4394
Integrated volumetric diffusion-weighted MR imaging and HPV genotyping in outcome prediction for stage IB-IV cervical cancer patients following chemoradiation therapy1Medical Imaging and Intervention, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan
Synopsis
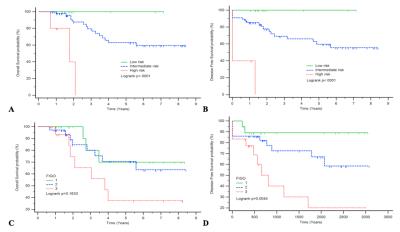
We evaluated the values of integration of pretreatment volumetric ADC analysis with human papillomavirus (HPV) genotyping in prediction of survival and recurrence for women with locally advanced cervical cancer in 82 women following concurrent chemoradiation therapy (CCRT). Independent poor prognostic indicators for OS and DFS by stepwise multivariate analysis, i.e., lower ADC10, advanced T or M stage and high-risk HPV status were composed to generate a novel outcome-predicting model, in which death was found in all the high-risk group patients whiles none of the low-risk group died or recurred during the follow up.
PURPOSE
To evaluate the values of integration of volumetrically derived apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) from pretreatment diffusion-weighted (DW) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging with human papillomavirus (HPV) genotyping in prediction of survival and recurrence for women with locally advanced cervical cancer following concurrent chemoradiation therapy (CCRT).METHODS
The institutional review board-approved prospective study enrolled 82 women (age 23 – 92 y; median, 53 y) with stage IB–IV cervical cancer treated with CCRT in 2007–2014. All patients underwent MR imaging for staging, including T2-weighted and DW MR imaging at 3.0 T. The mean, minimum, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, and 90th percentiles and maximal ADC values (ADCmean, ADCmin, ADC10, ADC25, ADC50, ADC75 and ADC90, respectively) of all voxels that comprised each tumor were extracted. The primary outcomes were overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). Uni- and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to evaluate the association of HPV genotyping, ADC parameters and relevant clinical variables with OS and DFS.RESULTS
Of the 82 women included 55 were free of disease at last follow-up. Median follow-up was 24 months (range, 8–102 months). Independent poor prognostic indicators for OS and DFS by stepwise multivariate analysis, i.e., lower ADC10, advanced T or M stage and high-risk HPV status were composed to generate a novel outcome-predicting model, in which death was found in all the high-risk group patients whiles none of the low-risk group died or recurred during the follow up.DISCUSSION
The majority of literature reports assessed tumor ADC data mostly within a single axial section 1 rather than three-dimensional volume.2 Furthermore, the prognostic value of ADC parameters generated by DW MR imaging integrating with the established predictive markers such as HPV genotyping and clinical FIGO stage was unknown. The present study is the first report attempting to integrate DW MR imaging information with HPV status, generating a novel scoring system which outperformed the FIGO stage, to predict OS and DFS for patients with cervical cancer following CCRT.CONCLUSION
The integrated volumetric DW MR imaging and HPV genotyping may be a useful clinical biomarker to predict survival and recurrence in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer treated with CCRT.Acknowledgements
Chang Gung Medical Foundation grant CMRPG-3B1923, CIRPG3E0021, National Science Council (Taiwan) NSC103-2314-B-182A-006. IRB No. 102-0620A3. Clinical trial ID: NCT01874548.References
1. Nakamura K, Joja I, Kodama J, Hongo A, Hiramatsu Y. Measurement of SUVmax plus ADCmin of the primary tumour is a predictor of prognosis in patients with cervical cancer. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2012;39(2):283-290.
2. Gladwish A, Milosevic M, Fyles A, et al. Association of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient with Disease Recurrence in Patients with Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer Treated with Radical Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy. Radiology. 2015;279(1):158-166.