3410
Diffusion weighted MR imaging–derived histogram Metrics for quantitative assessment of response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in local advanced rectal cancer: Initial Experience and Comparison between Single-Section and Volumetric Analyses1Shanxi Province Tumor Hospital, Taiyuan, People's Republic of China, 2MR Advanced Application and Research Center, GE Healthcare China, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
This retrospective study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values to assess the response to CRT in patient with local advanced rectal cancer by using histogram analysis derived from single-section (SS) and whole-tumor volume (WTV) regions of interest (ROIs). and found that Post-CRT ADC histogram metrics yield greater accuracy in discrimination between good and poor responders, especially in improving the specificity, compared with the mean ADC values.
Purpose:
Over the past decades, great changes for the treatment of patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) has shifted from surgery toward neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (CRT), with the choice of further therapy depending on the degree of response to CRT(1-2). Patient selection for organ-sparing treatment after good or complete response to CRT is challenging, highlighting the need for accurate assessment of tumor response to CRT (3). Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values to assess the response to CRT in patient with local advanced rectal cancer by using histogram analysis derived from single-section (SS) and whole-tumor volume (WTV) regions of interest (ROIs).Methods:
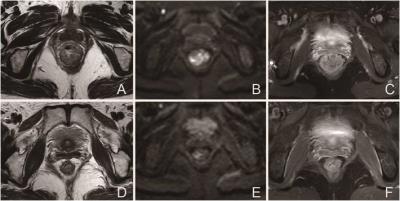
This retrospective study was approved by our institutional review board and written informed consent was waived. 48 patients with LARC underwent CRT and subsequent surgery, were enrolled in this study. All patients underwent pre- and post-CRT MRI at 3.0 T scanner with 8-channel phased array torso coils. ADCs were measured by two radiologists using SS and WTV ROIs methods on pre- and post-CRT diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). ADC histogram metrics and mean ADC values were then obtained respectively. Interobserver variability was analyzed by calculating intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Descriptive statistics and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were calculated to evaluate the diagnostic performance of ADC histogram metrics derived from two ROIs methods before and after CRT for prediction of histopathologic response.Results:
Interobserver agreement was excellent for WTV analysis (range, 0.77–0.89), but was only moderate for SS ROIs analysis (range, 0.61–0.73). Before CRT, none of the mean ADC values and the ADC histogram metrics correlated with subsequent tumor response (P>0 .28). While post-CRT, the mean ADC and some of the ADC histogram metrics derived from WTV and SS ROI analysis increased significantly and were significant higher in good responders than poor responders (P<0 .01) (Figure1). 25th ADCs showed the best diagnostic performance, and the specificity was significantly improved compared with the mean ADC.Discussion and Conclusion:
WTV analysis demonstrated better interobserver reproducibility than SS ROIs measurement. Post-CRT ADC histogram metrics yield greater accuracy in discrimination between good and poor responders, especially in improving the specificity, compared with the mean ADC values.Acknowledgements
NoReferences
1. Maas M, Nelemans PJ, Valentini V, et al. Long-term outcome in patients with a pathological complete response after chemoradiation for rectal cancer: a pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol 2010;11(9):835–844.
2. O’Neill BD, Brown G, Heald RJ, Cunningham D, Tait DM. Non-operative treatment after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. Lancet Oncol 2007;8(7):625–633.
3. Allaix ME, Fichera A. Modern rectal cancer multidisciplinary treatment: the role of radiation and surgery. Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:2921–2928.