4017
Correction of dynamic off-resonance in spiral 2D real-time MRI of speech1Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Synopsis
Spiral real-time MRI (RT-MRI) is a valuable tool in speech production research. A key drawback is off-resonance blurring artifact that appears at the boundaries of important articulators. In this work, we demonstrate dynamic off-resonance estimation that is directly captured from phase of single echo-time dynamic images after coil phase compensation. Multi-frequency reconstruction then provides deblurring and improved depiction of articulator boundaries including the tongue, hard palate, and soft palate.
Purpose
Spiral real-time MRI (RT-MRI) has become a valuable tool for speech production research because it provides non-invasive depiction of the vocal tract dynamics, allowing for a time efficient acquisition1–2. A key drawback of the spiral trajectory in vocal tract imaging is off-resonance blurring3 at the boundaries of important articulators, such as the lips, palate, and tongue. The blurring is severe for longer spiral readout and impairs the analysis of dynamic articulators in speech science. Current speech RT-MRI protocols mitigate this by using short duration readouts (~2.5 ms) and low field strength (1.5 T), compromising acquisition efficiency4–6. Several deblurring methods have been proposed7–12, most of which require measurement of field map using multiple echo times7–9. This requires compromising temporal and/or spatial resolution9. In this work, we demonstrate dynamic off-resonance estimation that is directly captured from phase of single echo-time dynamic images after coil phase compensation. We apply this method into longer readout (4.016 ms) RT-MRI and show that this method, when combined with multi-frequency reconstruction, improves sharpness of the vocal tract articulator boundaries in spiral 2D RT-MRI of speech.Theory
Dynamic Field Map Estimation
Consider spiral RT-MRI, where the phase of the image time series ($$$I_c(\textbf{r},t)$$$) for c-th coil is: $$ \varphi_c(\textbf{r},t) = \angle S_c(\textbf{r}) - 2\pi\Delta f(\textbf{r},t) TE $$ where $$$\textbf{r} \in (x,y)$$$ is image domain spatial coordinates, $$$\angle S_c(\textbf{r})$$$ is coil-phase that is spatially smooth and independent of time, and $$$\Delta f(\textbf{r},t)$$$ is dynamic off-resonance. Phase accrual during the spiral readout is ignored.
We estimate the coil sensitivity map $$$\widehat{S_c}(\textbf{r})$$$ and the coil-phase $$$\angle\widehat{S_c}(\textbf{r})$$$ using the sum-of-square method13 from a temporally-averaged and spatially-low-pass-filtered image $$$I_{avg,c}(\textbf{r})=LPF_{x,y}\{(1/N)\sum_{t=1}^{N}I_c(\textbf{r},t)\}$$$. We then combine the individual coil images $$$I_c(\textbf{r},t) $$$ into a single image, $$$I (\textbf{r},t)$$$ using optimal B1 combination13. We compute a dynamic field map estimate $$$\widehat{\Delta f} (\textbf{r},t) $$$ from $$$I(\textbf{r},t) $$$ as follows:$$\widehat{\Delta f} (\textbf{r},t) = \angle I(\textbf{r},t)/(-2\pi TE) $$
Note that this approach only captures the dynamic field map, i.e. there will be a residue ($$$
f
(\textbf{r},t) - \widehat{\Delta f} (\textbf{r},t)$$$) that equals $$$LPF_{x,y} \{ (1/N) \sum_{t=1}^{N} { \Delta f (\textbf{r},t) } \}$$$, a spatially low-pass filtered version of the time-averaged field map, where $$$LPF_{x,y}\{ \cdot\}$$$ is the same one used to generate $$$I_{avg,c}(\textbf{r})$$$.
Methods
Experiments were performed on a GE Signa Excite 1.5 T scanner with a custom 8-channel upper-airway coil6 and an 8-interleaf spiral fast gradient echo pulse sequence (readout time = 4.016 ms). A volunteer was scanned at the mid-sagittal plane while performing the speech task: “one-two-three-four-five” several times at a normal pace followed by several times at a fast pace (roughly 2x). Imaging parameters: spatial resolution = 2.4×2.4 mm2, slice thickness = 6 mm, FOV = 20cm2, TR = 7.508 ms, TE = 0.8 ms, BW = ±125 kHz, FA = 15°. Sliding-window image reconstruction (22.2 frames per second) was performed, using multi-frequency interpolation method7 based on the proposed dynamic field map estimate $$$\widehat{\Delta f} (\textbf{r},t) $$$.Results and Discussion
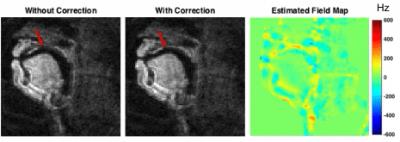
Figure 1 contains reconstructed image frames without and with the proposed correction, and the corresponding estimated dynamic field map. Near air-tissue interfaces, we observed rapid temporal variations.
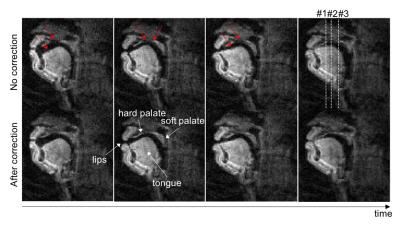
Figure 2 contains representative image frames without and with the proposed correction. The proposed correction improved the depiction of air-tissue boundaries, especially the hard palate, soft palate, and tongue boundaries (see red arrows).
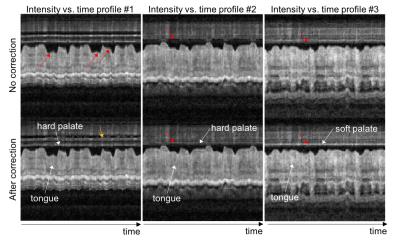
Figure 3 contains intensity vs. time profiles from different image locations (dotted lines in Fig. 2). The profiles allow one to easily appreciate the sharper air-tongue boundary. Correction also results in more temporally consistent signal intensity in the hard and soft palate (red arrows). This result agrees with the fact that the hard palate, which is a bony structure covered by a thin layer of tissue, does not change its shape during speech production14.
Conclusion
We have demonstrated a method for estimating dynamic field variation in spiral 2D RT-MRI of speech. This method, when combined with multi-frequency reconstruction, improves sharpness of the vocal tract articulator boundaries including the hard palate, soft palate, and tongue, which has the potential to improve the analysis of articulator motion in speech science. A limitation of this work is that the time-averaged field map is not corrected. Additional estimation of this field and/or improvements to pre-scan shimming may have a synergistic role.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute of Health under NIH-R01-DC007124 and National Science Foundation under NSF-1514544.References
1. Lingala SG, Sutton BP, Miquel ME, Nayak KS. Recommendations for real-time speech MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2016;43:28–44.
2. Bresch E, Kim YC, Nayak K, Byrd D, Narayanan S. Seeing speech: Capturing vocal tract shaping using real-time magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Signal Process Mag 2008;25:123–132.
3. Block KT, Frahm J. Spiral imaging: A critical appraisal. J Magn Reson Imaging 2005;21:657–668.
4. Narayanan SS, Nayak KS, Lee S, Sethy A, Byrd D. An approach to real-time magnetic resonance imaging for speech production. J Acoust Soc Am 2004;115:1771–1776.
5. Kim YC, Narayanan SS, Nayak KS. Flexible retrospective selection of temporal resolution in real-time speech MRI using a golden-ratio spiral view order. Magn Reson Med 2011;65:1365–1371.
6. Lingala SG, Zhu Y, Kim Y, Toutios A, Narayanan S, Nayak KS. A fast and flexible MRI system for the study of dynamic vocal tract shaping. Magn Reson Med 2016. doi:10.1002/mrm.26090.
7. Man LC, Pauly JM, Macovski A. Multifrequency interpolation for fast off-resonance correction. Magn Reson Med 1997;37:785–792.
8. Nayak KS, Tsai CM, Meyer CH, Nishimura DG. Efficient off-resonance correction for spiral imaging. Magn Reson Med 2001;45:521–524.
9. Sutton BP, Conway CA, Bae Y, Seethamraju R, Kuehn DP. Faster dynamic imaging of speech with field inhomogeneity corrected spiral fast low angle shot (FLASH) at 3 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010;32:1228–1237.
10. Noll DC, Pauly JM, Meyer CH, Nishimura DG, Macovski A. Deblurring for non-2D Fourier transform magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 1992;25:319–333.
11. Man LC, Pauly JM, Macovski A. Improved automatic off-resonance correction without a field map in spiral imaging. Magn Reson Med 1997;37:906–913.
12. Smith TB, Nayak KS. Automatic off-resonance correction in spiral imaging with piecewise linear autofocus. Magn Reson Med 2013;69:82–90.
13. Roemer PB, Edelstein WA, Hayes CE, Souza SP, Mueller OM. The NMR phased array. Magn Reson Med 1990;16:192–225.
14. Bresch E, Narayanan S. Region segmentation in the frequency domain applied to upper airway real-time magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2009;28:323–338.
Figures