4523
Increased cerebral level of GABA- in the acute phase of children’s mild traumatic brain injury.1Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russian Federation, 2Clinical and Research Institute of Urgent Pediatric Surgery and Trauma, Moscow, Russian Federation
Synopsis
There is not any information about [GABA] and [GABA]/[GLX] balance in human brain in acute phase of mTBI, but animal studies have shown alterations in concentrations of major inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters. [GABA-], [GABA+] and [GLX] were studied in vivo using MEGA-PRES pulse sequence in young patients (mean age - 16±2) with acute phase of mTBI. [GABA-]/[GLX] was significantly increased (p<0.05) in patients and [GABA-]/[tCr] had a trend for increase (p=0.09). This results correlates with animals experiments. [GABA+] didn't show any effects. Thus, [GABA-] MEGA-PRESS is more preferable for accurate [GABA] estimation.
Target audience:
Clinical scientists, Neuroscientists.Purpose:
1. These symptoms may be associated with disturbances of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission processes in central nervous system (CNS). MEGA-PRESS enables directly estimate in vivo concentrations of major inhibitory -gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) and excitatory glutamic acid (Glu) neurotransmitters. There are two variants of MEGA-PRESS: GABA+2 and GABA-3 that allow observation GABA with macromolecules (MM) and without MM respectively. According to4 [GABA+] and [GLX] did not change in long-term period after repeated concussions but it was revealed subtle alterations in inhibition/excitability balance in concussed athletes. There is not any information about [GABA] and [GABA]/[GLX] balance in human brain in acute phase of mTBI, however it was shown it is acute phase of mTBI that is accompanied with alterations of [GABA] and [Glu] in rat brain4. Thus, the main purpose of this study was to estimate cerebral GABA+, GABA- and GLX in the acute phase of children mTBI.Methods:
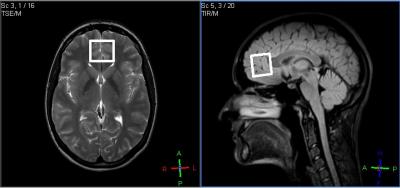
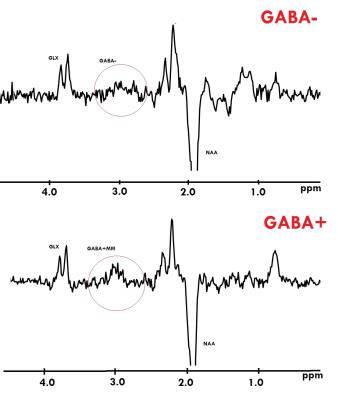
MR acquisition: All investigations were performed on scanner Phillips 3.0T Achieva TX. GABA+ (TE/TR=68ms/1900ms, NSA – 8, 14ms editing pulses applied at 1.9 ppm and 7.5 ppm , 42 averages.) and GABA- (TE/TR=80ms/1900ms, NSA – 8, 20ms editing pulses applied at 1.9 ppm and 1.5 ppm, 42 averages.) edited spectra were obtained using MEGA-PRESS sequence. REST slabs was used for suppressing unwanted water signal from ventricles. Corresponding PRESS spectra with the same parameters (TE/TR=68ms/1900ms, NSA – 64) and (TE/TR=80ms/1900ms, NSA – 64) were also performed for obtaining NAA, Cr, Cho and unsuppressed water signal intensities. All Voxels in size of 28×28×25mm were located in the frontal lobe (Fig.1). Fig.2. represents GABA- and GABA+ spectra acquired.
Quantification and statistical analysis: Edited spectra were processed by the algorithm Amares in the program jMRUI (ver. 5.2 Alpha). PRESS spectra were processed by Philips Spectroview routine. Absolute NAA+NAAG, tCr, tCho concentrations as well as [GABA+]/[tCr], [GABA-]/[tCr] and [GLX]/[tCr]ratios were calculated. Mann-Whitney U-test was used to reveal inter-group differences.
Subjects: Two groups of participants were included in the study: patients group consisted of 11 children hospitalized in the Clinical and Research Institute of Urgent Pediatric Surgery and Trauma, Moscow (5 males, 6 females, mean age - 16±2 years, mean time between trauma and MRI examination 40±20 hours, Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) - 15) with acute phase of mTBI; group of healthy volunteers consisted of 5 children (2 males, 3 females, mean age - 16±1 years) without history of any TBIs and other cerebral pathologies. Participants and their parents signed an informed consent
Results:
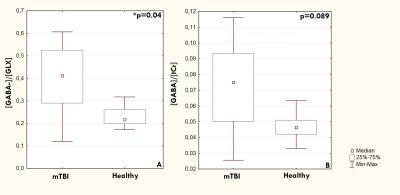
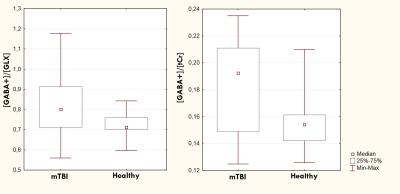
The main effect on the [GABA-]/[GLX] was found (Z=2.03, p<0.05), with the patients having higher [GABA-]/[GLX] as compared to the control group (Fig. 3A).We also found trend for increase of [GABA-]/[tCr] (Z=1.69, p=0.089) (Fig. 3B). The same ratios for GABA+ did not show significant alterations or trend for changing (Fig. 4). Absolute concentrations of NAA+NAAG, tCho, tCr and, [GLX]/[tCr] were also unchanged.Discussion:
This study for the first time revealed increased [GABA] as well as disorders in the [GABA]/[GLX] balance in the acute phase of children mTBI. According to5 concentration of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD67, M = 67 kDa), enzyme catalyzing Glu decarboxylation to GABA, was increased in rat brain within one hour after TBI. This fact may be responsible for [GABA] increase in the present study. Increased [GABA] was shown to correlate with degradation of working memory5. Increased GABA synthesis may slightly reduce local Glu concentration and as a result [GABA]/[GLX] will be more strongly increased. Acute phase of mTBI is not well studied. Accurate investigation of this phase is very important for understanding of damaging processes. Our study demonstrates that GABA- MEGA-PRESS could estimate [GABA] alterations more precisely than it GABA+ MEGA-PRESS does.Conclusion:
Postconcussion changes of neurotransmitter revealed in the present study could be promising for understanding of functional consequences of MRI negative TBI. The results obtained show [GABA-] MEGA-PRESS is more preferable for accurate [GABA] estimation.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1 Dean P, Sterr A, Long-term effects of mild traumatic brain injury on cognitive performance. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013; 7:30.
2. Mesher M, Merkle H, Kirsch J, et al. Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression. NMR Biomed. 1998; 11(6):266-272.
3 Edden R, Puts N, Barker P, Macromolecule-suppressed GABA-edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 3T. Magn Res Med. 2012; 68(3):657-61.
4 Guerriero R, Giza C, Rotenberg A, Glutamate and GABA Imbalance Following Traumatic Brain Injury. CurrNeurolNeurosci Rep. 2015; 15:27
5. Kobori N, Dash P. Reversal of brain injury-induced prefrontal glutamic acid decarboxylase expression and working memory deficits by D1 receptor antagonism. JNeurosci. 2006; 26:4236–46
Figures