3889
Multiple Instantaneous Switchable Scans interleaving T2W and DWI for Prostate Biparametric MRIWei WANG1, Xiubo QIN1, Juan WEI2, and Xiaoying WANG1
1Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, People's Republic of China, 2Philips Research China, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
Multiple Instantaneous Switchable Scans (MISS) is a type of interleaved scan method. In our study of prostate MRI, we combined the 3D-T2W and DWI by MISS into one scan, both of which are essential sequences for PIRADS v2. The combined sequences improved the scan efficiency (6min to 4min30s). The image quality and lesion display of MISS is similar to conventional T2W and DWI. The 3D-T2W in MISS showed better performance of seminal vesicles and lesion contrast and allowed for interactive multiplanar reformation.
Objective
To compare the multiple instantaneous switchable scans (MISS) which consisted of 3D T2W and DWI with conventional sequences of prostate MRI for image quality and lesion display.Subjects and methods
With IRB approval, 52 consecutive men who underwent prostate MRI were included. All the patients had suspected disease of the prostate with elevated PSA (4.4-2694ng/ml) but no prior treatment. All scans were done on a 3T scanner (Achieva TX, Philips, the Netherlands) using a 32-channel phased array coil. The conventional 2D T2W and DWI were included (total time: 6min). The additional MISS were the interleaved scans including 3D T2W and DWI (acquisition time: 4min30s). Each shot of the DWI scan was interleaved in the empty duration for SAR consideration between the two repeated cycles of 3D T2W scan so that T2W and DWI can be acquired simultaneously during one repetition time. The DWI in MISS is the same with convention. The images were reviewed by two radiologists in consensus. The delineation of the zonal anatomy, prostate capsule, seminal vesicles and image quality (sharpness, contrast, and artifact) were compared between MISS and conventional T2WI+DWI (CTD). Each of them was rated using a 3-point scale (1,poor; 2,moderate; 3,excellent). One reader measured and calculated the contrast of index lesion [(SINormal-SILesion)/SINormal, SI is the signal intensity on T2WI] and assigned PIRADS v2 scores for MISS and CTD. The other reader gave a preference from MISS and CTD using 3-point scale (1, prefer convention; 2, no preference; 3, prefer MISS). The Wilcoxon signed rank test was used.Results
There was no difference in the delineation of zonal anatomy, prostate capsule and image quality(p>0.05) between MISS-T2WI and conventional T2WI. MISS-T2WI showed better performance for seminal vesicles (2.98±0.14 and 2.56±0.57; p<0.001). There was no difference between MISS-DWI and conventional DWI of image quality (p>0.05). No difference was found for the PIRADS scores between the MISS and conventions(3.02±1.30, 3.00±1.28; p=0.317). For the lesion display, MISS-T2WI had higher contrast ratio(0.43±0.14, 0.35±0.13; p=0.007). For 30 cases, the performance of MISS was similar to CTD, but for the other 22 ones, the reader prefer MISS considering the diagnostic efficiency.Conclusion
The new scan mode of MISS could obtain two sequences for PIRADS in one scan and show superior performances than conventions.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
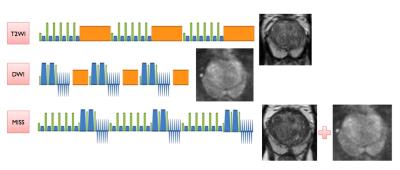
The first and second lines are the conventional T2W and DWI. The orange rectangle represents the waiting time. The third line showed the interleaved mode of T2W and DWI by MISS. The prostate images obtained are listed after the scan diagram.
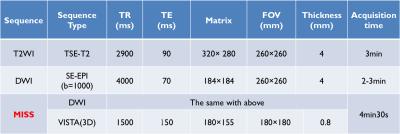
The table showed the
MR acquisition protocols.
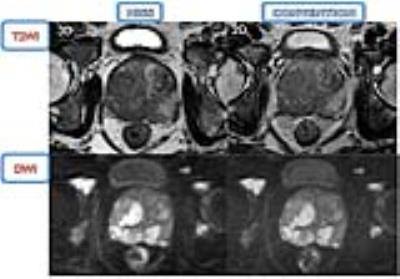
This is a patient with prostate cancer. The
PIRADS v2 score is 5. There is no obvious difference of image quality between
MISS and the conventional T2W+DWI. The 3D-T2W in MISS showed slightly better
lesion contrast than the convention.