4665
One shot 3D flow sensitive cine MR imaging using improved motion sensitized driven equilibrium(iMSDE)1Department of Radiology, Tokai University Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan, 2Graduate School of Medical Science, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 3Healthcare department, Philips Electronics Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Department of Radiology, Tokai University School of Medicine, Kanagawa, Japan
Synopsis
Dynamic improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium steady-state free precession (dynamic iMSDE SSFP) has been introduced to visualize the irregular flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which obtains this data in 2D. To improve visibility of CSF space at a wide range, we here proposed a new technique using 3D-free factor. The results showed that fluid motions were sensitively suppressed by iMSDE, similar to 2D acquisition. Thus, this technique may detect irregular CSF motion at the wide range.
PURPOSE
We have reported a new technique to visualize the irregular flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by using dynamic improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium steady-state free precession (dynamic iMSDE SSFP)1. This sequence has the primary advantages of highlighting various CSF motion in a rapid scan without gating, providing similar visibility to the conventional phase contrast (PC) technique. However, because the data in this method can be acquired only in one slice, it is impossible to apply to a large region, particularly in case of detecting a communication point between the CSF space and a large cystic lesion. To overcome this problem, we here propose a new technique for simultaneous multi-slices acquisition. The purpose of this study was to determine basic appropriate parameters and evaluate the feasibility of this technique.METHOD
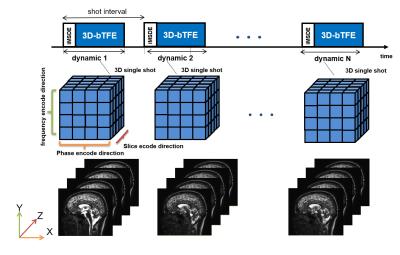
We used a new technique of k-space trajectory called 3D-free factor. The theory of one shot 3D flow sensitive cine MR imaging is shown in Figure1. The equipment we used was a 1.5T clinical scanner (Achieva nova dual, Philips, Best, the Netherlands) with either a 32ch SENSE torso cardiac coil (phantom study) or a 6ch SENSE head coil (volunteer study). The technique for cine MR imaging was based on 3D balanced TFE with iMSDE.
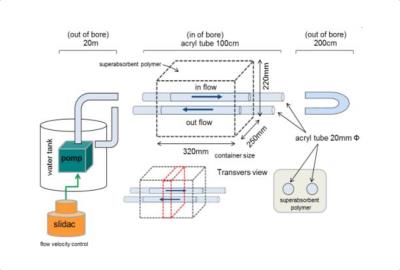
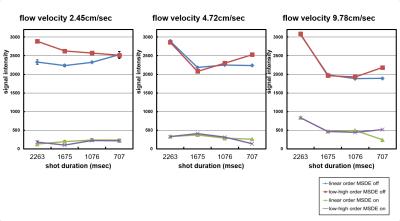
Phantom study: The flow phantom was made with superabsorbent polymer and tubes (Fig.2) with steady flow. The basic scan parameters were as follows: T2prepTE of 20ms, FOV of 350×350, matrix of 192 ×224, TR/TE = 4.5/2.2 ms, flip angle of 90°, slice thickness of 3 mm, reduction factor of 2.0, number of slices = 20, NSA:1, and dynamic scan = 20 (MSG-off:10, MSG-on:10). To evaluate the effect of motion sensitized gradients (MSG), the signal intensity of flowing water in the tube was measured with varying flow speed (0.9–9.78 cm/sec), k-space ordering (linear, low-high), and shot duration time (707–2263 ms) in cross section.
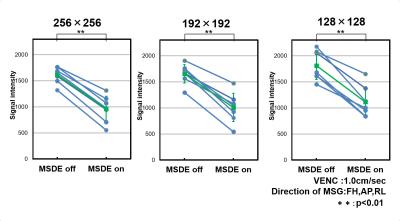
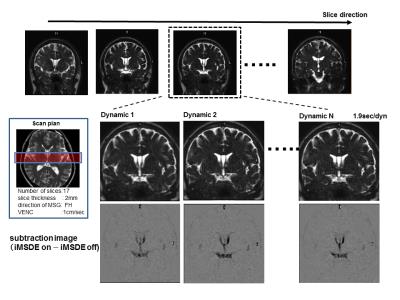
Volunteer study: The study was approved by the local institutional review board and written informed consent was obtained from all volunteers. To evaluate effect of iMSDE different voxel size, we scanned sagittal planes of the brain in seven healthy volunteers. The basic scan parameters were as follows: T2prepTE of 20 ms, FOV of 280×280 mm, matrix of 192 ×224, TR/TE = 4.5/2.2 ms, flip angle of 90°, reduction factor of 4.0, number of slices = 17, k-space ordering = linear, NSA = 1, velocity encoding (VENC)=1cm/sec (directions of MSG ; FH, AP, RL), and dynamic scan = 30 (MSG-off:15, MSG-on:15). The signal intensities of the fourth ventricle were measured with and without iMSDE on different slice thickness (1.5, 2.5, and 3.5 mm) and matrix size (256×256, 192×192, and 128×128). Differences in signal intensity with and without iMSDE were assessed using two-tailed paired t-tests. A P value of less than 0.01 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. To investigate the usefulness of the present sequence, one healthy volunteer with communication between the septum pellucidum and third ventricle underwent MRI with optimized parameters.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In the phantom study, signal suppression effect of iMSDE was shown at long duration time (Fig.3). This suggests that this scan condition permitted a large number of TFE factor. In the volunteer study, signal intensities in the third ventricle were significantly higher without iMSDE than with iMSDE in each slice thickness and matrix size (P < 0.01) (Fig.4). In this method, configurable TFE factor were determined by spatial resolution, number of slices, and temporal resolution. Thus, to observed fluid motion by cine imaging, scan parameters should be optimized for aim of examination. Representative cine MR images are shown in Fig.5. Irregular motion of the CSF can be observed by the optimized scan parameters.CONCLUSION
One shot 3D flow sensitive cine MR imaging using iMSDE can detect irregular CSF motion at the wide range.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement foundReferences
1. Horie T, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging technique for visualization of irregular cerebrospinal fluid motion in the ventricular system and subarachnoid space. World Neurosurgery. 2016 Jul 26. Pii:S1878-8750(16)30590-3.Figures