3443
Preliminary study for the quantification of fatty composition and relation to metabolic syndrome using modified Dixon method.1Radiology, Gifu University Hospital, Gifu City, Japan, 2Radiology, Gifu University Hospital, Gifu City, 3Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan, 4Gifu University Hospital, Gifu City, Japan
Synopsis
We successfully quantified fatty acid composition in the liver, subcutaneous, and visceral fat tissue using modified Dixon technique with flexible six echo times and seven-peak spectral model with lipid components. Our results suggested that fatty acid composition of depot fat was varied among the patients with different metabolic status. We also demonstrated the possible relationship of unsaturated fatty acid in depot fat to cholesterol level and insulin tolerance.
Purpose
Metabolic syndrome is a well-known cluster of metabolic and chronic conditions regarding blood sugar, cholesterol or triglyceride levels increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke and diabetes. It is closely related with patients’ lifestyle such as lipid intake, obesity, and inactivity (1). Especially fatty acid intake is one of the most-watched relative factors with metabolic syndrome (2). On the other hand, a previous basic research using migrating bird reported that fatty acid composition on depot fat is affected by intake fatty acid and unsaturated fatty acid in depot fat is effective for the dieting (3). Recently, several quantitative techniques have been developed in MRI regarding fat fraction. Based on the original method exploiting the periodic MR signal cancelation and addition during spin precession in water and lipids, modified Dixon techniques (mDixon) permit flexible six echo times (TE) not restricted to exact in-phase over out-of-phase values, included seven-peak spectral model with lipid components, and demonstrated excellent correlation with MR spectroscopy regarding the quantification of liver fat (4). So, the purpose of this preliminary study is to quantify the fatty acid composition in liver, subcutaneous, and visceral fatty tissue and to investigate a connection with metabolic syndrome.Materials and Methods
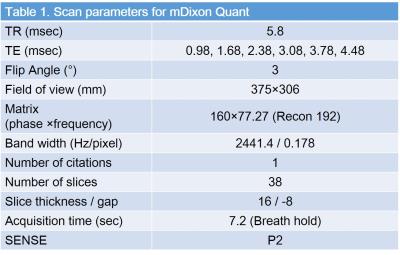
Thirty six-patients (23 men and 13 women, mean age: 68.1 years, age range; 37–85 years) underwent abdominal MR imaging for the evaluation of suspected tumor. All examinations were performed using a 3T clinical scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare) with a MultiTransmit RF system and a 32 channel phase-array receiver coil. Fatty acid composition was quantified using mDixon Quant (Philips Healthcare) method which was based on the six TEs (0.98, 1.68, 2.38, 3.08, 3.78, 4.48 msec) and seven-peak fatty acid model (Table 1). The fractions of total fatty acid, saturated fatty acid, and unsaturated fatty acid were calculated by mDixon with seven-peak model (FFtotal), mDixon with single-peak model (FFsaturated), and the difference between two (FFunsaturated = FFtotal - FFsaturated). FFs were calculated in three portions, such as subcutaneous fat tissue, visceral fat tissue, and liver using circular region-of-interest (ROI), which generated nine quantitative FF parameters examined. Quantitative nine parameters were correlated with body mass index (BMI), serum low-density (LDL), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Quantitative parameters were also compared with the presence of heart disease (HD) and type II diabetes mellitus (DM) by discrimination analyses.Results
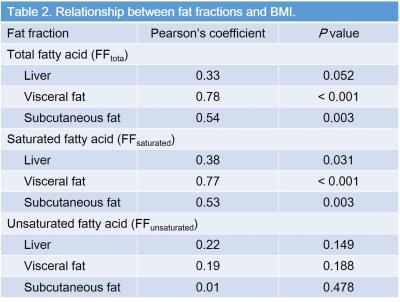
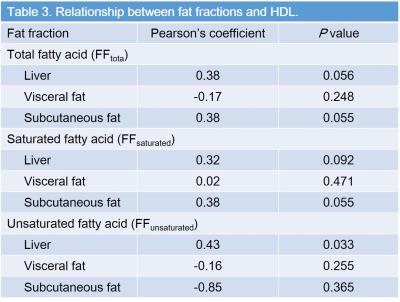
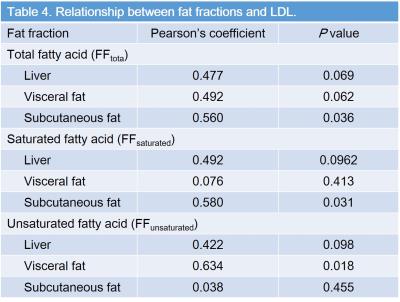
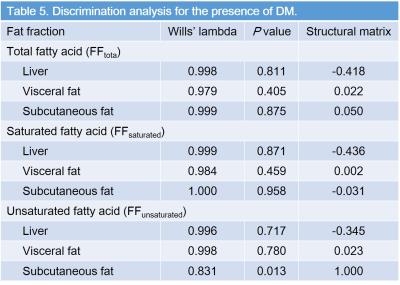
FFtotal in visceral (r = 0.78, P < 0.001) and subcutaneous fat (r = 0.54, P = 0.003), FFsaturated in liver (r = 0.34, P = 0.03), visceral (r = 0.77, P < 0.001), and subcutaneous fat (r = 0.53, P = 0.003) were significantly correlated with BMI (Table 2). FFunsaturated in liver was moderately correlated with serum HDL (r = 0.43, and P = 0.03), whereas no significant difference was found in other FFs (P = 0.06–0.37) (Table 3). FFtotal (r = 0.56, P = 0.04), FFsaturated (r = 0.58, P = 0.03) in subcutaneous fat and FFunsaturated in visceral fat (r = 0.63, P = 0.02) was moderately correlated with serum LDL (Table 4). FFs were not significant to differentiate the presence of HD (P = 0.39–0.83), whereas subcutaneous FFunsaturated was detected as a sole significant parameter related to DM (P = 0.002, r = 0.41) (Table 5). Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for the detection of presence of DM were 83.3%, 70%, and 72.2%.Discussion
mDixon method is one of the fast acquisition technique which enables simultaneous acquisition of quantitative and diagnostic images including fat fraction map, T2* map, water, fat, in- and out-of-phase images. mDixon scans were successfully performed in this clinical study and suggested an interesting result that fatty acid composition of depot fat was varied among the patients with different metabolic status. We also demonstrated the possible relationship of unsaturated fatty acid in depot fat to cholesterol level and insulin tolerance though, further nutritional study should be needed in the large cohort. In conclusion, calculation of fatty acid composition was feasible in clinical MR imaging using mDixon method. Unsaturated fatty acid in the depot fat seemed to be related to cholesterol metabolism and insulin tolerance.Acknowledgements
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.References
1. Maximino P, Horta PM, dos Santos LC, de Oliveira CL, Fisberg M. Fatty acid intake and metabolic syndrome among overweight and obese women. Rev Bras Epidemiol. 2015;18(4):930-42.
2. Watanabe K, Arozal W, Tanaka H, et al. Beneficial Effect of Food Substitute Containing L-Arginine, omega-3 Poly Unsaturated Fatty Acid, and Ribonucleic Acid in Preventing or Improving Metabolic Syndrome: A Study in 15 Overweight Patients and a Study of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Animals. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2009;44(3):266-74.
3. Pierce BJ, McWilliams SR, O'Connor TP, Place AR, Guglielmo CG. Effect of dietary fatty acid composition on depot fat and exercise performance in a migrating songbird, the red-eyed vireo. J Exp Biol. 2005;208(Pt 7):1277-85.
4. Kukuk GM, Hittatiya K, Sprinkart AM, et al. Comparison between modified Dixon MRI techniques, MR spectroscopic relaxometry, and different histologic quantification methods in the assessment of hepatic steatosis. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(10):2869-79.