4200
Brain abscess due to odontogenic infection: Insights from dental CT for differential diagnosis.1Radiology, Tobata Kyoritsu Hospital, Kitakyushu, Japan, 2Neurosurgery, Kitakyushu, Japan
Synopsis
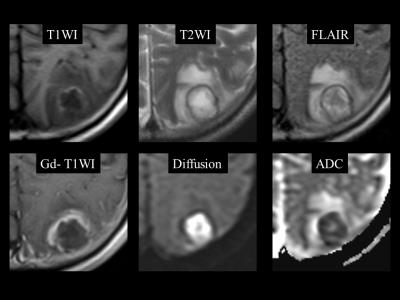
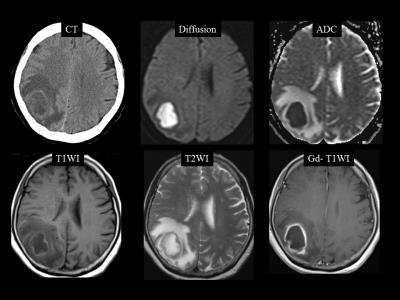
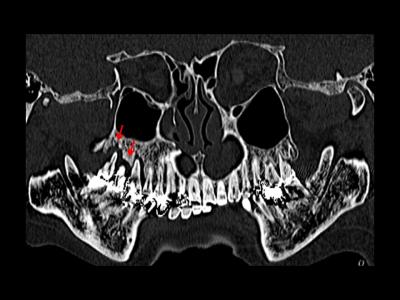
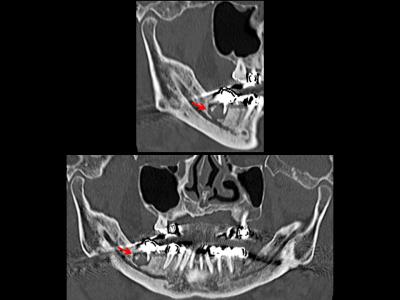
We herein report the 4 cases of brain abscess secondary to odontogenic infection due to an untreated tooth decay. In all cases, there were no abnormalities on physical and intraoral examinations, nor overt trismus or facial swelling. Dental CT showed a periapical radiolucency around the root tips of a decayed tooth, which revealed periodontal abscess. After the multidisciplinary therapy including antibiotics, abscess drainage, and dental treatments, all the patients recovered and discharged.
(Purpose)
The aim of this presentation is to call attention to the latent oral infections as the cause of brain abscess, and to describe the imaging features of the odontogenic infection, especially in dental CT.(Outline of Content)
Brain abscess is a rare life-threatening CNS infection, which is caused by various conditions; i.e. cranial trauma, post-surgery infections, following a septic focus elsewhere in the body, and directly spreading.
Odontogenic infections are rarely implicated in the causes of brain abscess. Clinical symptoms of brain abscess are nonspecific, because they could depend on the size and location of the disease. Diagnostic imaging, therefore, could play a very important role for the early diagnosis of brain abscess as well as a primary lesion, which must lead to a higher survival rate and lower complications. However it would be difficult to detect and diagnose the odontogenic infection because of its low incidence and unawareness of specific imaging features.
We herein report the 4 cases of brain abscess secondary to odontogenic infection due to an untreated tooth decay. In all cases, there were no abnormalities on physical and intraoral examinations, nor overt trismus or facial swelling. Dental CT showed a periapical radiolucency around the root tips of a decayed tooth, which revealed periodontal abscess. After the multidisciplinary therapy including antibiotics, abscess drainage, and dental treatments, all the patients recovered and discharged.