3401
Ex-vivo visualization of the human trigeminal pathways using 11.7T diffusion MRI and unique microscopy data1Department of Anatomy, Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition & Behaviour, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands, 2Department of Neurosurgery, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands, 3Oxford Centre for Functional MRI of the Brain, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, 4Faculty of Medical Sciences, Radboud University, Nijmegen, Netherlands, 5Department of Anesthesiology, Pain and Palliative Care, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands
Synopsis
To optimize neuromodulation therapy of orofacial pain, a more profound insight in the trigeminal pathways in the human brainstem is of crucial importance. Using ex-vivo, 11.7T magnetic resonance imaging, polarized light microscopy and myelin staining methods, both the ventral and dorsal trigeminothalamic tracts can be visualized in humans. The combination of these visualization techniques strengthens the validity of these findings although the number of specimens forms a limitation. Future research must show whether these results are reproducible in more human brains and whether the described tracts could lead to new neuromodulation targets for the treatment of orofacial pain.
Purpose
Based on tracing studies in animals, three intracerebral tracts of the trigeminal nerve can be distinguished: 1) the ventral trigeminothalamic tract (VTT), 2) the dorsal trigeminothalamic tract and 3) the intranuclear pathway1. Understanding the conduction of orofacial pain may provide new neuromodulation targets for treating patients2. In human anatomy, only existence of the VTT is known, but not the DTT1. This study aims to investigate the existence of the aforementioned trigeminal tracts in the human brainstem by using 11.7T MR imaging, complemented with microscopic techniques.Materials and methods
A formalin-fixed human brainstem including the pons and medulla was separated from the cerebrum and placed in a syringe filled with fluorinert. MR imaging was performed on a 11.7T Bruker Biospec preclinical MR system using a birdcage coil. Anatomical images were acquired with a multi-gradient echo sequence and dMRI data using a segmented spin-echo EPI (Table 1). After eddy current correction of the images, fibre orientations were obtained by applying BEDPOSTX3 to the dMRI data. Probabilistic tractography was performed in FSL by seeding from the left trigeminal rootlet. A waypoint was placed in the dorsal part of the brainstem near the principal sensory nucleus (PSN) to ensure that diminutive tracts would not be overshadowed by larger white matter tracts that run in the brainstem1,4. Characteristics of the derived probabilistic tractography can be found in Table 1. Tractography results were compared with polarized light imaging (PLI)5 data and myelin and nuclear stained sections of the brainstem. PLI data was acquired from 100 μm unstained sections of another formalin fixed brainstem. Images were acquired with a polarizing microscope (Axio Imager A.2, Zeiss) and microscopic fibre orientations were obtained by processing the data in MATLAB. The acquisition of the myelin-stained sections is described elsewhere6.Results MR imaging
The anatomical structures that are related to the trigeminal nerve can be recognized on the high-resolution structural MR images (Figure 1). From the seedmask streamlines were generated to enter the anterolateral pons. Within the brainstem, the trigeminal tract (TT) bends in a dorsomedial direction towards the lateral pontine tegmentum after penetrating the middle cerebellar peduncle. In the lateral pontine tegmentum, the principal sensory nucleus (PSN) can be found. Near the PSN, the TT divides into a descending and ascending part. The descending fibers form the spinal trigeminal tract (STT) and run in the dorsolateral part of the brainstem. The ascending fibers course in two directions. One portion runs through the PSN region and crosses over to the contralateral side as the VTT. The second portion courses towards the dorsal aspect of the brainstem and forms the DTT, which remains on the ipsilateral side (Figure 2).Results Histological sections
In the midpons section of Figure 3C, the TT can be recognized easily and seems to divide into two parts. One portion runs to the dorsal part of the brainstem towards the region that is appointed as the DTT region according to DW tractography. The other part runs in a more medial direction towards the medial lemniscus, where the VTT can be recognized as well.Results Polarized light imaging
The TT can be recognized in Figure 4. Near the PSN, the TT divides into 1) a tract that runs towards the median part of the brainstem, where the ML is located, and 2) a tract that runs to the dorsal aspect of the brainstem. The courses of these pathways are suggestive for the VTT and DTT, respectively.Discussion
This paper shows that the intracerebral trigeminal system consists of two major pathways in the brainstem: the VTT and DTT. Although the VTT is well-known in humans7-12, the DTT has never been showed in a convincing manner. The results of this study support the existince of the DTT in humans, however, this has only been observed in one specimen. We cannot state whether this tract is involved in the conduction of orofacial pain. Further research in this field should contribute to the general understanding of the pathophysiology of orofacial pain and its conduction pathways.Conclusion
This study provides strong evidence that next to the VTT, the DTT is also present in humans. When both tracts are involved in the conduction of noxious information, new neuro-modulation targets could be discovered in order to enhance the treatment of chronic orofacial pain.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Henssen DJ, Kurt E, Kozicz T, van Dongen R, Bartels RH, van Cappellen van Walsum AM. New Insights in Trigeminal Anatomy: A Double Orofacial Tract for Nociceptive Input. Frontiers in neuroanatomy. 2016;10:53.
[2] Nash PG, Macefield VG, Klineberg IJ, Gustin SM, Murray GM, Henderson LA. Bilateral activation of the trigeminothalamic tract by acute orofacial cutaneous and muscle pain in humans. Pain. 2010;151:384-93.
[3] Behrens TE, Berg HJ, Jbabdi S, Rushworth MF, Woolrich MW. Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: What can we gain? NeuroImage. 2007;34:144-55.
[4] Büttner-Ennever JA, Horn AKE. Olzewski and Baxter's Cytoarchitecture of the Human Brainstem. Basel: Karger; 2013.
[5] Axer M, Grassel D, Kleiner M, Dammers J, Dickscheid T, Reckfort J, et al. High-resolution fiber tract reconstruction in the human brain by means of three-dimensional polarized light imaging. Frontiers in neuroinformatics. 2011;5:34.
[6] Mollink J, van Baarsen KM, Dederen PJ, Foxley S, Miller KL, Jbabdi S, et al. Dentatorubrothalamic tract localization with postmortem MR diffusion tractography compared to histological 3D reconstruction. Brain structure & function. 2016;221:3487-501.
[7] Greenspan JD, Winfield JA. Reversible pain and tactile deficits associated with a cerebral tumor compressing the posterior insula and parietal operculum. Pain. 1992;50:29-39.
[8] Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, Huijzen Cv. The human central nervous system. 4th ed. New York: Springer; 2008.
[9] Bushnell MC, Duncan GH, Hofbauer RK, Ha B, Chen JI, Carrier B. Pain perception: is there a role for primary somatosensory cortex? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96:7705-9.
[10] Joo W, Yoshioka F, Funaki T, Mizokami K, Rhoton AL, Jr. Microsurgical anatomy of the trigeminal nerve. Clinical anatomy. 2014;27:61-88.
[11] Go JL, Kim PE, Zee CS. The trigeminal nerve. Seminars in ultrasound, CT, and MR. 2001;22:502-20.
[12] Torvik A. The ascending fibers from the main trigeminal sensory nucleus Am JAnat 1957;100: 1–15.
Figures
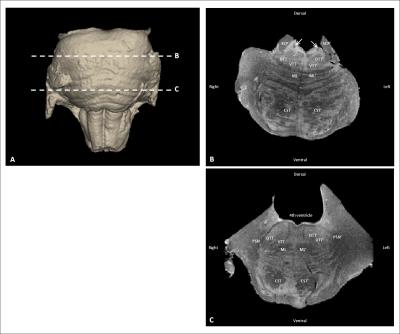
Figure 1 Anatomical MR images of the human brainstem
A) 3D visualization of the human brainstem, depicting the levels of the cutting planes of B and C
B) Transverse section
C) Transverse section
CST= Corticospinal tract, DTT= Dorsal trigeminothalamic tract, ML= Medial lemniscus, PSN= Principal sensory nucleus, SCP= Superior cerebellar peduncle, VTT= Ventral trigeminothalamic tract, White arrow= Location of the mesencephalic trigeminal tract
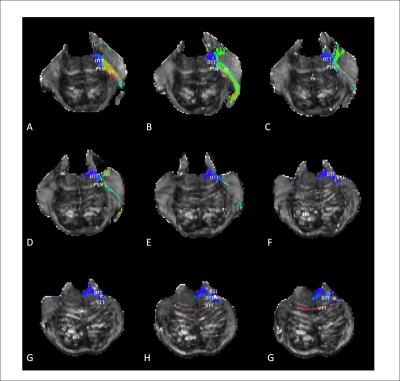
Figure 2 Tractography of the trigeminal tracts in the human brainstem superimposed on the FA-maps. Color indicates the direction of the streamlines
Transverse sections, resolution of 0,5mm; interplanar spacing from A till G consists of 8mm with A being the most cranial section
Red=Left-right; Green= Anterior-posterior; Blue= Caudal-rostral; DTT= Dorsal trigeminothalamic tract, PSN= Principal sensory nucleus, TT= Trigeminal tract, VTT= Ventral trigeminothalamic tract
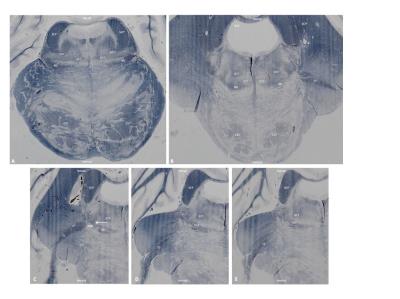
Figure 3 Histological sections of the human brainstem stained for myelin with a Heidenhain-Woelcke stain
A) Section through the upper part of the pons
B) Section through the mid part of the pons
C-E) Section through the pons at the level of the trigeminal entry zone
CST= Corticospinal tract, DTT= Dorsal trigeminothalamic tract, ML= Medial lemniscus, PSN= Principal sensory nucleus, SCP= Superior cerebellar peduncle, TT= Trigeminal tract, VTT= Ventral trigeminothalamic tract; White arrow= Location of the bifurcation of the TT into the VTT and DTT
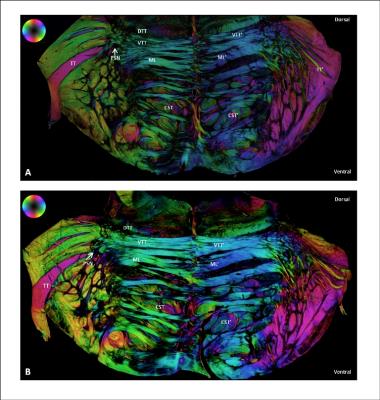
Figure 4 Polarized light imaging microscopy of the human brainstem. The in-plane orientation of myelinated fibres is color-coded according the HSV-sphere.
A) Rostral section through the mid part of the pons
B) Caudal section through the mid part of the pons
CST= Corticospinal tract, DTT= Dorsal trigeminothalamic tract, ML= Medial lemniscus, PSN= Principal sensory nucleus; TT= Trigeminal tract, VTT= Ventral trigeminothalamic tract
