3695
Dynamic shimming for multi-slice hyperpolarized metabolic imaging of the rat heart at 9.4T1Institute for Biomedical Engineering, ETH and University Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Synopsis
In this work dynamic shimming was implemented for multi-slice hyperpolarized metabolic imaging of the rat heart at 9.4T. Phantom experiments were carried out to test the switching between different shim sets and eddy current effects. The method was subsequently applied to assess cardiac metabolism in healthy rats after injecting hyperpolarized [1-13C] pyruvate. It is demonstrated that B0 inhomogeneity induced signal variations could be reduced with dynamic shimming when compared to static shimming.
Introduction
Metabolic magnetic resonance imaging using dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) is a promising tool to study myocardial metabolism1. However, at the high field strengths typically used in preclinical studies, obtaining a homogenous B0 field over the whole region of interest is challenging, especially when whole-heart coverage is desired. In this work, dynamic shimming2 was implemented for multi-slice hyperpolarized metabolic imaging of the rat heart at 9.4T. B0 field homogeneity was optimized for each slice individually and shim gradients where switched between the acquisitions of the different slices. Results obtained with the dynamic shimming approach were compared to static shimming.Methods
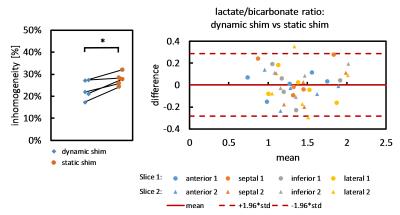
Experiments were performed on a Bruker BioSpec 9.4T system equipped with ParaVision 6.0.1 software (Bruker BioSpin, Ettlingen, Germany). Proton EPI measurements of a water-air phantom were carried out to test switching between different shim sets and to analyze eddy current effects. Time constants of B0 eddy current effects resulting from switching the z2 shim coil were characterized using PRESS acquisitions at different delays after shim switching. All animal experiments were performed in adherence to the Swiss Animal Protection law. Multi-slice metabolic imaging of the heart was performed in five healthy Sprague Dawley rats following injection of 1 mL hyperpolarized [1-13C] pyruvate. Hyperpolarization was performed using an experimental dissolution DNP setup as previously decribed3. First and second order shim terms were optimized for each of the two short-axis slices individually using field maps in a region-of-interest covering the left ventricle. Local frequencies were determined for each shim set with a PRESS volume in the corresponding slice. B0 eddy current compensation was employed by adding the previously determined frequency offset. Dynamic metabolic imaging was performed with a multi-echo single-shot EPI sequence with 7 echoes4 (FOV 60x40mm2, resolution 1.25x1.25mm2, slice thickness 3.5mm). The two slices were acquired within the same heart beat (Figure 1). To minimize respiratory motion artifacts, the 7 echoes were collected during end-expiration by synchronizing the respiration pump to the sequence (Figure 1). The 7 echoes were repeated every 1.5 seconds. A dual tuned 1H/13C volume resonator and a 13C receive surface coil (Rapid Biomedical, Wuerzburg, Germany) were used for radiofrequency transmission and reception. The five animals received two pyruvate injections each separated by 20 minutes to acquire a dataset with dynamic shimming and one with static shimming. In the static shim experiment the shim terms were optimized for the two slices jointly and left constant. The order of the two measurements was randomized. Pyruvate, lactate and bicarbonate metabolite maps were reconstructed using the IDEAL approach5. A correction for the surface coil sensitivity was applied using data acquired in a uniform 13C urea phantom. Area-under-the-curve (AUC) lactate/bicarbonate ratios were examined for four myocardial segments. A signal inhomogeneity score as defined below was calculated and compared between dynamic and static shim:
$$inhomogeneity = \frac{SD(\text{bicarbonate voxel intensities in myocardium})}{mean(\text{bicarbonate voxel intensities in myocardium})} * 100 [\%]$$Results
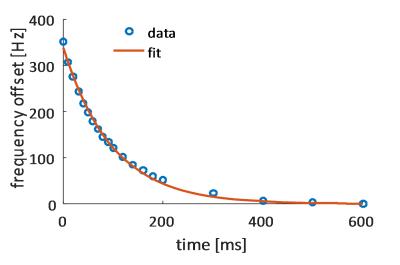
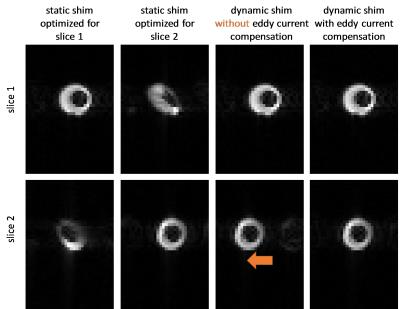
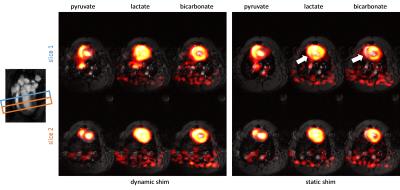
Significant eddy current effects were only observed when switching the z2 shim channel while offsets from the other shim channels had negligible effects on geometrical distortions of the image. Frequency offsets due to B0 eddy currents were characterized (Figure 2) and then used to adjust the center frequencies of the slices. This allowed to acquire slices at delays of as short as 5 ms between each other without any noticeable distortions or shifts. Multi-slice proton phantom experiments with dynamic shimming and B0 eddy current compensation showed comparable results when compared to single-slice experiments acquired with per-slice static shimming (Figure 3). Dynamic shimming was successfully implemented for in-vivo multi-slice hyperpolarized metabolic imaging (Figure 4). By employing B0 eddy current compensation, no eddy current artefacts were observed. Homogeneity of the bicarbonate signal in the myocardium was improved with dynamic shimming compared to static shimming (Figure 5).Discussion
Dynamic shimming for multi-slice experiments at 9.4T was successfully implemented, tested in phantoms and applied to metabolic imaging of the rat heart. The predominant eddy current effect resulted from switching the z2 shim coil and was addressed by dynamically adjusting the center frequency per slice. In-vivo, signal variations due to B0 inhomogeneity could be reduced with dynamic shimming. In this study, only two adjacent slices were used. However, the approach is easily extendible to more slices. Larger benefits from dynamic shimming than observed here are expected when the slices are further apart. For example, when acquiring slices in the heart and liver simultaneously6, dynamic shimming is expected to be of critical importance.Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge funding from the Swiss National Science Foundation, grant 320030_153014.References
1. Schroeder MA, Clarke K, Neubauer S, Tyler DJ. Hyperpolarized Magnetic Resonance A Novel Technique for the In Vivo Assessment of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2011;124:1580–1594.
2. Seuwen A, Wick M, Hennel F, Schroeter A, Rudin M. Multi-slice functional FID based spectroscopic imaging on mice using dynamic shimming at 9.4T. In: Proceedings 24st Scientific Meeting, ISMRM. ; 2016.
3. Krajewski M, Wespi P, Busch J, Wissmann L, Kwiatkowski G, Steinhauser J, Batel M, Ernst M, Kozerke S. A multisample dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization system for serial injections in small animals. Magn Reson Med 2016.
4. Sigfridsson A, Weiss K, Wissmann L, Busch J, Krajewski M, Batel M, Batsios G, Ernst M, Kozerke S. Hybrid multiband excitation multiecho acquisition for hyperpolarized 13C spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 2015;73:1713–1717.
5. Reeder SB, Wen Z, Yu H, Pineda AR, Gold GE, Markl M, Pelc NJ. Multicoil Dixon chemical species separation with an iterative least-squares estimation method. Magn Reson Med 2004;51:35–45.
6. Le Page LM, Ball DR, Ball V, Dodd MS, Miller JJ, Heather LC, Tyler DJ. Simultaneous in vivo assessment of cardiac and hepatic metabolism in the diabetic rat using hyperpolarized MRS. NMR Biomed 2016.
Figures