3892
Simultaneous acquisition of T1rho and T2 map of liver with black blood effect in a single breathhold1Imaging and Interventional Radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, New Territory, Hong Kong, 2Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, New Territory, Hong Kong, 3Philips Healthcare, New Territory, Hong Kong
Synopsis
T1rho is promising for early detection of liver fibrosis. However, the richness of blood vessels in the liver coupled with respiratory motion makes T1rho measurement prone to errors. In this work, we propose a pulse sequence to simultaneously obtain a T1rho and a T2 map of liver in a single
Purpose
Chronic liver disease is a major health problem worldwide. Liver fibrosis is a key feature in the early stage of chronic liver disease. When identified early, liver fibrosis may be reversible and the late complications can be avoided. A number of studies have reported that T1rho is promising for early detection of liver fibrosis1-2. T1rho has advantages in clinical practice as it does not require exogenous contrast agent or extra hardware. However, the richness of blood vessels in the liver coupled with respiratory motion makes T1rho measurement prone to errors. Recently a pulse sequence has been reported for quantitative T1rho imaging of liver with black blood effect3. In this work, we extend this pulse sequence to simultaneously obtain a T1rho and a T2 map of liver in a single breathhold with black blood effect.Method
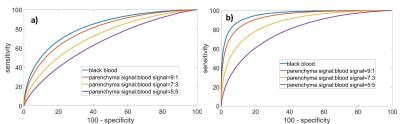
The diagnostic value of blood suppression during quantitive T1rho and/or T2 imaging of liver is demonstrated by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. In Figure 1, we generated the ROC curves using Monte Carlo simulations (10k trials for each curve) to compare the diagnostic value of T1rho and/or T2 for liver fibrosis at the various level of blood suppression. Increased effectiveness of blood signal suppression improves disease detectability as shown by the progressive improvement in ROC.
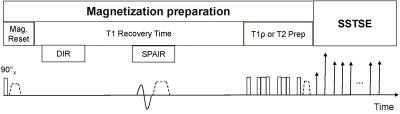
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the proposed pulse sequence. The pulse sequence concatenates T1rho-prep and T2-prep acquisition. Both T1rho-prep and T2-prep are followed with the same single shot fast spin echo (SSFSE) acquisition to utilize the inherent blood suppression of SSFSE acquisition. The T2 preparation contains a train of non-selective composite refocusing RF pulses 90x-180y-90x with the MLEV phase scheme. For the first time-of-spin lock (TSL) and the first TE, T1rho-weighted image is same as the T2-weighted image. Fat suppression is achieved by a spectrally selective inversion pulse. Additionally, the gradient reversal technology4 is applied during SSFSE echo train to improve fat suppression. Double inversion recovery (DIR) is used to suppress through-plane blood flow5.
Data sets were acquired from a Philips Achieva 3.0T system equipped with dual transmitter. Volunteer liver imaging were conducted under the approval of the Institutional Review. A 32 channel cardiac coil was used as the receiver. RF shimming was applied to reduce B1 inhomogeneity. The acquisition parameters include: TSL for T1rho 0, 10, 30, 50ms; TE for T2-prep: 0, 6.9, 20.5, 44.5ms; spin-lock frequency 500Hz; resolution 1.5mm x 1.5mm x 6mm; single slice. The scan time to collect the entire data sets is 14 seconds (a single breathhold).
Results
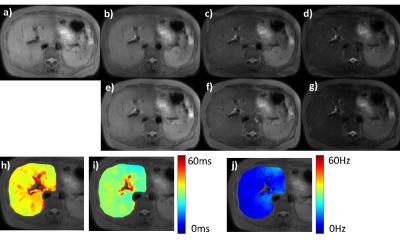
Figure 3 shows the T1rho-weighted and T2-weighted images and the corresponding T1rho map and T2 map. The good image quality suggests the proposed pulse sequence is an SNR efficient approach. Due to single breathhold acquisition, all images are well registered to each other. Since T1rho map and T2 map are registered to each other, a composite metric (R2 - R1rho) = (1/T2-1/T1rho) can be easily calculated.Discussion
Li et al6 reported an original approach of simultaneous T1rho and T2 quantification for cartilage imaging. The way we concatenate T2-prep and T1rho-prep for simultaneous T1rho and T2 quantification follows that approach. By combining this design with our previous black blood T1rho imaging sequence3, we demonstrated that both T1rho and T2 map can be acquired in a single breathhold.
Recently Russell et al 7 reported that the composite metric R1rho-R2 (R1rho=1/T1rho and R2=1/T2) is sensitive to early detection of osteoarthritis (OA). OA is characterized by depletion of proteoglycan and collagen. Since liver fibrosis is also associated with changes in proteoglycan and collagen, we expect this composite metric to have diagnostic value in the early detection of liver fibrosis. Further investigation is needed to understand the diagnostic value of the composite metric on liver diseases.
Conclusion
We proposed a pulse sequence for simultaneous T1rho and T2 quantification of liver. The data sets can be acquired within a single breathhold with black blood effect. Volunteer imaging demonstrated this pulse sequence is an SNR efficient data acquisition method for liver imaging.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong SAR (Project No. SEG CUHK02).References
1. Wang et al, Radiology. 2011; 259:712–9.
2. Singh et al, J Transl Med. 2015 Sep 8; 13:292
3. Chen et al, Quantitative imaging in medicine and surgery. 2016 Apr;6(2):168.
4. Park et al, Magn Reson Med. 1987; 4(6): 526-536.
5. Edelman et al, Radiology 1991; 181(3), 655-660.
6. Li et al, Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2014 May 1;39(5):1287-93.
7. Russell et al, Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2016 Sep 1.
Figures