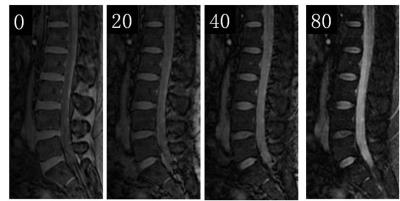
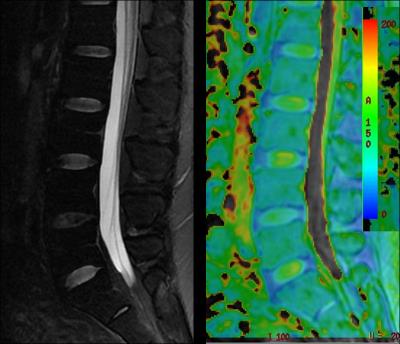
5141
T1rho Imaging Quantification of Early Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Pilots on 3.0T Magnetic Resonance1Radiology Department, The First People’s Hospital of Jingzhou,Jingzhou, China,People’s Republic of, Jingzhou, People's Republic of China, 2Department of CT&MRI, Air Force General Hospital, Beijing, China, People’s Republic of, 3GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, People’s Republic of
Synopsis
Degenerative
disc disease is an occupational disease of the military pilots, which seriously
influcenes their health and normal
training. Early disc degeneration begins with changes in biochemical
compositions which is mainly characterized by proteoglycan lose and cannot be
detected on conventional MRI imaging[1-2]. T1rho is
a quantitative imaging technique to reflect changes in the extracellular
matrix, such as modifications in the intervertebral disc PG content[3].
In this study,Bivariate correlation
analysis was performed to compare T1rho values to the degenerative grade, disc
space level, age and flight time of the pilots. T1rho values of Lumbar
intervertebral discs in pilots demonstrated significantly negative correlations
with degenerative grade, age and flight time, except for disk space levels. T1rho
can be potentially used as a valid clinical method in the quantitative diagnosis
of early intervertebral disc degeneration in asymptomatic Pilots.
Purpose
Method
Results
On pseudo-colour imaging of T1rho-map of normal Lumbar intervertebral discs, the central nucleus pulposus was displayed as orange red or yellow, while the surrounding gradually became blue. The annulus fibrosus was homogeneous blue, with a clear boundary between the nucleus pulposus and the annulus fibrous. The nucleus pulposus which degenerated seriously (Pfirrmann Ⅳ, Ⅴ) was homogeneous blue but without a clear boundary.(Figure.2)
The T1rho values of 170 intervertebral discs were achieved and categorized as grade 1 (n=25), grade 2 (n=29), grade 3 (n=84), grade 4 (n=29), and grade 5 (n=3). T1rho values were significantly negatively correlated with Pfirrmann grade Ⅰ~Ⅳ(r=-0.901, P<0.01) and ages (r=-0.709, P<0.01). There was a significant difference in T1rho values between Pfirrmann grade Ⅰ-Ⅳ(F=277.892,P<0.01) and among all the age groups (Welch=77.406,P<0.01). However, there was no significant difference in the T1rho values observed between each level (P>0.05). T1 rho values were significantly pairwise different among the flight time groups (Welch=41.641,P<0.01).
Discussion and conclusion
T1rho values of Lumbar intervertebral discs in pilots demonstrated significantly negative correlations with degenerative grade, age and flight time, except for disk space levels. T1rho can be potentially used as a valid clinical method in the quantitative diagnosis of early intervertebral disc degeneration in asymptomatic Pilots.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Southern E P, Fye M A, Panjabi M M, et al. Disc degeneration: a human cadaveric study correlating magnetic resonance imaging and quantitative discomanometry. Spine.2000; 25(17): 2171-2175.
[2 ] Luoma K, Vehmas T, Riihimäki H, et al. Disc height and signal intensity of the nucleus pulposus on magnetic resonance imaging as indicators of lumbar disc degeneration. Spine. 2001;26(6): 680-686.
[3 ] Johannessen W, Auerbach J D, Wheaton A J, et al. Assessment of human disc degeneration and proteoglycan content using T1ρ-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Spine. 2006;31(11): 1253-1257.
Figures