3174
Is voxel-wise ADC histogram repeatable?1Diagnostic Radiology, Sapporo Medical University, Sapporo, Japan, 2Division of Radiology, Sapporo Medical University Hospital, Sapporo, Japan
Synopsis
Skewness and kurtosis of voxel-wise apparent diffusion coefficient show low repeatability. Radiologist should take this characteristic into account when interpreting DWI of the prostate.
Purpose
Many investigations regarding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram have been performed and concluded that ADC histogram is of value differentiating cancer from benign lesion 1-4, classifying malignant potential 5-7, and predicting prognosis 8-11. However, repeatability and/or reproducibility of ADC histogram have yet to be assured sufficiently. The purpose of the present study is to evaluate repeatability of ADC histogram in the prostate.Materials and Methods
Consecutive 29 male patients who underwent pelvic MRI using whole-body clinical MRI systems (3T of Ingenia, Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherland) to evaluate prostate in our hospital from June to October in 2016 were included. All patients gave informed consents. Two sequential free-breathing single shot diffusion-weighted spin-echo echo-planar imaging (DWI) (b-factors=0, 100, 1000, and 1500 s/mm2) with identical positioning were obtained during examination. The region of interests (ROI) were assigned at 11 cancers, 21 peripheral zones, and 29 transitional zones of the prostate on the 1st DWI and pasted them to the 2nd DWI holding their size and location. Each voxel ADC was calculated by fitting signal intensity of each voxel on tree DWIs (b-factors=100, 1000, and 1500 s/mm2) into mono-exponential curve. The minimal, 10%, 25%, median, 75%, 90%, maximum, mean, skewness, and kurtosis of voxel-wise ADC within ROI were compared between two DWIs using linear regression and Bland-Altman plot, and repeatability coefficient and within-subject coefficient of variance were also calculated. p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
All parameters showed significance in linear regression with r2>0.92 but skewness (0.44) and kurtosis (0.45). ADC min, 10%, 25%, median, 75%, 90%, maximum, and mean showed high repeatability with standard deviation of bias in Bland-Altman plot < 13% but skewness (2003%) and kurtosis (898.3%), repeatability coefficient <0.19 but skewness (0.84) and kurtosis (1.19), and within-subject coefficient of variance < 8% but skewness (695%) and kurtosis (-9452%). The details were shown in the figures.Conclusion
ADC min, ADC 10%, ADC 25%, ADC median, ADC 75%, ADC 90%, ADC maximum, and ADC mean showed high repeatability but skewness and kurtosis of voxel-wise ADC not. Radiologist should take this characteristic of ADC histogram into account when interpreting DWI of the prostate.Acknowledgements
We express special thanks to Prof. Mori at Sapporo Medical University for the consultation on statistics.References
1. Suo S, et al. Characterization of breast masses as benign or malignant at 3.0T MRI with whole-lesion histogram analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient. J Magn Reson Imaging 2016; 43(4): 894-902.
2. Lin Y, et al. Correlation of histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient with uterine cervical pathologic finding. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015; 204(5): 1125-31.
3.Kierans AS, et al. Retrospective Assessment of Histogram-Based Diffusion Metrics for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Endometrial Lesions. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2016; 40(5): 723-9.
4. Guan Y, et al. Whole-Lesion Histogram Analysis of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for the Assessment of Cervical Cancer. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2016; 40(2): 212-7.
5. Ahn SJ, et al. Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient map of standard and high B-value diffusion MR imaging in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a correlation study with histological grade. Acad Radiol 2012; 19(10): 1233-40.
6. Zhang YD, et al. The histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging for differentiating the gleason grade of prostate cancer. Eur Radiol 2015; 25(4): 994-1004.
7. Rozenberg R, et al. Whole-Tumor Quantitative Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Histogram and Texture Analysis to Predict Gleason Score Upgrading in Intermediate-Risk 3 + 4 = 7 Prostate Cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2016; 206(4): 775-82.
8. Poussaint TY, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient histogram metrics correlate with survival in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: a report from the Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium. Neuro Oncol 2016; 18(5): 725-34.
9. Law BK, et al. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Can Pretreatment DWI Predict Local Failure Based on Long-Term Outcome? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2016; 37(9): 1706-12.
10. Zolal A, et al. Enhancing tumor apparent diffusion coefficient histogram skewness stratifies the postoperative survival in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patients undergoing salvage surgery. J Neurooncol 2016; 127(3): 551-7.
11. King AD, et al. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for the prediction of treatment response. Radiology 2013; 266(2): 531-8.
Figures
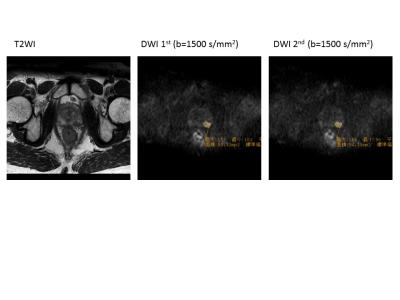
Figure 1. Representative case
ROI was assigned at cancer. FOV/Thickness=200/3 mm, T2WI: TR/TE=4000/80 ms, Matrix=320*295, DWI:TR/TE=3389.5/74.285 ms, Matrix=80*79
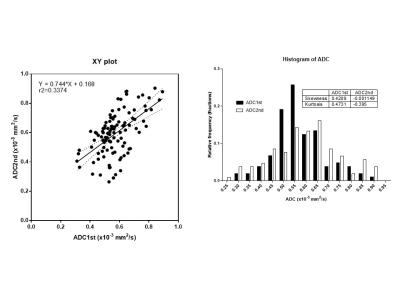
Figure 2. XY plot and Histogram of voxel-wise ADC within ROI of Figure 1
Voxel-wise ADC did not show high repeatability in each lesion.
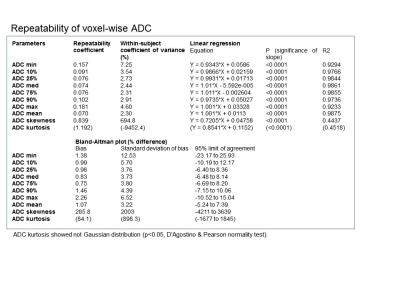
Figure 3. Repeatability of voxel-wise ADC
ADC minimum, 10%, 25%, median, 75%, 90%, maximum, and mean showed high repetability but skewness and kurtosis not in patient-based analysis.
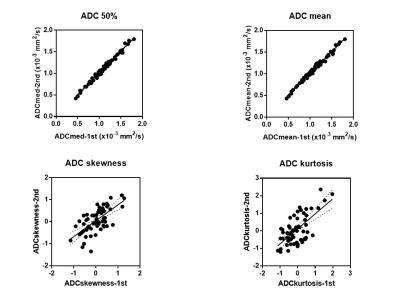
Figure 4. XY pot of ADC median, mean, skewness, and kurtosis
ADC median and mean showed high repetability but skewness and kurtosis not in patient-based analysis.
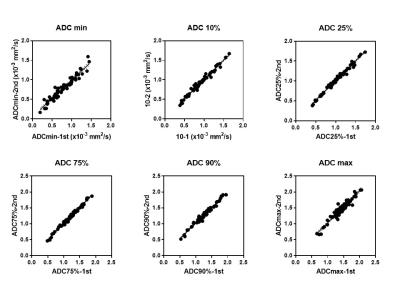
Figure 5. XY plot of ADC minimum, 10%, 25%, 75%, 90%, and maximum
ADC minimum, 10%, 25%, 75%, 90%, and maximum showed high repetability in patient-based analysis.