4138
Relationships among Cortical Glutathione Levels, Brain Amyloidosis, and Memory in Normal Older Adults Investigated in vivo with 1H MRS and PiB PET1Radiology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Weill Cornell Medicine, 3Radidology, Weill Cornell Medicine
Synopsis
Oxidative stress has been implicated as an important pathological mechanism in the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The purpose of this study was to assess whether J-edited 1H MRS levels of glutathione (GSH) – the primary antioxidant in living tissue – are associated with brain amyloidosis, as assessed with PET, and memory in a community-dwelling cohort of nondemented older adults. The results showed an inverse association relating GSH, a sensitive marker of oxidative stress, and amyloidosis, one of the pathological hallmarks of AD, and a weaker association with memory, thereby collectively further implicating oxidative stress in AD pathophysiology.
INTRODUCTION
Oxidative stress has been implicated as an important pathological mechanism in the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).1 Preclinical models of AD have suggested that oxidative stress due to age-related cellular mechanisms may promote b-amyloid plaque formation in the brain – the pathological hallmark of AD -- leading to dementia.1-4 Indeed, using positive positron emission tomography (PET) scans, with the amyloid tracer, Pittsburgh Compound B (PiB), it has been shown that advancing age is also associated with increased prevalence of brain amyloidosis, affecting 12% of nondemented individuals over the age of 60, 30% over the age of 70, and 50% over the age of 80 have.5 There is also evidence that increasing antioxidant levels may decrease amyloid deposition and cognitive deficits.6 The purpose of this study was to assess whether J-edited 1H MRS levels of glutathione (GSH) – the most abundant and one of the most important antioxidants in living tissue that protects against oxidative stress – are associated with brain amyloidosis, as assessed with PiB PET, and memory in a community-dwelling cohort of nondemented older adults.METHODS
Subjects: Fifteen cognitively normal subjects were prospectively enrolled in this study. All subjects underwent J-edited 1H MRS for GSH, a PiB PET scan, and memory testing using the Repeatable Battery for Neuropsychological Status (RBANS)7. Associations among GSH levels, brain amyloidosis, and memory were assessed using multivariate regression models.
In Vivo GSH J-edited 1H MRS Protocol: In vivo GSH spectra were recorded in 15 min on a 3T GE MR system from a 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 cm3 voxel prescribed in the medial parietal lobe to include the posterior cingulate gyrus and precuneus – a region chosen because multiple prior studies reported its early involvement in AD, using the J-editing technique (Figure 1) and an 8-channel phased-array head coil, with TE/TR 68/1500ms and 290 interleaved excitations. Levels of GSH were derived by frequency-domain fitting (Figure 1), and then expresses as peak area ratios relative to the unsuppressed intravoxel water (W) signal.
PiB PET Protocol: All subjects underwent an amyloid PiB PET scan on a Siemens Biograph PET-CT scanner (Siemens, Knoxville, TN; 1 mm FWHM, 25 cm FOV) using a standardized research protocol.8 All subjects received an intravenous catheter for injection of 15 mCi of 11C-Pittsburgh Compound B (PiB). Sixty minutes after injection, subjects were scanned for 30 minutes with their eyes open in a quiet, dimly lit room. A low-dose CT scan was acquired for attenuation correction, and all images were reconstructed into a 512 x 512 matrix.RESULTS
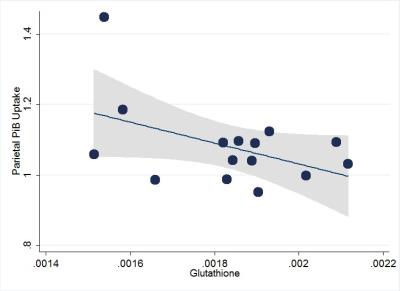
Lower GSH levels were associated with greater brain amyloidosis in the temporal (regression coefficient [rc]=-209±85, p=0.03) and parietal (rc=-308±143, p=0.05) (Figure 2) lobes, adjusted for apolipoprotein Ee4 carrier status. There were marginal trend-level positive associations between lower GSH levels and lower immediate (rc=317±198,p=0.14), as well as delayed memory (rc=232±171, p=0.20) scores.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The value of noninvasive measurement of GSH by J-edited 1H MRS lies in its potential to directly implicate and support a role for oxidative stress in the early stages of AD development. Using this technique, the present study sought to identify a role for oxidative stress in a prospective cohort of nondemented subjects, assessing for potential associations between cortical GSH levels and brain amyloidosis, and between GSH and cognition. The major findings were: 1) GSH levels measured with J-edited 1H MRS are negatively associated with brain amyloidosis as assessed with PiB PET in the temporal and parietal regions in this cohort, 2) GSH levels showed associations with immediate and delayed memory at the trend level, and 3) GSH levels may be related to obesity, a potentially modifiable risk factor for AD. Collectively, these findings provide evidence that implicate oxidative stress in AD through an association between levels of the antioxidant brain amyloidosis, a trend-level association with immediate and delayed memory, and a potential association with obesity, a risk factor for AD. In summary, this is the first study, to our knowledge, to explore in vivo associations between GSH and brain amyloidosis, as well as GSH and cognition in a nondemented cohort, which supports a role for 1H MRS measures of the ubiquitous antioxidant as a potential early biomarker of AD pathology and therapeutic response monitoring of existing or future disease-modifying interventions targeting oxidative stress.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Apelt J, Bigl M, Wunderlich P, et al. Aging-related increase in oxidative stress correlates with developmental pattern of beta-secretase activity and beta-amyloid plaque formation in transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer-like pathology. Int J Dev Neurosci 2004; 22:475-484.
Nunomura A, Perry G, Aliev G, et al. Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2001; 60: 759-767.
Pratico D, Uryu K, Leight S, et al. Increased lipid peroxidation precedes amyloid plaque formation in an animal model of Alzheimer amyloidosis. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 4183-4187.
Komatsu H, Liu L, Murray IV, Axelsen PH. A mechanistic link between oxidative stress and membrane mediated amyloidogenesis revealed by infrared spectroscopy. BBA Biomembranes 2007; 1768: 1913-1922.
Rowe CC, Villemagne VL. Brain amyloid imaging. J Nucl Med 2011; 52: 1733-1740.
Dumont M, Wille E, Stack C, et al. Reduction of oxidative stress, amyloid deposition, and memory deficits by manganese superoxide dismutase overexpression in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. The FASEB Journal 2009; 23: 2459-2466.
Randolph C, Tierney MC, Mohr E, et al. The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS): preliminary clinical validity. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 1998; 20: 310-319.
normal individuals with a family history of late-onset Alzheimer’s. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010; 107: 5949-5954.
Figures