4583
The Value of High-resolution MRI and Perfusion Weighted Imaging in the Middle Cerebral Artery Atherosclerotic Stenosis1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
This study aimed to explore the assessment value of HRMRI and PWI in patients of TIA with unilateral MCA atherosclerotic stenosis. 43 patients with MCA territory symptoms underwent preliminary DWI and MRA to exclude acute cerebral infarction and ascertain unilateral stenosis of MCA M1 segment. Thereafter, all the patients underwent HRMRI and PWI. HRMRI gets 155 positive slices,type Ⅲ of plaque 49 (31.6%), IV~Ⅴa 41 (26.5%),Ⅴb 4 (2.5%), Ⅵ 13 (8.4%),Ⅴc 48 (31.0%). The soft plaques(type Ⅳ~Ⅴa and VI) adds up to 54 (34.8%), hard plaques (type III,Ⅴb andⅤc) 101 (65.2%). HRMRI diagnosed four cases of mild stenosis, 11 moderate, 22 severe and 6 occlusion. 42 patients has hemisphere perfusion difference between the affected and normal MCA perfusion districts, with lower rCBF , longer rMTT and TTP (P <0.05) in the affected side. HRMRI can assess AHA sub-type and stability of atherosclerotic plaque, and stenosis rate of MCA, MTT, TTP can be found changes in early ischemic events, which are sensitive parameters to diagnose TIA.
Introduction
Intracranial atherosclerosis is the most common cause of ischemic disease in China.1 High-resolution MRI (HRMRI) is a promising tool for studying intracranial atherosclerotic disease (ICAD) in-vivo as it can visualize both the vessel lumen and the vessel wall.2 Perfusion weighted imaging (PWI) has an important role in detecting cerebral blood supply changes.3 This study aimed to explore the assessment value of HRMRI and PWI in patients of TIA with unilateral MCA atherosclerotic stenosis.Materials and methods
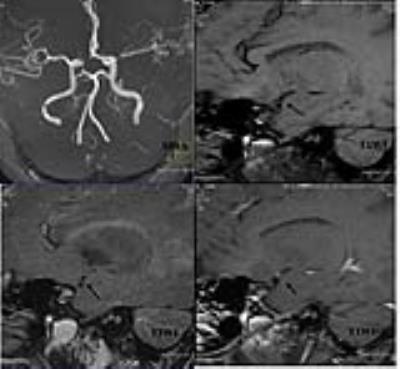
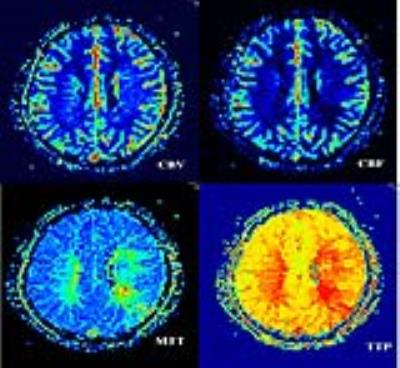
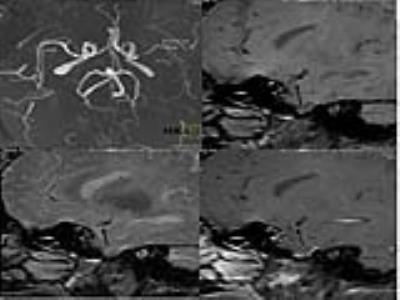
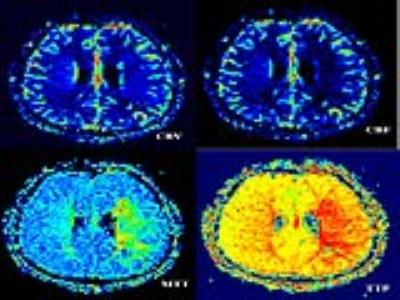
43 patients with MCA territory symptoms underwent preliminary DWI and MRA to exclude acute cerebral infarction and ascertain unilateral stenosis of MCA M1 segment. Thereafter, all the patients underwent HRMRI and PWI. All data were collected on a MAGNETOM Verio 3T MR scanner (Siemens AG, Erlangen, Germany). The T1WI and T2WI of HRMRI sequences were acquired with following parameters: TR/TE 861/18ms,FOV 130×130mm2,matrix 512×512,slice thickness=2mm,gap 20% and TR/TE 903/83ms,FOV 130×130mm2,matrix 512×512,slice thickness=2mm,gap 20% respectively. PWI were acquired using a gradient-echo echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequence with an intravenous bolus injection of gadolinium contrast agent (0.2ml/kg) with following parameters: TR/TE 1500/30ms, FOV 230×230mm2,matrix 128×128,slice thickness=4.0mm,gap 20%. We analyzed atherosclerotic plaques within the affected segment, distinguishing plaque stability and plaque AHA type, and calculated the degree of stenosis, subdivided into mild stenosis (﹤29%), moderate stenosis (30~69%), severe stenosis (70~99%), occlusion (100%). Then we postprocessed PWI data, getting the perfusion parameters of relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV), relative cerebral blood flow (rBCF), relative mean transit time (rMTT), time to peak (TTP) in the regions of interest.Results
HRMRI gets 155 positive slices,type Ⅲ of plaque 49 (31.6%), IV~Ⅴa 41 (26.5%),Ⅴb 4 (2.5%), Ⅵ 13 (8.4%),Ⅴc 48 (31.0%). The soft plaques(type Ⅳ~Ⅴa and VI) adds up to 54 (34.8%), hard plaques (type III,Ⅴb andⅤc) 101 (65.2%). There is no significant difference between hard and soft plaque distribution in bilateral MCAs (chi-square test P = 0.257> 0.05). HRMRI diagnosed four cases of mild stenosis, 11 moderate, 22 severe and 6 occlusion. 42 patients has hemisphere perfusion difference between the affected and normal MCA perfusion districts, with lower rCBF , longer rMTT and TTP (P <0.05) in the affected side. The degree of artery stenosis has no significant correlation neither with the values of rCBF and rCBV nor with the ratio of the affected side to the normal side of rCBF and rCBV(P>0.05). The degree of artery stenosis has significant correlation with the values of rTTP and rMTT in the affected side, as well as the ratio of the affected side to the normal side of rMTT and rTTP(P<0.05) in moderate stenosis, the Pearson’s r are 0.760, 0.688 and 0.896, 0.731 respectively. While in severe stenosis, the artery stenosis only has significant correlation with the ratio of the affected side to the normal side of MTT、TTP(P<0.05). The Pearson’s r are 0.450, 0.857 respectively.Conclusion
HRMRI can assess AHA sub-type and stability of atherosclerotic plaque, and stenosis rate of MCA, MTT, TTP can be found changes in early ischemic events, which are sensitive parameters to diagnose TIA.Acknowledgements
References
1. Wong KS,Huang YN,Gao S,et al.Intracranial stenosis in Chinese patients with acute stroke. Neurology.1998;50(3):812-813.
2. Ryu CW, Jahng G, Kim EJ, et al. High resolution wall and lumen MRI of the middle cerebra larteries at 3 Tesla.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;27(5):433-442.
3. Provenzale JM,Shah K,Patel U,et al.Systematic review of CT and MR perfusion imaging for assessment of acute cerebrovascular disease. AJNR. 2008;29(8):1476-1482.
Figures