3361
Does artifact correction in spinal cord DTI improve sensitivity at the group level?1Spinal Cord Injury Center, Balgrist University Hospital, Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2Department of Systems Neuroscience, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, 3Department of Neurophysics, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany, 4Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, UCL Institute of Neurology, London, United Kingdom
Synopsis
In this manuscript, we investigate how application of established post-processing methods (spatial registration and robust tensor fitting) and of a newly introduced outlier rejection technique referred to as reliability masking influence the statistical power of a clinical spinal cord DTI study. The assessment was performed using a previously published clinical dataset investigating microstructural correlates of spinal degeneration in cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM). We found that the established post-processing methods had almost no influence on the statistical power by which the microstructural differences is observed, whereas reliability masking increased the statistical power by more than 13%.
Introduction
Post-processing methods originally developed for the brain are now increasingly applied in spinal cord DTI to reduce the strong physiological and instrumental artifacts associated with this technique. It is well-established that post-processing-based artifact correction can substantially improve data quality at single-subject level1,2,3, however, its impact at the group level is yet to be investigated. In this study, we test established post-processing methods and a newly introduced method dubbed reliability masking for their ability to increase statistical power of group differences in a spinal cord DTI experiment. To compare the methods, we use a previously published clinical finding of lower fractional anisotropy (FA) values in the posterior column and lateral corticospinal tracts in CSM patients4.Methods
21 controls and 20 CSM patients were scanned on a 3T SkyraFIT MRI scanner equipped with a RF body transmit coil and a 16-channel receive-only head and neck coil. DTI was performed using a cardiac-gated reduced-FOV single-shot spin-echo EPI sequence with outer volume suppression. Four repetitions of 30 diffusion-weighted (b=500 s/mm2) and 6 T2w (b=0 s/mm2) volumes were acquired, resulting in 144 volumes. Each volume consisted of 10 axial-oblique slices centered at C2/C3 vertebral body. Acquisition parameters were: slice thickness=5 mm (10% gap), FOV=133x30 mm2, in-plane resolution=0.76x0.76 mm2, TE/TR=73/359 ms, nominal acquisition time=6:20 min. All volumes were corrected for motion and eddy-current distortions using volume- (VW) and slice-wise (SW) registration, respectively. The diffusion tensor was fitted by ordinary least squares approach and a robust tensor fitting approach described previously3. All DTI scalar maps were normalized using an in-house pipeline written in Matlab. After normalization, reliability masking was applied on the FA maps.
Background: Reliability masking is a novel outlier rejection technique that identifies outlier voxels in the DTI maps based on the corresponding root mean square model-fit error (ε). A voxel is considered unreliable and excluded from the analysis, if ε is higher than a threshold εthr .In contrast to previous methods operating at individual level, εthr is defined on the group-level and thus mainly driven by the signal-to-noise ratio of the DTI dataset, rather than the distribution of model-fit error in individual subjects. Reliability masking is implemented in MATLAB and will be integrated into the freely available ACID toolbox.
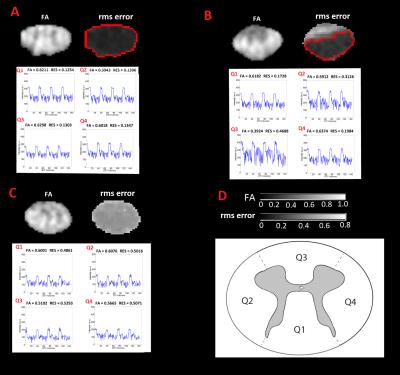
To test the effect of post-processing on a published clinical finding4, two-sample t-test was applied on the normalized FA maps between the control and patient groups within the region-of-interest (ROI) defined in Figure 1C. To assess the relative improvements achieved by post-processing method i, the average t-value within the ROI was divided by the corresponding value of the unprocessed dataset.
Results
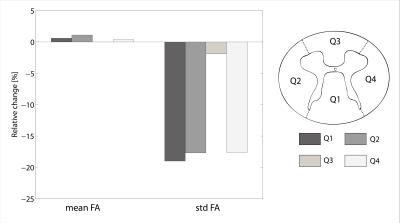
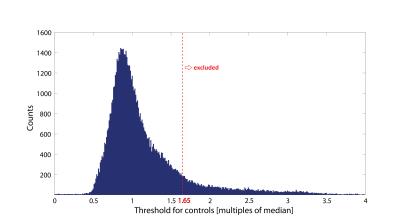
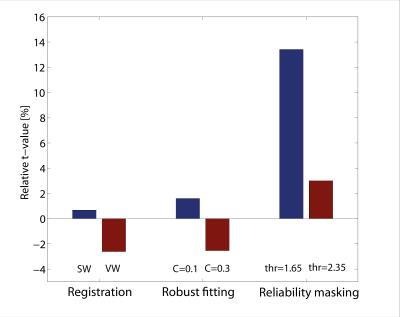
When applying reliability masking, the relative t-value had a maximum at εthr,c=1.65·median(εcontrols) for controls, and had no maximum but reached a plateau at around εthr,p=2.85·median(εpatients) for patients (see Figure 1.). Qualitative validation of reliability masking in the controls revealed that masking removes voxels with artefactual fractional anisotrophy (FA) values with great spatial specificity (Figure 2.). After applying reliability masking in the controls (using optimal threshold), the group-level standard deviation of FA decreased substantially by 2-20% (depending on the region), while the mean FA increased slightly by 0-1% (Figure 3.). At this threshold, 13.4% of the voxels were excluded from the control group (Figure 4.) Reliability masking increased the relative t-value by 13.4% compared to the unprocessed case, while the effect of registration and robust tensor fitting was minimal (0.7% and 1.6%, respectively) (Figure 5.).Discussion
Our work compares the effect of multiple spinal cord DTI post-processing techniques on the statistical power of a reported clinical finding and introduces reliability masking, a novel outlier rejection technique operating on the model-fit error. We found that standard post-processing methods have minimal effect on the statistical power, whereas reliability masking greatly improves it (>13%). The threshold value for reliability masking substantially affects the performance of the method, and we recommend to explore the optimal value in each study. We found an optimal value for controls but not for patients. A possible explanation might be that in pathological tissue the model-fit error can be elevated not only due to outliers, but also due to inappropriate diffusion tensor model.Conclusion
Established spinal cord DTI post-processing methods, although improving the quality of DTI index maps at single-subject level, do not increase the statistical power of DTI studies at group level. We present a novel outlier rejecting technique that significantly increases statistical power and reliability of group-level results. The approach is particularly attractive to clinical studies where low inter-subject variability within the control group is of outmost importance in order to achieve high effect size.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
(1) Zwiers MP. Patching cardiac and head motion artefacts in diffusion-weighted images. Neuroimage. 2010 Nov 1;53(2):565-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.014.
(2) Middleton DM, Mohamed FB, Barakat N, Hunter LN, Shellikeri S, Finsterbusch J, Faro SH, Shah P, Samdani AF, Mulcahey MJ. An investigation of motion correction algorithms for pediatric spinal cord DTI in healthy subjects and patients with spinal cord injury. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Jun;32(5):433-9.
(3) Mohammadi S, Freund P, Feiweier T, Curt A, Weiskopf N. The impact of post-processing on spinal cord diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage. 2013 Apr 15;70:377-85.
(4) Grabher P, Mohammadi S, Trachsler A, Friedl S, David G, Sutter R, Weiskopf N, Thompson AJ, Curt A, Freund P. Voxel-based analysis of grey and white matter degeneration in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Scientific Reports 6, Article number: 24636 (2016)
(5) Meer P, Mintz D, Rosenfeld A, Kim DY (1991), Robust regression methods for computer vision: a review. Int J Comput Vis 6: 59-70.
Figures