4038
Utilization of T1ρMR imaging in Sjögren’s syndrome with normal appearing parotid glands: initial findings1Department of Radiology, Drum Tower Hospital, School of Medicine, Nanjing University, Nanjing, People's Republic of China, 2Department of Rheumatology, Drum Tower Hospital, School of Medicine, Nanjing University, People's Republic of China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
Sixteen SS patients and age- and gender- match healthy volunteers underwent parotid MR imaging to evaluate whether T1ρ values could diagnose of SS patients. T1ρ values between the patients and healthy volunteers were compared. ROC analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of the T1ρ values. The T1ρ values of SS patients were significantly higher than those of healthy volunteers. With a cutoff value of 88.02 ms, the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of the parotid T1ρ value was 75.0% and 100.0%, respectively. Parotid T1ρ MR imaging held the potential in the diagnosis of SS without morphological changes of glands.
PURPOSE
To explore the feasibility of parotid spin-lattice relaxation time in the rotating frame (T1ρ) MR imaging in the diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) without morphological changes of the parotid glands in conventional MR imaging.
METHODS
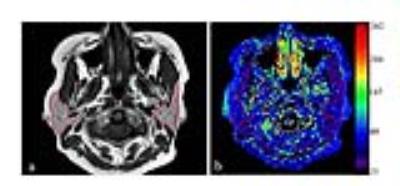
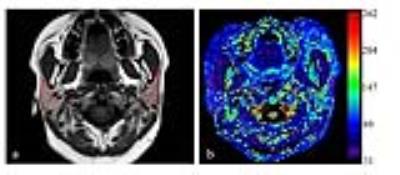
Sixteen consecutive SS patients without morphological changes of parotid glands in conventional MR imaging and 16 age- and gender- match healthy volunteers underwent parotid 3.0 T MR imaging, including T1ρ sequence. All the subjects underwent T1ρ MR scanning again after 3 months. T1 signal intensities and T1ρ values of bilateral parotid glands were compared using paired samples t-test. Parotid T1 signal intensities and T1ρ values between the patients and healthy volunteers were compared using two independent samples t-test. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of the parotid T1ρ values. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was calculated to evaluate the reproducibility of parotid T1ρ measurements.RESULTS
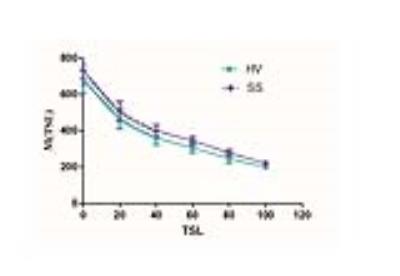
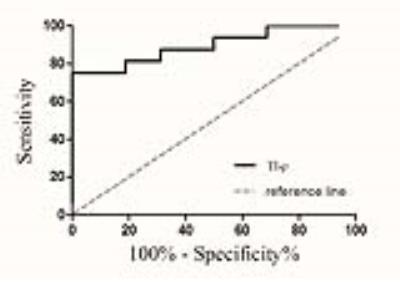
There were no significant differences of T1 signal intensities and T1ρ values between bilateral parotid glands in whether SS patients or healthy volunteers (all P > 0.05). The parotid T1ρ values of SS patients (96.47 ± 15.38 ms) were significantly higher than those of healthy volunteers (84.25 ± 6.11 ms) (P < 0.001), while there were no significant differences of T1 signal intensitiesbetween SS patients and healthy volunteers (P = 0.655). With a cutoff value of 88.02 ms, the sensitivity and specificity of the parotid T1ρ value was 75.0% and 100.0% in the diagnosis of SS, respectively. The reproducibilityof parotid T1ρ measurement was excellent (ICC: 0.934 -0.995).DISCUSSION
T1ρ imaging was a sensitive modality to investigate the macromolecular composition and proton exchanges in tissues. We speculated that the increased parotid T1ρ values in SS patients might be due to the increased expression and activation of ECM and elevated levels of proteins such as LMs. In addition, Paez et al. detected increased protein levels of ECM in SS1 patients with low interacinar fibrosis rather than SS2 patients with advanced morphological changes.CONCLUSION
Parotid T1ρ MR imaging held the potential in the diagnosis of SS without morphological changes of parotid glands.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Vitali C, Monti P, Giuggioli C, et al. Parotid sialography and lip biopsy in the evaluation of oral component in Sjogren's syndrome. Clinical and experimental rheumatology 1989;7(2):131-135. 7.
2.Kalk WW, Vissink A, Spijkervet FK, Bootsma H, Kallenberg CG, Roodenburg JL. Parotid sialography for diagnosing Sjogren syndrome. Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology, oral radiology, and endodontics 2002;94(1):131-137.
3.Tomiita M, Ueda T, Nagata H, et al. Usefulness of magnetic resonance sialography in patients with juvenile Sjogren's syndrome. Clinical and experimental rheumatology 2005;23(4):540-544
4.Kato H, Kanematsu M, Toida M, et al. Salivary gland function evaluated by diffusion-weighted MR imaging with gustatory stimulation: preliminary results. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI 2011;34(4):904-909.
Figures