4367
Prediction of Individual Breast Tumor Therapeutic ResponseCharles S. Springer, Jr.1, Xin Li1, Megan L. Troxell2, Karen Y. Oh3, Arpana Naik4, Kathleen A. Kemmer5, Aneela Afzal1, May H. Mishal1, Alina Tudorica3, and Wei Huang1
1Advanced Imaging Research Center, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, United States, 2Pathology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, 3Radiology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, 4Surgical Oncology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, 5Medical Oncology, Oregon Health & Science University
Synopsis
Synopsis: A kio parametric image maps Na+,K+ATPase activity with intra-tumor resolution. For breast tumors, the kio hot spot fraction decreases after one NACT cycle if the tumor goes on to be cancer-free after NACT completion, but not if it maintains residual cancer. Also, though kio hot spots are reduced after one NACT cycle, new ones appear in different loci. This is consistent with metabolic competition between different cancer cell populations within the tumor.
Introduction:
Recently, a high-resolution metabolic MRI method was introduced to map metabolic heterogeneity even within, for example, an individual breast tumor.1-3 The use of Shutter-Speed [SS] [Dynamic-Contrast-Enhanced] DCE-MRI allows evaluation of the kio biomarker, the rate constant for equilibrium cellular water efflux. It has been shown that kio is proportional to the cellular metabolic rate of Na+,K+‑ATPase [cMRNKA], the vital cell membrane ion pump whose activity is a major goal of intermediary metabolism.1 Interestingly, whole tumor kio values, <kio>tum, averaged over sub‑populations of breast cancer subjects undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy [NACT] showed significant changes after just the first NACT cycle.4 For those who would exhibit complete [pathology-assessed] response after all cycles, <<kio>tum>n decreased by 24% after the first cycle while, averaged for all other subjects, it increased.4 For truly personalized cancer medicine, the accurate prediction of therapy response for an individual tumor is crucial. Here, we show changes in tumor kio maps after only one NACT cycle.Methods:
Twenty-eight women with grade 2-3 breast cancer (in a protocol described previously1,4) consented to 3T DCE-MRI studies, before, during, and just after the entire NACT course. The bi-lateral, fat-suppressed 3D acquisitions included 96-128 slices, and temporal resolution 14.6-20.2 s.1,4 The nominal voxel volumes were (0.94-1.1 mm)2 x 1.4 mm. The data were analyzed with an SS model assuming a single 1H2O signal.1,4,5Results:
Results from two exemplary subjects are shown in the Figure. Panels a and b display kio maps obtained before NACT for grade 2 invasive ductal carcinoma tumors that were HER2 + [ER -, PR -] and luminal B [ER +, PR +]/HER2 + genomic molecular subtypes, respectively. The tumor kio maps after one NACT cycle is shown in panels c and d, respectively. Since three weeks separate the acquisitions of a/c and b/d, the image slices cannot be perfectly registered. Before NACT, the two tumors differ. The luminal B tumor [b] is smaller [3.4 cc] than the HER2 tumor [a] [20.0 cc], but has a larger proportion of elevated kio. In the luminal B image slice [b] 20%, while in the HER2 slice [a] 14%, of pixels have kio exceeding 10 s-1. Correspondingly, the <kio>tum values are 3.1 and 1.7 s-1 for the whole luminal B and HER2 tumors, respectively. The therapy responses also differ. Both tumor volumes were reduced by the first NACT cycles: luminal B [b/d] to 1.6 cc [53% down]; and HER2 [a/c], to 14.1 cc [29% down]. Pharmacokinetic biomarkers indicate that tumor capillary density also decreases after one NACT treatment for each tumor [not shown]. However more interestingly, the kio responses differ in sign. After first NACT, high kio [≥10 s-1] pixels decrease to 16% for the luminal B tumor slice [d] but actually increase to 15% for the HER2 tumor slice [c].Discussion:
Invasive carcinoma cells have large kio,6 possibly due to the membrane ion channel overexpression in cancer cells, causing chronic depolarization and altered ion gradients. This has been linked directly to the K‑Ras signaling system for uncontrolled cell proliferation.7 The cMRNKA would be expected to be elevated, in a [futile] attempt to restore the membrane potential. After 18 weeks of NACT [six 3 week and eight 2 week cycles, respectively], the HER2 tumor was found by surgical pathology to still have ~7.5% cancer cells, while the luminal B tumor was cancer-free. Thus, the kio responses after one NACT cycle for these individual patients reflected the group-averaged predictions for therapeutic response.4 The <kio>tum values increased from 1.7 to 2.3 s-1 and remained unchanged [at 3.1 s-1], respectively, for the HER2 and luminal B tumors. Even in the map image slices, the fraction of high kio pixels increased from 14% to 15% in [a/c] while it decreased from 20% to 16% in [b/d], respectively. The HER2 patient died from her cancer four years post-diagnosis. Changing to a novel therapy trial after the first cycle kio finding might possibly have prolonged survival. There is another interesting aspect of the a/c and b/d image pairs. In almost every instance, a kio hot spot has its value decreased after one therapy cycle, but other regions show kio increases. This is consistent with heterogeneous intra-tumor cellular metabolic competition; a corollary of which is that cytosidal therapy could preferentially kill the more metabolically active cell types, leaving others to flourish.8Acknowledgements
Grant Support: NIH: UO1-CA154602; R44-CA180425References
1. Springer, Li, Tudorica, Oh, Roy, Chiu, Naik, Holtorf, Afzal, Rooney, Huang, NMR Biomed. (2014) 27: 760-773. 2. Huang, Tudorica, Oh, Chiu, Roy, Troxell, Naik, Kemmer, Chen, Holtorf, Afzal, Li, Springer, PISMRM (2016) 24: 2653. 3. submitted to this meeting. 4. Tudorica, Oh, Chiu, Roy, Troxell, Naik, Kemmer, Chen, Holtorf, Afzal, Springer, Li, Huang, Trans. Oncol. (2015) 9: 8-17. 5. Li, Cai, Moloney, Chen, Huang, Woods, Coakley, Rooney, Garzotto, Springer, JMR (2016) 269: 104-112. 6. Springer, Li, Tudorica, Oh, Chui, Roy, Troxell, Naik, Kemmer, Chen, Holtorf, Afzal, Huang, PISMRM (2016) 24: 2722. 7. Zhou, Wong, Cho, van der Hoeven, Liang, Thakur, Luo, Babic, Zinsmaier, Zhu, Hu, Venkatachalam, Hancock, Science (2015) 349: 873-876. 8. Marusyk, Polyak, Science (2013) 339: 528-529.Figures
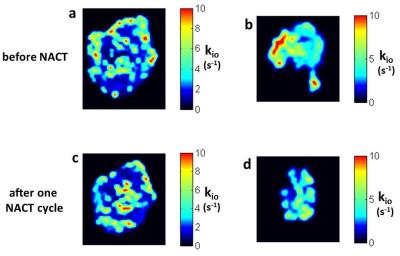
Figure. Two different breast cancer kio maps. Panels a/c are for a HER2 tumor, panels b/d are for a luminal B tumor. Panels a and b are pre-NACT, panels c and d after application of only one NACT cycle. After NACT completion [18 weeks], the luminal B tumor was cancer-free, while the HER2 tumor still harbored cancer. After one NACT cycle, the kio hot spot fraction is reduced for the luminal B tumor [d], but not decreased for the HER2 tumor [c]. In general, kio hot spots are decreased after one NACT cycle, but new ones appear.