3293
Apparent diffusion coefficient histogram shape analysis for monitoring early response in patients with advanced cervical cancers undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy1Department of Radiology, Drum Tower Hospital, School of Medicine, Nanjing University, Nanjing, People's Republic of China, 2Department of Radiology, Drum Tower Hospital, School of Medicine, Nanjing University, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 4Department of Oncology, Drum Tower Hospital, School of Medicine, Nanjing University
Synopsis
Thirty-two patients with advanced cervical cancer underwent DWI before CCRT, at the end of 2nd and 4th week during CCRT and immediately after CCRT completion to explore whether ADC histogram shape could assess the treatment response. Whole lesion ADC histogram analysis generated several histogram shape including skewness, kurtosis, s-sDav, width, standard deviation, as well as first-order entropy and second-order entropies. Skewness and kurtosis both showed high early decline rate at the end of 2nd week of CCRT. All entropies kept decreasing since 2 weeks after CCRT. ADC histogram shape analysis held the potential in monitoring early tumor response during CCRT.
PURPOSE
To explore the role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram shape related parameters in early assessment of treatment response during the concurrent chemo-radiotherapy (CCRT) course of advanced cervical cancers.METHODS
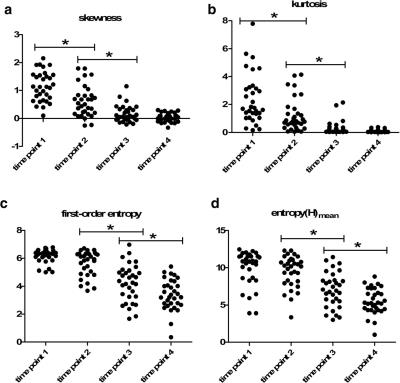
This prospective study was approved by the local ethics committee and informed consent was obtained from all patients. Thirty-two patients with advanced cervical squamous cell carcinomas underwent diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (b values, 0 and 800 s/mm2) before CCRT, at the end of 2nd and 4th week during CCRT and immediately after CCRT completion. Whole lesion ADC histogram analysis generated several histogram shape related parameters including skewness, kurtosis, s-sDav, width, standard deviation, as well as first-order entropy and second-order entropies. The averaged ADC histograms of 32 patients were generated to visually observe dynamic changes of the histogram shape following CCRT.RESULTS
All parameters except width and standard deviation showed significant changes during CCRT (all P < 0.05), and their variation trends fell into four different patterns. Skewness and kurtosis both showed high early decline rate (43.10 %, 48.29 %) at the end of 2nd week of CCRT. All entropies kept decreasing significantly since 2 weeks after CCRT initiated. The shape of averaged ADC histogram also changed obviously following CCRT. ponse. t-family: SxqkyqAdvTT86d47313;color:#131413;mso-font-kerning:0pt'>av’s increase occurred at a very late stage of CCRT. Therefore, it may not be a suitable indicator for early detection of cervical cancer treatment response.DISCUSSION
Skewness, kurtosis and entropy all kept decreasing, indicating that the distribution of ADC values became less heterogeneous following CCRT, along with a good response to therapy. Visually, those changes reflected on the averaged ADC histogram which gradually moved toward the right and turned into a more symmetrical shape with conspicuous descending peak following effective therapy. s-sDav represents width of the waist of ADC histogram. In this study, s-sDav’s increase occurred at a very late stage of CCRT. Therefore, it may not be a suitable indicator for early detection of cervical cancer treatment response. t-family: SxqkyqAdvTT86d47313;color:#131413;mso-font-kerning:0pt'>av’s increase occurred at a very late stage of CCRT. Therefore, it may not be a suitable indicator for early detection of cervical cancer treatment response.CONCLUSION
ADC histogram shape analysis held the potential in monitoring early tumor response in patients with advanced cervical cancers undergoing CCRT.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Somoye G, Harry V, Semple S, et al Early diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging can predict survival in women with locally advanced cancer of the cervix treated with combined chemo-radiation. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:2319-2327
2. Harry VN, Semple SI, Gilbert FJ, Parkin DE. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the early detection of response to chemoradiation in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;111:213-220
3. Downey K, Riches SF, Morgan VA, et al. Relationship between imaging biomarkers of stage I cervical cancer and poor-prognosis histologic features: quantitative histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted MR images. AJR. American journal of roentgenology.2013; 200:314-320
4. Guan Y, Shi H, Chen Y, et al. Whole-Lesion Histogram Analysis of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for the Assessment of Cervical Cancer. Journal of computer assisted tomography.2016; 40:212-217
Figures