3848
Simultaneous Multi-Slice Radial Phase Contrast MRILiyong Chen1,2 and David Feinberg1,2
1Advanced MRI Technologies, LLC, Berkeley, CA, United States, 2Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute, Univ of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States
Synopsis
The purpose was to develop and evaluate a novel approach to MR phase imaging of blood flow by combining radial cine phase contrast (radial cine-PC) with simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) technique to measure velocity in several slice planes simultaneously. Comparisons were made between SMS radial and SMS Cartesian 2D cine-PC and the velocity curves measured in cerebral vessels were similar between them. The higher acquisition efficiency of SMS radial cine PC allows for simultaneous cross-sectional hemodynamic quantification and may be useful for medical diagnoses.
Introduction
Phase contrast (PC) MRI is a common hemodynamic velocity measurement technique on commercial scanners by incorporating bipolar gradient pulse to encode the flow velocity1. Cardiac-gated 2D GRE sequence with small flip angle is widely used to generate cine velocity images2-3 . Our previous work used simultaneous multi-slice technique (SMS) 2D Cartesian cine-GRE to acquire velocity images in multiple planes to have more spatial coverage without increasing acquisition time4. Radial sampling is well-known for its motion robustness and benign undersampling behavior which may benefit parallel imaging and compressed sensing, and it has been successfully applied to phase contrast MR imaging5-6. In this work, we develop and evaluate a SMS 2D cine-GRE PC MRI with radial sampling to further speed up the velocity measurement.Methods
A 2D FLASH sequence with cine acquisition, radial sampling and prospective cardiac gating was modified to excite with multiband (MB) rf pulses; bipolar velocity gradient was used to encode the flow, as shown in Fig 1. Controlled aliasing7 was performed by phase cycling the MB pulse, for 2 slices (0.0) (0,180) across different rays. Imaging was performed in 3 normal subjects with both SMS Cartesian and SMS radial cine-PC for blood velocity in 32ch head coil. Imaging parameters for cine-PC 2D radial SMS: SMS=2 with 64 mm slice gap, TR=8.4ms, TE=4.6ms, BW=280 Hz/pixel, FA=15°, FOV=192×192mm2, matrix=256x (36~128), in-plane resolution=0.8x0.8mm2, slice thickness= 4mm and through-plane direction VENC=90cm/s. For comparison purpose, cine-PC 2D Cartesian SMS with matrix size 256x128 was acquired with the other parameters the same. The preparation time for spatial sensitivity data, single band and dummy scans was short, about 2s. The generalized SENSE was used to reconstruct the images8-9.Results/ Discussions
Figure 2 shows the comparison of the magnitude and phase images of Cartesian, radial sampling with different number of rays. It shows that the radial SMS has some streaking artifact especially with small ray number. Figure 3 shows the velocity curves of two regions of interest in cerebral vessel using different methods. It shows the velocity curves of radial SMS of 128, 64 and 36 rays matched well with Cartesian SMS of 128 PE lines and the slight shift of the curves may be due to the heart rate changes across different scans.Conclusions
SMS with radial sampling pattern is demonstrated to be able to acquire multiple cine velocity images in different slice planes simultaneously, gaining more acceleration than Cartesian SMS without much image degradation. Larger SMS factor would allow higher acquisition efficiency as proportional to SMS factor. Compressed sensing with more complicated sampling, such as various sampling across different cardiac phases, can be incorporated to gain more acceleration thus further increase spatial and temporal resolution.Acknowledgements
NIH R44MH112210References
1. Hahn J, Geophys 1960 2. Bryant et al, JCAT 1984 3. Enzmann et al, AJNR 1993 4. Feinberg D, Chen L et al page 320, ISMRM 2016 5. Thompson et al, MRM 2004 6. Gu et al, MRM 2005 7. Yutzy et al, MRM 2011 8. Pruessmann et al, MRM 2001 9. Zahneisen et al, Neuroimage 2014Figures
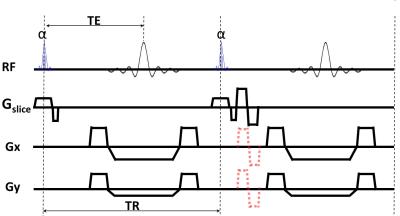
Fig 1. SMS radial Cine-PC pulse sequence. Excitation
multiband rf pulses (blue) is with phase cycling for controlled aliasing across
different rays. Only velocity in through-plane direction was acquired in this
work; velocities in other directions as shown in red dash gradients have not
been implemented.
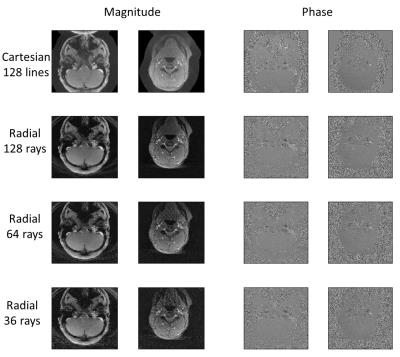
Fig 2. Average magnitude and phase images of cerebral vessels with different methods, including SMS 2D Cartesian with 128 lines, SMS 2D radial with 128, 64 and 36 rays.
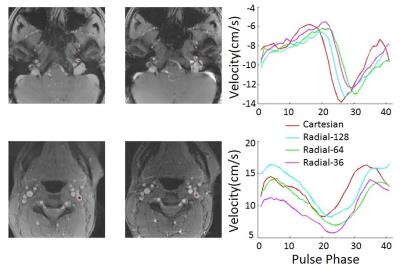
Fig 3. (Left-Middle) Magnitude images of SMS 2D Cartesian/SMS 2D Radial with 128 lines showing location of curve measurements. (Right) Comparison of velocity curves in SMS 2D Cartesian with 128 lines, SMS 2D radial with 128, 64 and 36 rays.