3577
Prospective longitudinal evaluation of patients with low-grade cartilage injury using gagCEST at 7T1High Field MR Centre, Department of Biomedical Imaging and Image-Guided Therapy, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 2Department of Orthopaedics, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 3Christian Doppler Laboratory for Clinical Molecular MR Imaging, Vienna, Austria, 4Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research, Basel, Switzerland, 5Research Unit of Medical Imaging, Physics and Technology, University of Oulu and Oulu University Hospital, Oulu, Finland, 6Depatment of Traumatology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Synopsis
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that employs gagCEST for the longitudinal evaluation of untreated articular cartilage defects. We demonstrate that gagCEST at 7T has the potential of discriminating between cartilage defects, weight bearing and non-weight bearing femoral cartilage and therefore might serve as a biomarker for the evaluation of novel cartilage therapies. Furthermore, our study implies that proper fixation of the examined knee may help to increase the reliability of gagCEST experiments.
Purpose
Cartilage injury and degeneration are major challenges in orthopaedic practice. Due to a very limited regenerative potential of articular cartilage, timely diagnosis is pivotal for favorable treatment outcome. At the same time, there is strong demand for a tool that allows for reproducible and repetitive assessment of cartilage quality and for evaluating efficacy of novel pharmacological and surgical treatment options. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of gagCEST to detect and monitor untreated low-grade cartilage defects.Methods
This study was approved by the local ethics committee and written informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to enrolment. Sixteen patients (mean age, 47.4 ± 10.2 years; 9 males) were included in the study. As inclusion criteria served at least one MRI confirmed cartilage defect in the knee joint (ICRS Grade I or II) and additional risk factors for disease progression. All patients were examined on a 7T whole-body research MR scanner (Magnetom, Siemens Healthineers, Germany) using a 28-channel knee array coil (Quality Electrodynamics, OH, USA). Each patient was measured at four time points (baseline (B), 8 days (8D), 3 months (3M) and 6 months (6M)). T2-weighted 3D- double echo steady-state (DESS) images (0.5 mm isotropic resolution, TR/TE = 8.68/2.55 ms; TA 3:58 min) were acquired for morphological evaluation and segmentation. For CEST experiments, a prototype segmented 3D RF-spoiled gradient-echo (GRE) sequence (TE = 3.1 ms, TR = 7.9 ms, resolution = 0.9 x 0.9 x 2.2 mm3, measurement time = 20:30 min) was used. Selective presaturation was performed using ten 60-ms adiabatic full passage hs2 RF pulses with variable frequencies (± 10, ± 20 Hz) with an interpulse delay of 20 ms [1]. Nineteen offsets (stepsize of 92 Hz) in the range of ±2.8 ppm around the water resonance and a scan without saturation were acquired. After image registration, the asymmetry of the Z-spectra (MTRasym) was calculated from integrals over the offset range ±∂ = 0.6–1.8 ppm relative to the minimum of each individual Z-spectrum using an in-house Matlab script [2].
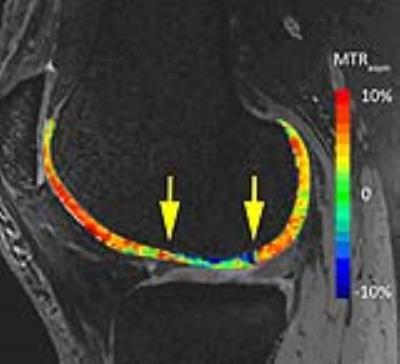
For image analysis, an expert musculoskeletal radiologist identified one cartilage defect in each patient based on a routine 3T exam and identified the corresponding T2-weighted DESS images for the regions of interest (ROI) analysis. All ROIs (weight-bearing, non-weight-bearing femoral cartilage and the defect) were defined in 3D DESS morphological images and subsequently transferred onto CEST maps by one reader. Paired Student’s t-test was used to determine the differences in MTRasym between weight bearing femoral cartilage and the defect. A two-way mixed intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was calculated to assess the reproducibility between B and 8D. Differences between weight-bearing, non-weight-bearing and defects were analyzed using one way ANOVA. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
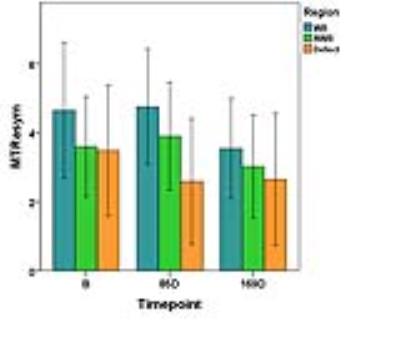
Eleven patients completed all measurements so far, four patients completed the first three measurements. One patient dropped out after B and 8D. Overall ICC between B and 8D was 0.48 but differed according to the region, with 0.68 for weight-bearing, 0.35 for non-weight-bearing and 0.27 for the defect region. During the study we introduced a fixation device to address the issue of patient movement already on a mechanical level. While three of the 36 imaging data sets measured without the fixation device were corrupted due to motion, none of the 21 scans obtained with the fixation device were lost. Over all time points, MTRasym was higher for weight-bearing femoral cartilage than for the defects (B: p =0.06, 85D: p = 0.003, 169D: p = 0.34).Discussion
These preliminary results show that gagCEST at 7T has a potential to differentiate between different cartilage regions and defects. Whereas there is still room for improvement regarding the reproducibility of individual scans, e.g., by including a separate scan for pixel-by-pixel B0 correction [3], the mean values over our cohort demonstrate the potential of gagCEST for mapping GAG concentration in knee cartilage. Furthermore, our preliminary results indicate that the GAG content remains relatively constant after an acute cartilage injury.Conclusions
Our preliminary results indicate that gagCEST might be sensitive to the concentration of GAG in normal and pathological articular cartilage. After further improvement in the reproducibility, this method could serve as a valuable biomarker for the diagnosis and follow-up of low grade cartilage defects.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Mlynarik V, Zbyn S, Schreiner M, et al. Comparison of gagCEST and sodium MRI in evaluating knee cartilage in vivo at 7 tesla. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 23, 4231 (2015).
2. Schreiner MM, Zbyn S, Schmitt B, et al. Reproducibility and regional variations of an improved gagCEST protocol for the in vivo evaluation of knee cartilage at 7T. Magn Reson Mater Phys 29, 513 (2016).
3. Kim M, Gillen J, Landman BA, et al. Water saturation shift referencing (WASSR) for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) experiments. Magn Reson Med 61, 1441 (2009).
Figures