3426
Evaluation of the reduced field-of-view Diffusion Weighted Imaging for staging of endometrial adenocarcinoma1Radiology, Shin-Yurigaoka General Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan, 2Faculty of Advanced Techno-Surgery (FATS), Institute of Advanced Biomedical Engineering and Science, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 3Research Institute for Medical Imaging, Shin-Yurigaoka General Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan, 4Neurosurgery, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 5Neurosurgery, Shin-Yurigaoka General Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan
Synopsis
The objective of this retrospective study is to evaluate the differences of the accuracy in endometrial adenocarcinoma using FOCUS DWI compared to that using conventional SS-EPI DWI. We calculated the accuracy by the interpretation of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and the pathology. The accuracy in the FOCUS DWI was significantly better than that in the SS-EPI DWI. This may be due to the decrease of distortion in DWI, which induced the artifacts. There was improvement of the accuracy using the FOCUS DWI in the patient who had suspected endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Background/Purpose
Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) is known to have high sensitivity in endometrial adenocarcinoma. In many cases Single-Shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) DWI has a large distortion and low special resolution on the principle1,2. Therefore, it might be difficult to detect the small lesion and the grade of myometrial invasion in the adenocarcinoma. Field-of-view (FOV) optimized and constrained undistorted single-shot (FOCUS) DWI is used to obtain low distortion and high special resolution without residual aliasing by reducing the FOV in the phase-encode direction with a 2D echo-planar RF excitation pulse3-6. Thus, it is reported to use FOCUS DWI in evaluating endometrial adenocarcinoma. However, there is no report about the accuracy in diagnostic of endometrial adenocarcinoma using FOCUS DWI. The objective of our preliminary study is to retrospectively evaluate the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy in endometrial adenocarcinoma using FOCUS DWI compared to general examination using SS-EPI DWI.Methods
This retrospective study was approved by the ethical committee at our hospital. Two hundred and one patients (age range: 52.3±12.7), who had magnetic resonance (MR) imaging examinations for suspected endometrial adenocarcinoma between August 2012 and July 2016, were retrospectively enrolled in our study. Eight patients, who were not performed the pathology diagnosis, was excluded from the analysis. The remaining 193 patients were analyzed (SS-EPI DWI: 122 patients; FOCUS DWI: 71 patients). The MR imaging equipment used was the Discovery MR750w 3.0T DV25 and Signa HDxt 1.5T OptimaEdition manufactured by GE Healthcare. We identified the true positive, true negative, false positive and false negative from the results, which is interpreted by MR imaging and the pathology, and we calculated the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy. Furthermore, we also calculated the sensitivity of the myometrial invasion of adenocarcinoma.Results
The overall diagnostic specificity (91.9%; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 82.5%, 96.9%) and accuracy (84.5%; 95% CI: 74.7%, 89.8%) in the FOCUS DWI was significantly better than that in the SS-EPI DWI (specificity, 82.3% [95% CI: 76.2%, 87.1%]; accuracy, 78.7% [95% CI: 70.8%, 84.9%]), there was not obvious difference of the sensitivity (FOCUS DWI, 76.5% [95% CI: 66.3%, 82.0%]; SS-EPI DWI, 72.1% [95% CI: 61.0%, 81.0%]) The sensitivity (32.1%; 95% CI: 14.8%, 49.4%) for the evaluation of the myometrial invasion of adenocarcinoma in the FOCUS DWI was better than that in the SS-EPI DWI (sensitivity, 23.3%; 95% CI: 8.2%, 38.5%).Discussion
The reason why the specificity in the FOCUS DWI was improved, may be due to the amelioration of the false positive by the decrease of the unique distortion in DWI, which induces the artifacts. Furthermore, the sensitivity in the evaluation of the myometrial invasion of the adenocarcinoma was also improved. This may be because the FOCUS DWI clearly visualizes the relationship between the endometrial adenocarcinoma and the myometrium. The limitations included retrospective study, the different interpretation of MR imaging by various radiologists (The experience range from 5 to 35 years), and the difference of the quality of machine.Conclusion
There was improvement of the specificity and accuracy using the FOCUS DWI in the patient who had suspected endometrial adenocarcinoma. In addition, we detected the better sensitivity using FOCUS DWI for the evaluation of the myometrial invasion of adenocarcinoma. This suggests that the FOCUS DWI can provide useful information for staging the endometrial adenocarcinoma.Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the radiologists and MR imaging technologists for their assistance.References
1. Andre JB, Zaharchuk G, Saritas E, et al. Clinical evaluation of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging of the cervical and thoracic spine and spinal cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(10):1860-6.
2. Korn N, Kurhanewicz J, Banerjee S, Starobinets O, Saritas E, Noworolski S. Reduced-FOV excitation decreases susceptibility artifact in diffusion-weighted MRI with endorectal coil for prostate cancer detection. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;33(1):56-62.
3. Feng Z, Min X, Sah VK, et al. Comparison of field-of-view (FOV) optimized and constrained undistorted single shot (FOCUS) with conventional DWI for the evaluation of prostate cancer. Clin Imaging. 2015;39(5):851-5.
4. Kim H, Lee JM, Yoon JH, et al. Reduced Field-of-View Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Pancreas: Comparison with Conventional Single-Shot Echo-Planar Imaging. Korean J Radiol. 2015;16(6):1216-25.
5. Saritas EU, Cunningham CH, Lee JH, Han ET, Nishimura DG. DWI of the spinal cord with reduced FOV single-shot EPI. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60(2):468-73.
6. Zaharchuk G, Saritas EU, Andre JB, et al. Reduced field-of-view diffusion imaging of the human spinal cord: comparison with conventional single-shot echo-planar imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(5):813-20.
Figures
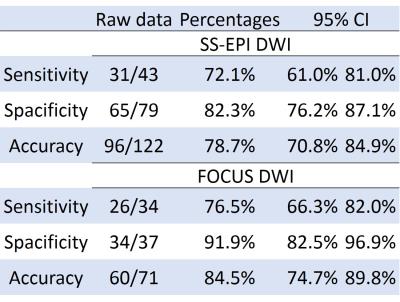
Table 1: The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of DWI in endometrial adenocarcinoma
CI=confidence interval, SS-EPI=single-shot echo planner imaging, DWI=diffusion weighted imaging, FOCUS= FOV optimized and constrained undistorted single-shot
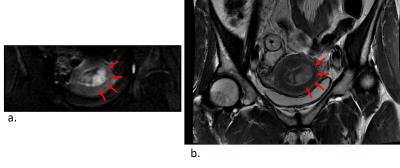
Figure 1: The endometrial adenocarcinoma for (a) FOCUS DWI is obtained lesion of high intensity, and (b) T2WI is visualized weak high intensity.
FOCUS= FOV optimized and constrained undistorted single-shot, DWI=diffusion weighted imaging, T2WI=T2 weighted imaging