4960
Quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective self-control study between single and dual input arterial function1Department of Radiology, Nantong Third People’s Hospital, Nantong University, Nantong, People's Republic of China, 2GE healthcare, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
This prospective self-control study was designed to explore if there is difference between single and dual arterial input function (AIF) for analyzing quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Our result showed that there is no statistical difference of quantitative parameters Ktrans, Ve, Vp between single and dual AIF groups. The parameter Kep was different between two groups, but it had a parallel relationship with CD34-MVD of HCC, for that, dual AIF didn’t have advantage over single AIF.
Introduction
Dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is a MR imaging method based on contrast agent pharmacokinetics, which can noninvasively investigate microvascular structure and function. A appropriate arterial input function (AIF) is critical to the accuracy of DCE-MRI. The liver has a dual blood supply derived from the hepatic artery and portal vein, and most researchers are preferred to use dual AIF to estimate quantitative parameters of liver and liver diseases. However, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accepts blood supply predominantly from hepatic artery, using single AIF for hepatic DCE-MRI analysis is a controversy and divergence to date. This study was designed to explore the difference between single and dual AIF for analyzing quantitative DCE-MRI of HCC.Methods
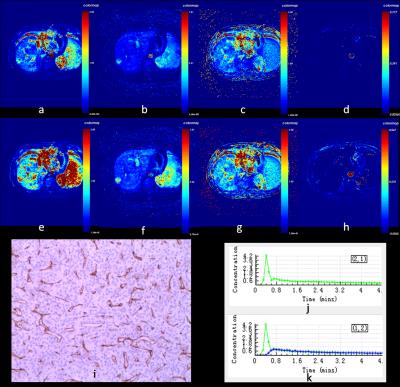
This prospective self-control study was approved by the local research and ethics committee and each patient informed consent was obtained. The newly admitted patients who were diagnosed as HCC by conventional MRI were performed by DCE-MRI scans. These patients had not received surgery, interventional therapy, and any other treatment before. The patients who had embolus in their portal vein were excluded in this study. DCE-MRI data were processed based on the Extended Tofts Linear model with both single and dual AIF to estimate quantitative parameters including Ktrans, Kep, Ve, Vp of each HCC. The CD34-microvascular density (CD34-MVD) of tumor was measured in surgical specimen. The differences of quantitative parameters between single and dual AIF groups were analyzed using the Paired-sample t test. The Spearman correlation coefficient was determined between quantitative parameters and CD34-MVD, and the correlation coefficient was compare between two groups by U test. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
Thirty-seven patients with forty HCC in total were included in this study. Twenty-seven HCC got surgical removal and CD34-MVD of tumor was measured. The difference of Kep of forty HCC was statistically significant between single and dual AIF groups (P<0.05), but the differences of Ktrans, Ve, Vp between these two groups were not (P>0.05, P>0.20, P>0.05). While twenty-seven HCC’s parameter Ktrans, Ve, Vp of both single and dual AIF groups didn’t relate to CD34-MVD (P>0.05,P>0.05, P>0.05), Kep were positively correlated with CD34-MVD of HCC (r=0.459,P<0.05; r=0.432,P<0.05), but there was no significant difference between two groups(P>0.20).Discussion
Our results showed that there is no statistical difference of quantitative parameters Ktrans, Ve, Vp between single and dual AIF groups. The parameter Kep was different between two groups, but it had a parallel relationship with CD34-MVD of HCC, for that, dual AIF didn’t have advantage over single AIF. Interestingly, our results didn’t reveal the relationship between Ktrans and MVD reported by Moon J et al1,2. The reasons may come from the difference of antibody immunohistochemical staining for MVD, or difference between animal and human. Beside, JPB O’Connor et al3 pointed out that, Ktrans does not purely measure capillary permeability in any models (although it is often assumed to do so). Instead, its exact meaning depends on the kinetic model used for analysis. Ktrans is a composite parameter representing perfusion and permeability of tissue in fact, and CD34-MVD may not reveal the permeability of tissue and still needs further study.Conclusion
DCE-MRI of HCC could obtain similar quantitative parameters including Ktrans, Ve, Vp computed by either single or dual AIF, and Kep obtained by both this two kinds of AIF had a paralleled correlation with CD34-MVD of HCC, for this, dual AIF didn’t have advantage over single AIF.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Moon J, Kim JH, Choi D, et al. Correlation of quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with microvascular density in necrotic, partial necrotic, and viable liver tumors in a rabbit model. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016;17(5):6314.
2. Chen J, Qian T, Zhang H, et al. Combining dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and microvessel density to assess the angiogenesis after PEI in a rabbit VX2 liver tumor model. Magn Reson Imaging.2016;34(2):177-82.
3. JPB O’Connor, A Jackson, GJM Parker, et al. DCE-MRI biomarkers in the clinical evaluation of antiangiogenic and vascular disrupting agents. British Journal of Cancer.2007;96(2):189-195.
Figures