4709
Comparative study of zero TE ASL MRA and 3D-TOF MRA in diagnostic value of cerebral arteriovenous malformations at 1.5T1Beijing Hospital, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
3D TOF MRA is susceptible to hemodynamic artifacts and is not sensitive to the slow blood flow, which results in the unsatisfied image quality for the diagnosis of AVMs. So we compared the use of zero TE ASL MRA (zTE MRA) and traditional 3D-TOF MRA in assessment of AVMs at 1.5T, taking DSA as standard. It was demonstrated that ASL MRA features significantly better consistency with DSA for AVMs as compared to TOF. In detail, zTE MRA can demonstrate the size, internal details, the feeding arteries and draining veins more clearly and accurately compared with TOF MRA.
Purpose
The evaluation of the anatomic characteristics of intracranial arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) is important for the accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and follow-up of the lesions1. Intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (DSA) remains the gold standard for the assessment of intracranial AVMs by the direct visualization of cerebral vessels. Contrast-enhanced MRA and CT pose risks associated with contrast agents and/or radiation exposure2. 3D TOF MRA is used for intracranial vascular evaluation without contrast medium injection. However, it is susceptible to hemodynamic artifacts and is not sensitive to the slow blood flow. ASL MRA with zero TE acquisition has potential advantages of CE MRA without its shortcomings. Its application on AVMs has been rarely reported, especially on 1.5T. In this study, we compared the use of zero TE ASL MRA (zTE MRA) and traditional 3D-TOF MRA in assessment of AVMs at 1.5T, taking DSA as standard.Methods
A total of 12 patients with AVMs were enrolled in this study from December of 2015 to June of 2016, including 7 males and 5 females, aged 21-58, and informed consent forms were obtained. Both TOF and zTE MRA were performed on a 1.5T whole body scanner (MR360, GE,USA) equipped with an 8 channel head coil, and DSA was performed within three days of the MR exams and the diagnosis of AVMs. Parameters for 3D TOF: 3D SPGR, TR/TE=5/2ms, FA=20, slice = 1.4mm, 32 slices and 3 slabs. Parameters for zTE MRA: TR/TE = 0.5/0ms, FA=5, 1mm isotropic, The MR image assessments were performed by two experienced radiologists and the DSA image was assessed by one interventional neurologist. AVMs were divided into three types according to the size: small (less than 3 cm in diameter),medium (3-6cm in diameter) and large (more than 6 cm in diameter). The characteristics of AVMs, including the type of AVM, feeding arteries and draining veins, were assessed and compared between the TOF and DSA, between zTE MRA and DSA, zTE MRA and TOF respectively.Results
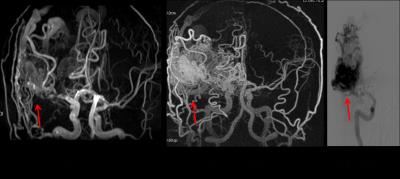
In visualization of AVMs, 12 cases were all detected by zTE MRA and traditional 3D-TOF MRA. A typical set of DSA, TOF and zTE MRA images of a patient with AVM are shown in Fig. 1. There was complete concordance between zTE MRA and DSA, between TOF and DSA in identifying the type of AVMs (100%). But zTE MRA can demonstrate the size and internal details more clearly and accurately than 3D-TOF MRA (Fig. 1). In visualization of feeding arteries, the coincidence rate was 78.5% between the TOF and DSA and 92.8% between zTE MRA and DSA. In visualization of draining veins, there was a higher coincidence rate between zTE MRA and DSA (100%), between the TOF and DSA (93.3%). Compared with TOF MRA, zTE MRA can demonstrate the feeding arteries and draining veins more clearly and accurately (Fig. 1).Discussion and conclusion
MRA is gaining importance for use in cerebral vascular lesions and has become a potential alternative for both diagnosis and follow-up. TOF MRA itself has intrinsic limitations. Zero TE ASL MRA features the advantages of contrast enhanced MRA while being contrast free. In this study, it was demonstrated that ASL MRA features significantly better consistency with DSA for AVMs as compared to TOF. Both zTE MRA and TOF provided the satisfied capability to detect AVMs. But zTE MRA can demonstrate the size, internal details, the feeding arteries and draining veins more clearly and accurately as compared with TOF MRA.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Hadizadeh DR, von Falkenhausen M, Gieseke J, et al. Cerebral arteriovenous malformation: Spetzler-Martin classification at subsecond-temporal-resolution four-dimensional MR angiography compared with that at DSA. Radiology. 2008;246:205-213.
2. Weisbord SD, Mor MK, Resnick AL, et al. Incidence and outcomes of contrast-induced AKI following computed tomography. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:1274–1281.