3294
Evaluation of renal allograft function after transplantation using diffusion kurtosis imaging1MRI, The First Affiliated Hospital of ZhengZhou University, ZhengZhou, People's Republic of China, 2MR Research China, GE Healthcare, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
To evaluate the feasibility of DKI in assessment of renal allograft function after transplantation, 13 patients with renal allograft underwent DKI of kidneys,which were divided into two groups according to eGFR. Maps of fractional anisotropy FA, MK, Ka, Kr and MD were generated. There was significant differences in FA, MK, Ka, Kr values of both the cortex and medulla of kidney between two groups. There was significant correlation between eGFR and cortical FA, MK, Ka, Kr, medullary FA, Ka. DKI could be a useful tool in the evaluation of renal function in allograft after transplantation.
Purpose
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) have demonstrated clinical potential to evaluate renal functions in patients with kidney disease and transplantation. However, inconsistent assessments of renal functions were obtained using DWI/DTI in patients with allografts [1-3]. Based on non-Gaussian properties of water diffusion, diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) can offer additional information about microstructural complexity of biological tissues. Recently, due to respiratory triggering technique, the feasibility of DKI in human kidneys has been confirmed [3, 4]. The purpose of this study is to prospectively investigate the value of DKI in renal allografts after kidney transplantation.Materials and Methods
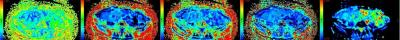
This study was approved by the institutional ethical review committee, and written informed consent was obtained. A total of 13 renal allograft recipients (M/F=8/5 age range, 37±12y) 1 month after transplantation underwent renal DKI with a 3.0T MR scanner (GE DISCOVERY MR 750, USA) . DKI sequence was performed in axial orientation with an eight channel torso coil by using three b values (0, 500, 1000 sec/mm2) and 15 directions. Recipients were divided into two groups according to their estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (group A: eGFR>60mL/min/1.73 m2; group B: eGFR≤60 mL/min/1.73m2) . Relationships between fractional anisotropy (FA), mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (Ka), radial kurtosis (Kr), mean diffusivity (MD), and allograft function, determined by eGFR, were assessed by using Pearson correlation coefficient. DKI parameters were compared between group A and group B by using a student t test. P<0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.Results
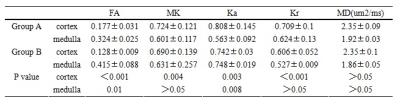
FA, MK, Ka, Kr values of the renal cortex was significantly higher in group A compared with group B (P <0.001, P =0.004, P=0.003, and P <0.001, respectively). FA, Ka of renal medulla were significantly lower in group A than in group B (P =0.01 and P =0.008, respectively). The difference in MD of both renal cortex and medulla were not significant between two groups(P>0.05). There was significant correlation between eGFR and cortical FA(r =0.43, P <0.005), cortical MK (r = 0.61, P =0.002), cortical Ka(r=0.40, P<0.005), cortical Kr(r=0.52, P =0.037), medullary FA(r=0.31, P<0.001), medullary Ka (r =0.45, P =0.009).Discussion and Conclusion
This study demonstrates that there is a significant difference of cortical FA, MK, Ka, Kr values and medullary FA, Ka values in patients with good renal function (group A), compared to those of patients with impaired renal function (group B). There was significant correlation between eGFR and cortical FA, cortical MK, cortical Ka, cortical Kr, medullary FA, medullary Ka. The preliminary results suggest that renal DKI produces reliable results to assess renal allograft function after transplantation.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Liu Z et al. Chronic kidney disease: pathological and functional assessment with diffusion tensor imaging at 3T MR. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(3):652-60.
2. Wen-jun Fan, Tao Ren ,Qiong Li,et al. Assessment of renal allograft function early after transplantation with isotropic resolution diffusion tensor imaging [J]. Eur Radiol, 2016,26:567–575.
3. Toya R et al. Correlation between estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the kidneys. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2010;9(2):59-64.
4. Pentang G et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging of the human kidney: a feasibility study. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;32(5):413-20.
Figures