4468
Papillary thyroid carcinoma with hobnail pattern: unique MRI features and correlated with the histopathologic findings1Shanghai Minhang District Central Hospital, shanghai, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
Hobnail
papillary thyroid carcinoma (HPTC) is a moderately differentiated PTC variant
with aggressive clinical behavior and significant mortality.The
purpose of this study was to recognize the unique MRI features of HPTC .61 patients with PTC
confirmed histopathologically[19 lesions of HPTC and 42 NHPTC (PTC without hobnail
features)lesions] undergoing
MRI with T1W, T2W,DWI and contrast material–enhanced sequences prior to thyroidectomy
were included retrospectively. there was a significant
tendency toward T2WI significantly high signal 、T2WI linear low signal 、Lace levy 、Gyrus-like structure 、higher ADC values 、irregular shape present in
HPTCs. HPTC lesions have unique
MRI features.
Purpose
Hobnail papillary thyroid carcinoma (HPTC) is a recently described rare variant that appears to behave more aggressively[1]. PTC with a prominent hobnail pattern is a moderately differentiated PTC variant with aggressive clinical behavior and significant mortality regardless of location by a higher rate of initial presentation at an advanced tumor stage and poor outcome[2-4]. Although the number of reported cases of PTC with a prominent hobnail pattern is small, it is important to note that the long-term survival rate of the variant is much lower than that of classic PTC[4]. And micropapillary carcinoma is a histologic pattern, rather than an independent entity[2]. So it is more important to comment on clinically relevant morphological characteristics of the tumor, rather than religiously trying to classify an individual tumor into a particular variant[5]. Identification of the hobnail pattern can be used not only for the diagnosis of PTC, but also for predicting aggressive PTC[6]. The purpose of this study was to recognize the unique MRI features of papillary thyroid carcinoma with hobnail pattern(HPTC) to help to reduce the rate of missed diagnosis and misdiagnosis of this rare variant before surgery.Method
61 patients with PTC confirmed histopathologically[19 lesions of HPTC and 42 NHPTC (PTC without hobnail features)lesions] undergoing MRI with T1-weighted, T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) and contrast material–enhanced sequences prior to thyroidectomy were included retrospectively. Images were evaluated by two observers for age,sex,tumor size, Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) value , ADC value classification and MRI features (lesion shape,T1WI 、T2WI、DWI signal uniformity, significantly high signal、linear low signal、lace levy、gyrus-like structure on T2WI, early enhancement degree, delayed enhancement pattern) on images obtained with each sequence. Descriptive statistics and t-test were used to determine the difference of age、tumor size and ADC value of HPTC and NHPTC. Chi-square test were used to determine the difference of sex 、ADC value classification and each MRI features. The sensitivity、 specificity、 positive predictive value、 negative predictive value and accuracy of some significant features were determined. A correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between the T2WI significantly high signal ratio and Hobnail pattern components ratio. A binary logistic regression model was developed to identify features that were independently predictive of HPTC. A statistical analysis was performed using P values less than 0.05 considered statistically significant.Result
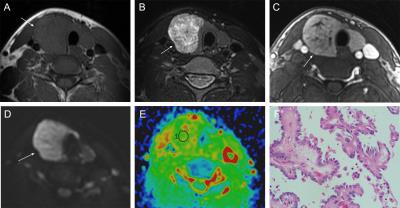
Comparing HPTC to NHPTC: The age of patient of HPTC was significantly younger (37.632 ,P=0.026) ;The lesion size of HPTC was larger (1.747, P=0.013); Irregular was more (65.7% ,P=0.043); the ADC value of HPTC was significantly higher (1.559,ADC value≥1.4×10-3 mm2/s at a percentage of 84.2%, P=0.000);The frequency of T2WI significantly high signal ,linear low signal, lace levy, gyrus-like structure of HPTC was significantly higher (100%,100%,68.4%,52.6%, P=0.000 all); T2WI signal of HPTCs showed mixed signals Most (94.7%, P=0.005); Slightly hyperenhanced was more on early enhancement degree(57.9%, P=0.024). No significant differences were found between HPTC and NHPTC with respect to sex (P=0.095), T1WI signal uniformity (P=0.094), DWI signal uniformity(P=0.153), Delayed enhancement pattern(P=0.543). The following indicators was all more than 90%: sensitivity of T2WI significantly high signal、T2WI linear low signal、 T2WI Mixed signal; specificity of T2WI significantly high signal、 Lace levy 、Gyrus-like structure 、ADC classification(≥1.4); positive predictive value of Gyrus-like structure; negative predictive value of T2WI significantly high signal 、T2WI linear low signal、 T2WI Mixed signal 、ADC classification(≥1.4); accuracy of T2WI significantly high signal 、ADC classification(≥1.4). By binary logistic regression analysis, Lace levy and ADC value classification were two very strong independent indicators of HPTC (odds ratio : 23.111、116.276; 95% confidence interval: 5.012-106.570, 10.026-1348.547; P value:0.007、0.000; respectively).There was significant correlation between T2WI significantly high signal ratio and Hobnail pattern components ratio,r2=0.5627,P=0.0002.Discussion/Conclusion
HPTCs are not completely solid tumors, including liquid components.They showed loosely or individually arranged cancer cells without classic papillary or follicular structures at the periphery of tumor with loss of cellular cohesiveness of the cancer cells, which lead to a gap between their cell mass, and the abundant extracellular fluid filling caused more water. These pathologic features can cause T2WI significantly high signal 、higher ADC values. In our study, there was a significant tendency toward T2WI significantly high signal 、T2WI linear low signal 、Lace levy 、Gyrus-like structure 、higher ADC values 、irregular shape present in HPTCs. The Multivariate Statistical Results suggest that Lace levy and high ADC value may be imaging marker that can guide critical diagnostic recommendations for patients with HPTCs. So HPTC lesions have unique MRI features from NHPTC.Acknowledgements
I am very grateful to Bin Song, and he has made a lot of comments on the innovative aspects of the article and has given much support in image analysis and statistical data. Thanks to Hao Wang and Zedong Dai in data collection and image analysis support.References
1. Amacher AM, Goyal B, Lewis JS, Jr., El-Mofty SK, Chernock RD (2015) Prevalence of a hobnail pattern in papillary, poorly differentiated, and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: a possible manifestation of high-grade transformation. Am J Surg Pathol 39:260-265
2. Lino-Silva LS, Dominguez-Malagon HR, Caro-Sanchez CH, Salcedo-Hernandez RA (2012) Thyroid gland papillary carcinomas with "micropapillary pattern," a recently recognized poor prognostic finding: clinicopathologic and survival analysis of 7 cases. Hum Pathol 43:1596-1600
3. Asioli S, Erickson LA, Sebo TJ et al (2010) Papillary thyroid carcinoma with prominent hobnail features: a new aggressive variant of moderately differentiated papillary carcinoma. A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular study of eight cases. Am J Surg Pathol 34:44-52
4. Lee YS, Kim Y, Jeon S, Bae JS, Jung SL, Jung CK (2015) Cytologic, clinicopathologic, and molecular features of papillary thyroid carcinoma with prominent hobnail features: 10 case reports and systematic literature review. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:7988-7997
5. Sak SD (2015) Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Multiple Faces of a Familiar Tumor. Turk Patoloji Derg 31 Suppl 1:34-47
6. Lee JS, Choi HS, Park IA, Ryu HS (2013) Liquid-based fine needle aspiration biopsy of papillary thyroid carcinoma: logistic regression analysis with conventional and new cytomorphologic features. Acta Cytol 57:233-240
Figures