4166
An application of histogram analysis for multiparameters from multimodal MRI combining DCE, IVIM-DWI and 3D-Asl in predicating the Glioma grading and survival1Tangdu Hospital, Xi'an, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
To find the early biomarkers for predicting the histological grading and prognosis of glioma, the study compared the discriminating efficiency of multiple metrics from DCE, Multi-b DWI and 3D-ASL with a histogram analysis approach, and further evaluated the combined accuracy and the survival association. The accuracy of assessing glioma grading and survival would not significantly improved by a univariate parameter, but highly promoted by combining the multiple parameters of histogram analysis from various MRI modality. We will further utilize the machine learning to evaluate the classifying accuracy.
Introduction
The prognosis of glioma to some extent related with the histological WHO grading, however, postoperative histological grading may retard therapy selection and patient prognosis.1-3 Several advanced MRI series including Dynamic Contrast Enhanced(DCE), Multiple-b Diffusion Weighted Imaging (multi-b DWI) and three dimensional pseudo-continuous Arterial Spin Labeling(3D-Asl) were utilized separately in predicting the histogolical grading or survival analysis.4,5 However, the accuracy of every series are not comparable in different crowds, and the conventional paremeter like the mean value would not explain the tumor heterogeneity especially distinctive in glioma. To find the best biomarkers for predicting the histological grading and prognosis, the study compared the discriminating efficiency for multiple metrics from DCE, Multi-b DWI and 3D-ASL with a histogram analysis approach, and further evaluated the combined classified accuracy of effective parameters and their survival association.Method
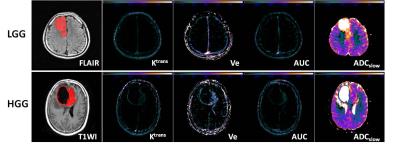
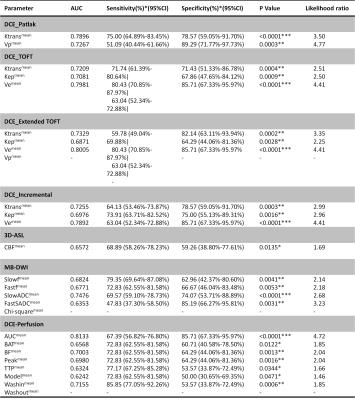
120 glioma patients were finally included in the study(57 Low Grade Gliomas (LGGs), 63 High Grade Gliomas(HGGs)). For each patient, conventional and advanced MRI including DCE, multi-b DWI, 3D-Asl were implemented on 3.0T MRI (MR750, GE Healthcare). The DCE data and multi-b DWI data were calculated by different mathematical module from nordicICE(Version 4.0, Nordic-NeuroLab), in order to obtain Ktrans, Ve, Kep, Vp and perfusion parameter AUC maps from DEC and ADCslow, ADCfast, f, Dfast and chi-square maps from multi-b DWI, and the Cerebral CBF map for 3D-Asl were directly derived from GE workstation. The conventional MRI were used to draw the Volume of Interest(VOI) which overlaid the whole extent of lesion excluding the necrosis and peripheral edema. The pixel by pixel values of each parameter were extracted from the VOI so as to calculate histogram values such as the mean, median, max, min, skwessness, kurtosis, energy, entropy as well as the cumulative histogram parameters which is expressed as nth percentile. An unpaired Student’s t test was employed to compare univariate value between the LGG and the HGG. In the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, area under the curve(AUC) for each histogram parameters were assessed comparatively, and the cutoff points determined by maximizing the sum of the sensitivity and specificity were calculated to differentiate the LGG from HGG. To estimate the diagnosed efficiency of multimodality MRI, multivariables Logistic regression were accomplished. The Log-rank analysis for optimal predictor among the multiple parameters were perform to assess Overall Survival(OS)of 12m, 15m and 18m, and the patient lost to follow up were dismissed. All the results with p values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.Results
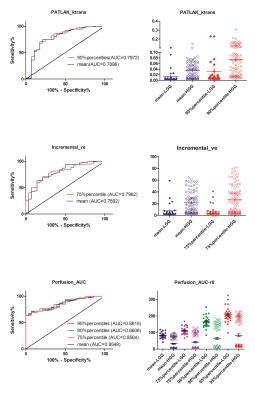
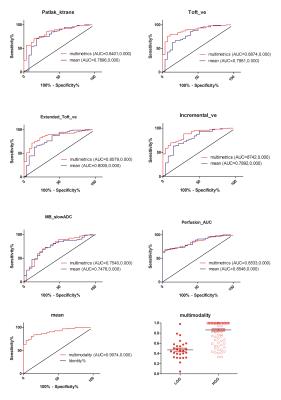
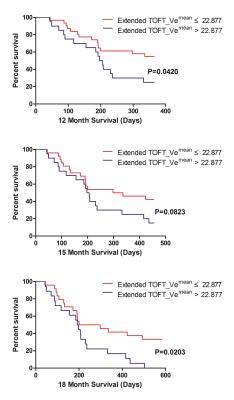
The univariate ROC analysis for the mean of all parameters in multimodality MRI showed that the mean of the paremeters like the Ktrans for PATLAK, the Ve for extended TOFT, the Ve for Incremental modals, the firstpass AUC for DCE perfusion and the ADCLOW for IVIM-DWI have the relative higher AUC for differentiating LGG from HGG(Table 1). In the same modality, the unvariate ROC analysis of each histogram paremeters compared with the ROC analysis of the mean, showed that part of histogram parameters just have slight increases in AUC, including the 90th percentile of Ktrans for PATLAK, the 75th percentile of Ve for incremental madals as well as the 75th, 90th and 95th of firstpass AUC for DCE-perfusion(Fig 1). Although without significant efficiency promotion in univariate parameter of histogram analysis, the multi-metrics and multimodal analysis from histogram data were proved to be having higher diagnostic efficiencies than that of the univariate analysis(Fig 2). The mean value of all subjects’ Vemean for extended TOFT could stratify OS of 12m and 18m examed by Log-rank analysis(Fig3).Discussion and conclusion
Comparing the diagnosed efficiency of various parameters for multimodal MRI within the same crowd, Our study demonstrated that the DCE MRI and IVIM DWI have higher efficiency than 3D-Asl. Contrast with the mean value, the histogram parameters just have slight increases in diagnosed accuracy for the glioma grading. We further evaluated the accuracy of multi-metrics in the same and different MRI modality for glioma grading , and found that multiparameters would intensively improve the diagnostic efficiency. The univariate parameters with the highest accuracy would evaluated prognosis of OS. In conclusion, the accuracy of assessing glioma grading and survival would not significantly improved by a univariate parameter from histogram analysis, but highly promoted by combining the multiple paremeters of histogram analysis from various MRI modality. However, the conventional statistical method can not integrate the whole features to evaluate the grading and prognosis of Glioma, we will further uitilize the mechine learning to do the research.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Law, M., S. Yang, H. Wang, et al., Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2003. 24(10): p. 1989-98.
2. Li, X., Y. Zhu, H. Kang, et al., Glioma grading by microvascular permeability parameters derived from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and intratumoral susceptibility signal on susceptibility weighted imaging. Cancer Imaging, 2015. 15: p. 4.
3. Togao, O., A. Hiwatashi, K. Yamashita, et al., Differentiation of high-grade and low-grade diffuse gliomas by intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Neuro Oncol, 2016. 18(1): p. 132-41.
4. Zollner, F.G., K.E. Emblem, and L.R. Schad, SVM-based glioma grading: Optimization by feature reduction analysis. Z Med Phys, 2012. 22(3): p. 205-14.
5. Svolos, P., E. Tsolaki, E. Kapsalaki, et al., Investigating brain tumor differentiation with diffusion and perfusion metrics at 3T MRI using pattern recognition techniques. Magn Reson Imaging, 2013. 31(9): p. 1567-77.
Figures