5148
Texture analysis based on intra-voxel incoherent motion MR imaging for the differentiation of benign and malignant bone tumors1Zhengzhou University First Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou,Henan, People's Republic of China, 2Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
This work investigated and evaluated the role of texture analysis based on intra-voxel incoherent motion(IVIM) MR imaging to characterize the bone tumors,and furtherly evaluate the ability of the texture parameters to differentiate benign and malignant bone tumors by using a couple of classifiers, which might be helpful for clinical diagnosis and studies. The texture parameters have the ability to character the bone tumor and the naïvebayes classifier showed the best performance in the differentiation of benign and malignant bone tumors.
Purpose
Recent studies have shown that IVIM can reflect the information of perfusion and diffusion in complex biological tissues in various tumors1,2.And texture analysis was also applied for the characterization of the tumors in recent studies3. In this work, the texture analysis based on IVIM parameter maps were carried out to investigate the application on bone tumors and furtherly evaluate the ability of these texture parameters to differentiate benign and malignant tumors by using a couple of classifiers.Methods
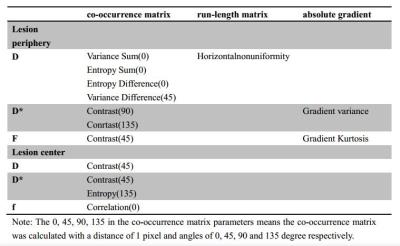
Thirty-one patients (14 males and 16 female saged 36.7±19.2 years old) with bone tumors (diagnosed according to pathological biopsy) were included in this study.Based on the WHO Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone(2012) criteria, 30 patients were divided into two groups:11 for benign tumors and 19 for malignancies. All the patients were scanned by MR IVIM sequence based on a 3T MR scanner (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands). The IVIM scanning was performed with 10 b-values of 0, 10, 30, 50, 75, 100, 150, 300, 500, 800s/mm2.The IVIM related parameters of tissue diffusivity (D), pseudo-diffusion coefficient (D*) and perfusion fraction (f) were calculated by using a Philips development software (Version 3.0). The corresponding texture parameters (based on histogram, co-occurrence matrix, run-length matrix, absolute gradient) were extracted within the periphery (ROI1)and center (ROI2) of the lesions by using Mazda software. Totally 77×2×3 (77 texture parameters within 2 ROIs of periphery and center regions for 3 IVIM parameter maps of D, Dstar and f) were obtained for each subject. All the above texture parameters extracted from benign and malignant patients were compared by using Mann-Whitney U test with SPSS software (version 16.0). A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. And furtherly, the parameters with a significant difference were combined as the feature vectors for the furtherly classification by using naïvebayes, random forest and artificial neural network classifiers.Results
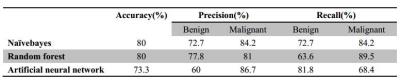
The results revealed that some texture parameters showed a significant difference between benign and malignant bone lesions (P<0.05) and the details were summarized in Table 1. There is no any histogram parameter showed a statistical difference and the co-occurrence matrix parameters showed the best ability for the bone lesion diagnosis.The classification results of the benign and malignant bone lesion were summarized in Table 2. The results showed that the naïvebayes showed the best performance with a high classification accuracy (80%), precision (72.7% and 84.2% for benign and malignant lesions) and recall (72.7% and 84.2% for benign and malignant lesions).Discussion
The texture parameters can be used to character the spatial distribution of the image intensities, which can reflect the texture features of the lesions. This work aims to demonstrate the feasibility of using texture analysis to characterize the bone lesions based on IVIM imaging. The results showed some texture feature are effective in the differentiationof benign and malignant bone lesion. The classifiers especially the naïvebayes method showed the ability to differentiate the malignant from benign lesions and this would be helpful for the clinical diagnosis and corresponding treatment plans.In the future, more patients will be included in our study and furtherly to evaluate the clinical application of texture analysis and classifiers in clinical bone diseases.Conclusions
Texture parameters based on D value, D* value and f value images are effective to demonstrate the characteristics of bone lesions. And classifier such as naïvebayes is able to identify patients with a high accuracy by using texture parameters, which might be helpful to distinguish malignant tumors from benign ones.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Vincenza Granata, Roberta Fusco, Orlando Catalano, et al. Intra-voxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) for Hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with histologic grade [J].Oncotarget,2016,[Epub ahead of print].
2. C. Federau, R. Meuli, K. O’Brien, et al. Perfusion Measurement in brain gliomas with intra-voxel incoherent motion MRI [J].Am J Neuroradiol,2014,35: 256-262.
3. Karoline Skogen, Anselm Schulz, Johann Baptist Dormagen, et al. Diagnostic performance of texture analysis on MRI in grading cerebral gliomas[J].European Journal of Radiology,2016,85:824-829.