3554
Black Blood T2-weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Imaging of the Liver with DANTE Preparation Module1Department of Radiology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 3Philips Healthcare (Suzhou), Suzhou, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
The purpose is to implement high resolution black blood T2-weighted TSE liver imaging in order to facilitate focal liver lesion detection and characterization. DANTE black blood preparation module, T2 weighted Multivane XD multi-slice acquisition and respiratory trigger were combined together. 8 healthy volunteers underwent MRI scanning on 3T Ingenia MR Syste. The black blood T2-weighted sequence showed high image quality and no artifacts. Hepatic veins, portal vein and their main branches were all suppressed successfully. No significant difference was shown in the SNR between black blood and routine T2-weighted images. In conclusion, the black blood T2-weighted imaging could provide robust and good imaging quality.
Introduction & Purpose
T2-Weighted turbo spin-echo (TSE) imaging with fat suppression proved to be very efficient for the morphologic assessment and the detection of focal liver lesions (1). The main drawback of liver lesion detection lies in the differentiation between focal lesions and surrounding peripheral vessels which shows similar signal intensity to malignant lesions. Low b-value diffusion was applied to suppress the signal from liver vasculatures (2). However, the image quality is quite limited due to inherent limitations of EPI especially in abdominal imaging such as image distortions, poor SNR, low spatial resolution, etc. The purpose of our study is to implement high resolution black blood T2-weighted TSE liver imaging so as to facilitate focal liver lesion detection and characterization.Methods
Pulse Sequence To effectively attenuate signals from hepatic and portal veins and better preserve static tissue signal, we adopted DANTE black blood preparation module for its B1 inhomogeneity insensitivity and less T2 decay. T2 weighted Multivane XD multi-slice acquisition which rejects poorly correlated data and respiratory trigger were combined together to provide superior motion free images. Imaging Parameters Optimized choices for the preparation module include: flip angle 8°, number of pulses 80, repetition interval 1 ms, gradient strength 16 mT/m. Acquisition parameters were: TR/TE 2750/76 ms, flip angle 90°, TSE factor 29, voxel size 1.5x1.5x5 mm3, FH coverage 154 mm, SENSE factor 2, scan time 2min 24s. MR Experiment 8 healthy volunteers underwent black blood T2-Weighted TSE imaging on 3T Ingenia MR System (Philips, Best, the Netherlands) with standard quadrature body coil and a phased-array 32-channels dS Torso coil. Image Analysis All images were reviewed by two independent radiologists with more than 3 years of experience in abdominal imaging. Overall image quality, degree of artifacts and suppression of the blood signal inside the hepatic vessels were compared on a 5-point scale (1= unacceptable, 2=poor, 3=moderate, 4=good, 5=excellent). The SNR and CNR was analyzed as the quantitative evaluation. Liver-to-spleen CNR was used as an indication for liver-to-lesion contrast. The SI was normalized to the standard deviation (SD) of back-ground noise of the liver SI and showed as SNR.CNR was calculated as the difference in SI between liver and spleen, normalized to the SD of back-ground noise. 5 and 3 region-of-interest (ROI) measurements were performed in the liver and spleen, respectively. Averages of the SI were used to measure the SNR and CNR. A Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-ranks test was performed to prove significance at a significance level of P < 0.05.Results
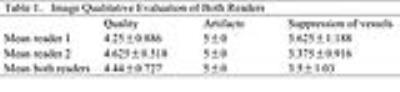
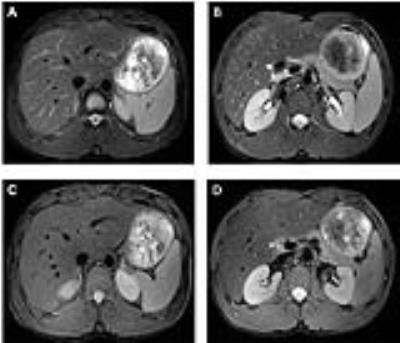
The black blood T2-weighted sequence showed high image quality (average score of both readers 4.44) and no artifacts (average score of both readers 5). The details results were shown in Table 1. Figure 1 showed the T2-weighted (A and B) and black blood images (C and D) with two different slices. Compared with routine T2-weighted images, the black blood sequence induced consistent high image quality and no artifacts. Hepatic veins, portal vein and their main branches were all suppressed successfully,e.g. right and left main branches, right anterior branch, as well as lateral segmental branch. No significant difference was shown in the SNR between black blood and routine T2-weighted images (Z=1.572, P=. 116). However, CNR of the routine T2-weighted images was higher than that of black blood images (Z=1.992, P=. 046)Discussion
In comparison with routine T2W imaging, black blood T2-weighted imaging may enhance the conspicuity of focal liver lesions against the mainly dark background of the liver parenchyma and vessels. In this preliminary study, black blood T2-weighted imaging shows high image quality, consistent with that of the routine images. This sequence may provide supernumerary contribution for liver lesion detection. We considered the limited case partially contributed to the lower CNR with the black blood images. More studies involving patients are required to evaluated the CNR of liver-to-lesion and validate the diagnostic value of the proposed sequence.Conclusion:
Black blood T2-weighted imaging is feasible by adopting DANTE preparation module. Our experiment showed that the black blood T2-weighted imaging could provide robust and good imaging quality.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Schieda, N., et al. "Low b-value (black blood) respiratory-triggered fat-suppressed single-shot spin-echo echo-planar imaging (EPI) of the liver: Comparison of image quality at 1.5 and 3 T." Clinical radiology 69.11 (2014): 1136-1141.
2. Zech, Christoph J., et al. "Black-blood diffusion-weighted EPI acquisition of the liver with parallel imaging: comparison with a standard T2-weighted sequence for detection of focal liver lesions." Investigative radiology 43.4 (2008): 261-266.
3. Li, Linqing, Karla L. Miller, and Peter Jezzard. "DANTE-prepared pulse trains: A novel approach to motion-sensitized and motion-suppressed quantitative magnetic resonance imaging.” Magnetic resonance in medicine 68.5 (2012): 1423-1438.