhole based approach: SCITH. Our preliminary data showed increased BOLD CNR and resting-state functional connectivity(FC), less temporal FC fluctuation and more consistent inter-subject FC in the same population.
Purpose
Multi-echo (ME) acquisition and its independent component analysis (ICA)-based denoising process have been demonstrated to be a powerful approach to improve individual functional connectivity (FC),1,2 but the number of echoes is limited due to the fast T2* decay. The purpose of this study is to increase the number of echoes and determine whether the increased number of echoes improves the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) and FC reliability.Methods
To acquire more echoes within a limited time, we implemented a within-repetition-time (TR) keyhole-based approach: Spatial Compensated Intrashot Turbo key-Hole (SCITH). The rationale is that the periphery area of k-space will be excluded since it contains mainly anatomical details that can be considered unchanged within sub-second. The hypothesis is that SCITH acquisition can be used to increase the BOLD contrast, and the resulting CNR enhancement will effectively improve the reliability of functional MRI (fMRI). The acquisition diagram is illustrated in Figure 1. In SCITH, the first two echoes are fully sampled, and all subsequent echoes are keyhole acquired within the center half, along the phase-encoding (PE) direction in k-space. The PE polarity is reversed between echoes to implement a dynamic fieldmap correction.3 The samples excluded by the keyhole-acquired echoes were substituted with samples from the fully acquired echoes. The (echo-time) TE-dependent signal decay was compensated following equation 1 $$S_{keyhole}=S_{full}\times\exp\frac{TE_{full}-TE_{keyhole}}{T2^{\star}}$$ by fitting T2* for each line using samples from the first two echoes. Important scan parameters include TR=2.5 s, matrix size=64×64×22, in-plane resolution=3.75 mm, slice thickness=4+1.5 mm, ASSET=2. TEs and reconstructed images of each echo are listed in Figure 2. Eight healthy, age-matched (25±3 years) young subjects were recruited for a one-hour fMRI scan on a GE MR750 3T human scanner; Subject 001 was scanned twice, with a one-week gap between scans. Each scan includes two task fMRIs (30 s on/off right hand only finger tapping, total duration of five minutes), one using a conventional single echo (SE), TE=25 ms acquisition and one using the SCITH approach. Similarly, two five-minute resting-state fMRIs were acquired with parameters identical to the task fMRI. The SCITH acquired data were denoised with MEICA, and SE data were denoised with standard noise regressors.1Results
SCITH + MEICA (hereafter referred to as SCITH for simplicity) showed higher CNR in the activated region. Figure 3 presents the results of the task fMRI; the time series and activation pattern from Subject 005 are presented as an example. In the SCITH data, the time series has a smoother profile, and the activation pattern has fewer statistically significant voxels and a higher peak value. Similar results also are reported by a peer’s recent work.4 Both the individual and group results showed higher CNR in the SCITH data, except for Subject 006 (whose the field map correction result was ill-functioned).
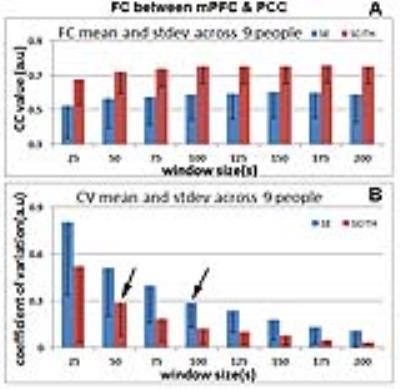
SCITH showed more reliable intra-subject and inter-subject resting-state FC(Figure 4). We measured the FC between the medial prefrontal cortex and prefrontal cortex regions using a sliding window approach at eight different window sizes. At each window size, the FC mean (Figure 4A) and coefficient of variation (CV), that is, the ratio of standard variation over mean (Figure 4B), across a sliding window series were measured. At all window sizes, SCITH data have stronger FC than the SE data (Figure 4A), which indicates better BOLD CNR in the resting state. Less between-subject variation indicates that FC is more consistent across all subjects, which increased the statistical power of the specific population. On the other hand, at all window sizes, the SCITH data have a smaller CV than the SE data (Figure 4B). Specifically, when comparing the group CV mean across different window sizes, the group CV mean of the SCITH data at the 50 s window is the same as the CV mean of the SE data at the 100 s window (indicated by arrows). The SCITH data reach the same level of CV using a shorter sliding window than the SE data, which potentially will reduce the scan duration required for data of the same statistical significance. The individual FC comparison also showed stronger a FC mean and smaller CV in eight out of nine subjects; results are not shown.
Conclusion
Our preliminary results demonstrated SCITH approach successfully improved BOLD CNR and FC reliability. Not only did the SCITH approach reduce individual’s FC dynamics, it also reduced the between-subject FC variation, which makes SCITH a more reliable imaging option for both individual and group fMRI studies. Next, we plan to compare SCITH to conventional ME method to measure the improvement from more echoes.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Kundu P, Inati SJ, Evans JW, et al. Differentiating BOLD and non-BOLD signals in fMRI time series using multi-echo EPI. Neuroimage, 2012, 60 (3): 1759-1770.
2. Kundu P, Brenowitz ND, Voon V, et al. Integrated strategy for improving functional connectivity mapping using multiecho fMRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110 (40): 16187-16192.
3. Weiskopf N, Klose U, Birbaumer N, et al. Single-shot compensation of image distortions and BOLD contrast optimization using multi-echo EPI for real-time fMRI. Neuroimage, 2005, 24 (4): 1068-1079.
4. Gonzalez-Castillo J, Panwar P, Buchanan LC, et al. Evaluation of multi-echo ICA denoising for task based fMRI studies: Block designs, rapid event-related designs, and cardiac-gated fMRI. Neuroimage, 2016
Figures