4500
Diffusion MRI can provide non-invasive early biomarkers of the outcome of irreversible electroporation tumor treatment in a mouse model.1Radiology, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States
Synopsis
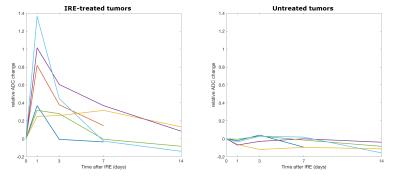
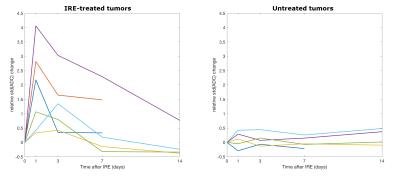
This study investigates diffusion MRI changes after treatment with irreversible electroporation (IRE) in a murine cancer model. The mean and standard deviation of the ADC in regions of interest covering the whole tumors increased 1 day after treatment and then returned gradually to the pre-treatment values. A strong correlation was found between the volume increase and the maximum relative change in ADC mean and standard deviation. Therefore we propose diffusion MRI as an early tool to predict the outcome of IRE treatment in tumors.
Purpose
Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) is a relatively recent technique for non-thermal tumor ablation, consisting in the application of short high-intensity pulses of electric field that create nanopores in the cellular membrane and ultimately lead to apoptosis in the target tissue1. It has shown promising results in terms of efficiency and lack of side effects, and is thus increasingly being used in cases in which surgery is not recommended2-7. Imaging has a fundamental role in planning IRE treatment and assessing its effects, but advanced MRI techniques have been applied only sporadically and a better understanding of the longitudinal changes in the tumor microenvironment is still needed. The purpose of this study is to assess if diffusion MRI (dMRI) biomarkers, indices of microstructural alterations8-9, can characterize the tumor evolution after IRE treatment.Methods
PANC-2 cells, derived from human pancreas carcinoma, were injected in both flanks of 6 female C57BL/6 mice. When tumors reached a diameter of about 5 mm, each mouse underwent baseline MRI, then IRE treatment was performed on the right-side tumor using five 2500-V pulses by a BTX ECM 830 electroporator (Harvard Apparatus, Holliston, MA, USA). MRI experiments were repeated 1, 3, 7 and 14 days after IRE on a 7 T preclinical scanner (ClinScan, Bruker BioSpin, Ettlingen, Germany). The MRI protocol included a T2-weighted (TE/TR=40/4550 ms, voxel size=0.078x0.078x1 mm3, FOV=30x30 mm2) and a dMRI sequence (TE/TR=40/4800 ms, voxel size=0.3x0.3x1.5 mm3, FOV=30x30 mm2, b=0, 50, 100, 200, 400, 650, 900, 1200 s/mm2, 3 orthogonal gradient directions). Two of the mice were terminated after the 7-days MRI because of adverse general health conditions, the others were euthanized after the 14-days MRI. Tumors were excised, fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin; 4 µm-thick slices were cut, fixed and stained using antibodies against cleaved caspase-3 (Biocare Medical, Concord, CA). The number of apoptotic cells was counted under microscopy in 6 views for each control or IRE-treated tumor. The volume of each lesion was measured by manual segmentation of T2-weighted images. The map of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) was calculated by a custom Matlab (Mathworks, Natick, MA, USA) code, and Regions of Interest (ROIs) were delineated on the whole tumors on dMRI images.Results
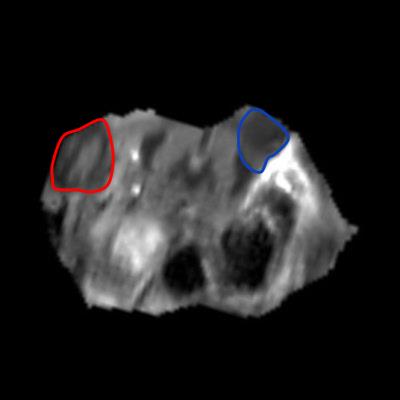
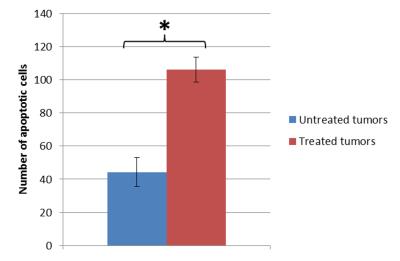
All the untreated tumors grew with time, from 57.71 mm3 at baseline to 235.61 mm3 at the last time point on average. On the other hand, three of the treated tumors remained fairly constant in size but the other three grew, even much more than the contralateral in one case. The mean ADC in the untreated tumors remained constant, whereas in the treated ones it increased 1 day after treatment and then it gradually returned to the baseline values (figure 1). The treated tumors appeared inhomogenous on ADC maps at the first timepoints after the IRE procedure (figures 2 and 3). Both the mean ADC and the inhomogeneity were higher in the tumors that appeared to be grown more at the final MRI. Indeed, there was a strong positive correlation between the volume increase in the last MRI scan compared to baseline and the maximum relative change in ADC mean value or standard deviation (occurring 1 or 3 days post-treatment): r=0.83, p=0.04; r=0.86, p=0.03, respectively. Histology data showed a significantly higher number of apoptotic cells in treated tumors than in controls (106.25±7.50 vs. 44.25±8.73, p<0.001, figure 4).Discussion and conclusion
We observed a transient increase of the mean ADC in all the tumors treated with IRE. Previous works provided contradictory results: no effect on dMRI on rats10 and an ADC increase in mice11 30 minutes after IRE, ADC reduction 1, 3 and 24 hours after treatment and normal values 1 to 6 months later in patients12-14. Our histology results showed necrosis and increase of the intracellular space 30-60 minutes after IRE, followed by inflammation in the next 24 hours and finally apoptosis (unpublished data). The different extent and timing of these mechanisms could explain the observed discrepancies; future work will be devoted to systematically examine short- and long-term ADC changes and to identify the correlation between MRI biomarkers and changes in tumor microenvironment.
A potentially very important result is the correlation we found between the acute increase of ADC mean value and standard deviation and the final volume increase of the tumor. If this result is confirmed in a larger population and in clinical research, dMRI can be an extremely important non-invasive tool for the early prediction of the outcome of IRE treatment that could allow immediate re-treatment planning when needed, thus improving ultimate IRE efficacy.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Davalos RV, Mir IL, Rubinsky B. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann Biomed Eng 2005; 33: 223-231.
2. Scheffer HJ, Nielsen K, de Jong MC, van Tilborg AA, Vieveen JM, Bouwman AR, Meijer S, van Kuijk C, van den Tol PM, Meijerink MR. Irreversible electroporation for nonthermal tumor ablation in the clinical setting: a systematic review of safety and efficacy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2014; 25: 997-1011; quiz 1011.
3. Valerio M, Stricker PD, Ahmed HU, Dickinson L, Ponsky L, Shnier R, Allen C, Emberton M. Initial assessment of safety and clinical feasibility of irreversible electroporation in the focal treatment of prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2014; 17: 343-347.
4. Paiella S, Butturini G, Frigerio I, Salvia R, Armatura G, Bacchion M, Fontana M, D'Onofrio M, Martone E, Bassi C. Safety and feasibility of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: results of a prospective study. Dig Surg 2015; 32: 90-97.
5. Rossmeisl JH, Jr., Garcia PA, Pancotto TE, Robertson JL, Henao-Guerrero N, Neal RE, Ellis TL, Davalos RV. Safety and feasibility of the NanoKnife system for irreversible electroporation ablative treatment of canine spontaneous intracranial gliomas. J Neurosurg 2015; 123: 1008-1025.
6. Wagstaff PG, de Bruin DM, Zondervan PJ, Savci Heijink CD, Engelbrecht MR, van Delden OM, van Leeuwen TG, Wijkstra H, de la Rosette JJ, Laguna Pes MP. The efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation for the ablation of renal masses: a prospective, human, in-vivo study protocol. BMC Cancer 2015; 15: 165.
7. Chen X, Ren Z, Zhu T, Zhang X, Peng Z, Xie H, Zhou L, Yin S, Sun J, Zheng S. Electric Ablation with Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Vital Hepatic Structures and Follow-up Investigation. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 16233.
8. Le Bihan D. Molecular diffusion, tissue microdynamics and microstructure. NMR Biomed 1995; 8: 375-386.
9. Le Bihan D, Iima M. Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging: What Water Tells Us about Biological Tissues. PLoS Biol 2015; 13: e1002203.
10. Hjouj M, Last D, Guez D, Daniels D, Sharabi S, Lavee J, Rubinsky B, Mardor Y. MRI study on reversible and irreversible electroporation induced blood brain barrier disruption. PLoS One 2012; 7: e42817.
11. Zhang Z, Li W, Procissi D, Tyler P, Omary RA, Larson AC. Rapid dramatic alterations to the tumor microstructure in pancreatic cancer following irreversible electroporation ablation. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014; 9: 1181-1192.
12. Calmels L, Al-Sakere B, Ruaud JP, Leroy-Willig A, Mir LM. In vivo MRI follow-up of murine tumors treated by electrochemotherapy and other electroporation-based treatments. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2012; 11: 561-570.
13. Barabasch A, Distelmaier M, Heil P, Krämer NA, Kuhl CK, Bruners P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings After Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation of Liver Metastases: A Systematic Longitudinal Study. Invest Radiol 2016 [Epub ahead of print]
14. Granata V, de Lutio di Castelguidone E, Fusco R, Catalano O, Piccirillo M, Palaia R, Izzo F, Gallipoli AD, Petrillo A. Irreversible electroporation of hepatocellular carcinoma: preliminary report on the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance, computer tomography, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound in evaluation of the ablated area. Radiol Med 2016; 121: 122-131.
Figures