5169
A Novel Method to Increase SNR of GRAPPA Reconstruction1UIH America, Inc., Houston, TX, United States, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
We propose a novel method to improve GRAPPA reconstruction when blood vessel pulsation artifacts appear. It removes the artifacts in the ACS lines, and boosts the SNR of GRAPPA reconstruction. Volunteer study confirmed that the proposed method improved image quality of GRAPPA reconstruction in 3T FSE knee scan.
Introduction
GRAPPA [1] reconstruction is a widely used parallel imaging technique that trades SNR for imaging speed. Therefore, low SNR is one of the major drawbacks of GRAPPA. Recently, we observed that excessive noise/low SNR in GRAPPA reconstruction when blood vessel pulsation artifacts were significant in 2D fast spin echo (FSE) images of knee. We hypothesize that the SNR degradation was caused by the existence of pulsation artifacts in GRAPPA ACS lines, and propose a new GRAPPA reconstruction method to boost image SNR by suppressing the pulsation artifacts in ACS lines in image space. The new method was tested in volunteer studies, and the image quality improvement was confirmed by a radiologist.Methods
Parallel imaging methods such as GRAPPA and SENSE [2] utilize coil sensitivity information either implicitly or explicitly. If the coil sensitivity map is corrupted by artifacts, the reconstructed image will be degraded. Since ACS lines contain coil sensitivity information used in GRAPPA reconstruction, pulsation artifacts in ACS lines leads to sub-optimal GRAPPA reconstruction.
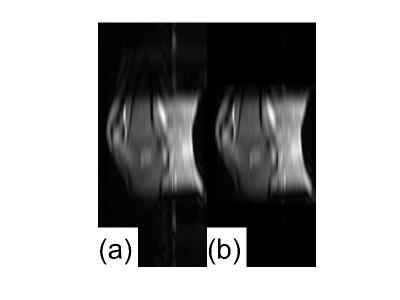
Our study focused on GRAPPA reconstructed FSE image of knee. Since the blood vessel pulsation is problematic, two saturation bands were placed above and below the region of interest. In our scenario, blood vessel pulsation caused high signal in the saturated region and distorted the sensitivity map, see Fig 1a. A degraded sensitivity map may cause noise amplification due to the unfolding process of GRAPPA reconstruction. A novel solution was proposed to remove the blood vessel pulsation artifacts of ACS lines in the saturated region in image space by applying a spatial mask. More specifically, it has five steps: 1) Zero-padding ACS lines to the size of full k-space; 2) transform ACS lines into image space; 3) mask out signal in the saturated region, see Fig 1b; 4) transform back to k-space; 5) remove all zero-padded k-space lines. Since the proposed method removes pulsation artifacts of ACS lines in saturation bands, we expect the GRAPPA reconstruction quality will be improved.
Two
healthy volunteers underwent FSE knee scan on a 3.0T uMR 750 MR system (United
Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China). Imaging parameters were: matrix 384 x
384, phase resolution 80%, 32 slices, band width: 200Hz/pixel, FOV: 150mm x
150mm, TR: 2000 ms, TE: 36.8 ms, slice thickness: 3.5 mm, flip angle: 150
degree. Images were reconstructed off-line and reviewed by a radiologist.
Results
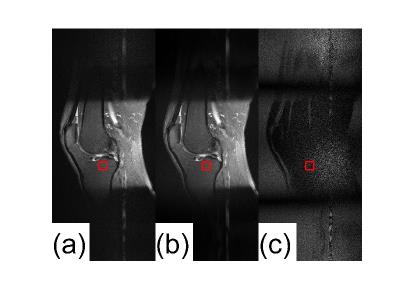
Figure 2 demonstrates the GRAPPA reconstruction using traditional and proposed methods. It is clear that pulsation artifacts suppression in ACS lines improves the GRAPPA reconstruction SNR. SNR of the ROI shown in the figure has more than 30% increase. Images reconstructed with traditional and the proposed GRAPPA methods were anonymized and randomized. A radiologist who reviewed the images concluded the proposed method improved image quality.Discussion
We found that the blood vessel pulsation artifacts in ACS lines cause excessive noise in GRAPPA reconstruction. A novel method was proposed to suppress the artifacts in ACS lines. Volunteer studies show that it improves the image SNR and the image quality significantly. The proposed method is a straight-forward way to clean contaminated k-space ACS lines / training data used in k-space parallel imaging techniques. It applies to the scenario that MR signal in part of FOV is nulled, e.g. due to saturation band or low proton density. Other Reconstruction methods such as SPIRiT [3] may also benefit from this method when the training data is contaminated by artifacts.
Conclusion
We proposed a novel method to improve GRAPPA reconstruction when blood vessel pulsation artifacts appear. Volunteer study demonstrates that it improves GRAPPA reconstruction SNR significantly. It is an easy-to-implement method, and potentially can be applied to other parallel imaging techniques. Further research is warranted to understand the effectiveness and the robustness of this new technique in a larger patient cohort.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Griswold, et al. Mag Res. Med. 47(6): 1202-1210 (2002);
2. Pruessmann, et. al. Mag Res. Med. 42(5): 952-962 (1999);
3. Lustig, et. al. Mag Res. Med. 64(2): 457-471 (2010);
Figures