5004
Assessment of Spontaneous Mechanical Activities in Musculature by Simultaneous Multi-Slice Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Fiber-Tractography Data Validation1Section on Experimental Radiology, University of Tuebingen, Tuebingen, Germany, 2Institute of Signal Processing and System Theory, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 3Biomedical Magnetic Resonance, University of Tuebingen, Tuebingen, Germany
Synopsis
Simultaneous multi-slice diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) was applied on human right calf for imaging Spontaneous Mechanical Activity in Musculature (SMAM) in multiple slices in order to improve assessment of the spatial extension of these spontaneous activities. For data validation, diffusion-tensor images (DTI) were acquired with subsequent fiber tractography to fuse anatomical fiber orientation to spontaneous events in DWI. High accordance between both modalities and reliable application of simultaneous multi-slice diffusion-weighted imaging is demonstrated.
Introduction
Spontaneous
Mechanical Activities in Musculature (SMAM) are observable in series of DWI as
signal voids1, but each SMAM is a unique event which cannot be
repeated for a second measurement. Previous works have shown that SMAMs have a
three dimensional extension. However, the utilized imaging sequence was
restricted to single-slice acquisition (by 2D echoplanar imaging)1.
To get a more detailed insight into the spatial characteristics of SMAM in DWI,
simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) DWI was applied on human musculature to acquire
multiple slices with diffusion-sensitizing at the same time. Moreover, DTI were
acquired to show the relation between SMAMs and muscle fiber orientation based
on fiber tractography.Methods
MR acquisition: Three healthy volunteers (age: 35±15 years, BMI: 25.8±3 kg/m²) were examined on a 3 T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany ) with a 15-channel Tx/Rx-coil. A series of 500 DW images was acquired with spin-echo SMS-DWI by the parallel multi-slice sequence provided by CMRR, University of Minnesota2. Optimized protocol parameters were: matrix-size: 64 x 48; FoV: 192 x 144 mm²; TE: 34.6 ms; TR: 500 ms; slice-thickness: 6 mm; b-value: 100 s/mm²; BW: 2695 Hz/px with 4 simultaneous excited slices (slice-distance: 200 %). It was ensured that all reference images for kernel calibration in SMS acquisition were free of SMAM distortions. Inter-slice leakage as underlying process of signal voids in adjacent slices was excluded by applying the SMS-DWI with same parameters on a motion phantom, which is able to generate local incoherent motion in one slice of the concurrent excited slices. DTI was performed with DWI-EPI sequence with parameters: matrix-size: 64 x 64; FoV: 192 x 192 mm²; number of slices: 40; TE: 26 ms; TR: 10600 ms; slice-thickness: 3 mm; b-value: 0/700 s/mm²; BW:2365 Hz/px, averages: 6, diffusion-directions: 12. Post-Processing: SMAM-affected regions in SMS-DWI and DTI were slice-wise evaluated by an automatic graph-based segmentation approach3. To ensure reliable DTI datasets, SMAM-affected regions were discarded before averaging. Diffusion-tensor fitting was executed based on the method from Barmpoutis et al.4,5, which incorporates positive definiteness constraints in tensor fitting. For muscle fiber tracking, the Euler method according to Basser et al.6 was implemented in MATLAB® (The Mathworks, Inc., USA) with 1 mm step-size and stop tracking conditions following to Lansdown et al.7: FA (fractional anisotropy) < 0.1 or FA > 0.5, fiber angle > 90°. Evaluation: SMS-DWI datasets were evaluated regarding the multiple occurrences of SMAMs in adjacent slices within same muscle region. Furthermore, the in-plane distance between SMAMs was evaluated to exclude possible FoV/4-shifts due to inter-slice leakage. The relation between anatomical fiber orientation and SMAMs in adjacent slices is evaluated by fusion of both modalities.Results & Discussion
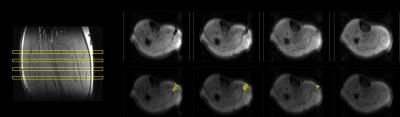
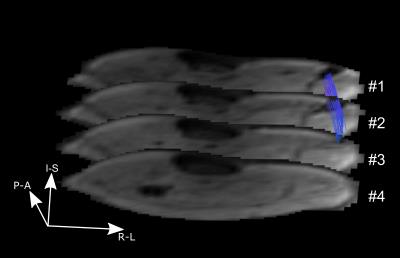
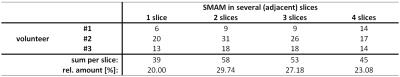
Distance between SMAMs in adjacent slices differs clearly from a critical FoV/4-shift and thus no inter-slice leakage as underlying reason is assumed. Fig. 1a shows the coronal view of human right calf T1-weighted anatomical image with the four simultaneous excited DWI slices (indicated in yellow). Three of four slices show a SMAM in m. gastrocnemius medialis (Fig. 1b #1-#3 and segmentation in Fig. 1c). In Fig. 2, the fusion of fiber tractography and SMS-DWI is given. It can be seen that there is a high accordance which shows that the SMAM extension is along fiber orientation. Tab. 1 shows the distribution of SMAMs over 1, 2, 3 or 4 adjacent slices in same muscle region. It can be seen that only 20 % of all SMAM are restricted to one slice in SMS-DWI, whereas 29.74 %, 27.18 % and 23.08 % were visible in 2, 3 or 4 slices, respectively, which is equivalent to a longitudinal spread of 18, 36 or 54 mm (in good accordance to 15-70 mm detected in previous work in sagittal images1).Conclusion
It is shown that SMS-DWI for the assessment of SMAMs in multiple slices is a feasible technique with promising results. Moreover, the relation between the extension of SMAMs and underlying anatomical fiber orientation was demonstrated by mapping DTI information on SMS-DWI slices.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]:
Steidle G, and Schick F.: "Addressing spontaneous signal voids in
repetitive single-shot DWI of musculature: spatial and temporal patterns in the
calves of healthy volunteers and consideration of unintended muscle activities
as underlying mechanism". NMR Biomed
2015;28:810-10
[2]: Moeller, S. et al.:
"Multiband multislice GE-EPI at 7 tesla, with 16-fold acceleration using
partial parallel imaging with application to high spatial and temporal
whole-brain fMRI". Magn Reson Med
2010;63(5):1144-1153
[3]:
Schwartz, M. et al.: "Graph-based segmentation of signal voids in time
series of diffusion-weighted images of musculature in the human lower
leg". Proc. ISMRM 2016,
Singapore
[4]: Barmpoutis, A. and Vemuri,
B.C.: "A Unified Framework for Estimating Diffusion Tensors of any order
with Symmetric Positive-Definite Constraints". Proc. ISBI 2010, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
[5]: Barmpoutis, A. et al.:
"Tensor splines for interpolation and approximation of DT-MRI with
applications to segmentation of isolated rat hippocampi". IEEE Trans Med Imag 2007;26(11):1537-46
[6]: Basser, P.J. et al.: "In
Vivo Fiber Tractography Using DT-MRI Data". Magn Reson Med 2000;44:625-632
[7]: Lansdown, D.A. et al.:
"Quantitative diffusion tensor MRI-based fiber tracking of human skeletal
muscle". J Appl Physiol
2007;103:673-681
Figures