3171
A cardiac stationary phase based ECG trigger (CaspECG) of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion MR in left liver lobe.1Department of Radiology, Panyu Center Hospital of Guangzhou, 8 Fuyu Dong Road, Panyu District Guangzhou, P.R. China 510080, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China, 2Panyu Center Hospital of Guangzhou, 8 Fuyu Dong Road, Panyu District Guangzhou, P.R. China 510080, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China, 3Siemens Healthcare, Application NE Asia, Guangzhou, China, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China, 4Siemens Healthcare, MR Scientific Marketing NE Asia, Guangzhou, China, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China, 5Siemens Healthcare, MR Collaboration NE Asia, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 6Department of Radiology, Guangdong General Hospital, 106 Zhongshan Er Road, Guangzhou, P.R. China 510080, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China, 7Department of Radiology, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, USA, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Synopsis
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) showed high clinical value in liver disease evaluation. However, it suffers from signal loss and motion artifacts due to cardiac and respiratory movement, especially in the left lobe. To improve robustness and reproducibility of parameter estimation for IVIM DWI, a novel DWI acqusition technique was introduced, which uses ECG trigger with delay time optimized by the periods of cardiac relative stationary phase. The results showed that the proposed acquisition method improves SNR of DWI data, and the repeatability and stability of IVIM-DWI derived parameters.
Purpose
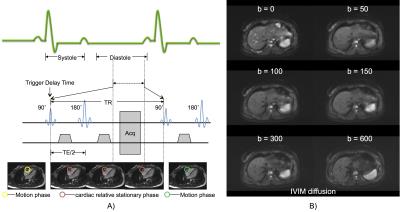
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) in liver suffers from signal loss and motion artifacts due to physiological motion, such as cardiac and respiratory movement, especially in the left lobe. To improve image quality, a novel acquisition method was proposed to combine DWI sequence with optimized ECG trigger based on cardiac motion period, and called cardiac stationary phase based ECG trigger (CaspECG). The proposed method was applied to data acquisition of Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) DWI for evaluation, with comparison to conventional free-breathing (FB) acquisition.Method
Twenty-two healthy volunteers underwent MRI scans. All the data were collected on a 1.5 T MR scanner (Magnetom, Avanto, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with 6-channel body coil and spine coil. The technical methods were as follows: 4-chamber heart cinema with FOV =340×276 mm, TR = 45.9 ms, TE = 1.28 ms, Average = 1, Slice thickness = 6 mm, and TA = 9 s. ECG triggered IVIM DWI sequence were acquired with 6 b values (0, 50, 100, 150, 300, 600), with following parameters: FOV = 400×262 mm, TR = 110ms, TE = 66ms, Matrix 128×128, Average = 2, Concatenation = 5, Slices = 5, Slice thickness = 5mm, and TA = 9:40 min. The free-breathing DWI sequence used Concatenation = 1, TR 3000 ms, TE = 74 ms, without ECG trigger, and the other parameters are the same. Before ECG triggered IVIM-DWI was performed, the trigger delay time and the sampling duration time were determined by 4-chamber heart cinema. The beginning of cardiac relative stationary states was set as the trigger delay time, and the time interval of the cardiac relative stationary was set as the sampling duration time (TR), the detail timing is shown in Figure 1.
The IVIM-DWI data from both FB and CapsECG acquisitions were fitted by bi-exponential decaying model1: $$S_{b}=S_{0}\star(f \times e^{-b\star D^{*}} + (1-f)\times e^{b\star D})$$using in-house software written using MATLAB 2013a, and the perfusion fraction f , true diffusion factor D and Pseudo diffusion factor D* were acquired. Three ROIs in left liver lobe were drawn on three consecutive middle slices of DWI images, respectively. The IVIM images quality were evaluated by calculating signal noise ratio (SNR) as drawing the ROIs of left liver lobe. The average values of D, D*, f values in ROIs were also calculated for two methods and compared by non-parametric Wilcoxon test. The reproducibility of two acquisition methods were assessed by the Bland-Altman method2.
Result
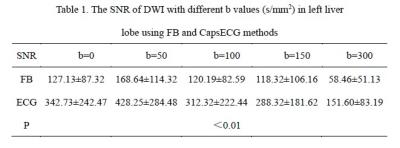
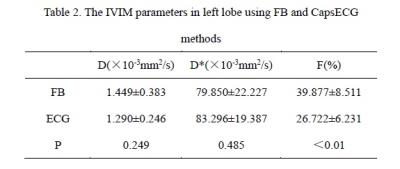
Compared to FB method, the DWI data of proposed ECG triggered method showed significant higher SNRs (P<0.01) in left lobe of liver (Table 1). In addition, the mean of D and f values from proposed method were significantly lower than those from FB method, while D* was higher, but only f values had significant differences (P<0.01) (Table 2). The Bland-Altman methods showed that the reproducibility of IVIM-DWI with ECG trigger was better than that of FB , and D values showed the highest reproducibility.Discussion & Conclusion
Previous study3,4 reported that the image quality of DWI in left liver lobe could affected by heartbeats motion. In this study, we found that the proposed ECG-triggered method showed higher SNR in DWI data of left liver lobe than FB method, indicating its robustness to cardiac motion and can avoid motion-induced signal loss. Further, it provides good image quality and is helpful in advanced diffusion application, such as DWI with high b values. In additional, the proposed method also showed high repeatability and stability of the multi-parameters of IVIM-DWI, and will benefit the quantitative clinical diagnosis and treatment assessment of liver disease, with significant improvement in left liver lobe.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from The National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.81671853),The Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (No.2015A030313753), The Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (No. 201510010002)and The Panyu Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (No. 2014-Z03-24).References
1. Woo S, Lee J M, Yoon J H, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with enhancement degree and histologic grade. Radiology, 2013;270(3):758-767.
2. Suguru Kakite MD PhD, Dyvorne H, Cecilia Besa M D, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Short-term reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters at 3.0T. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2014;41(1):149-156.
3. Watanabe H, Kanematsu M, Goshima S, et al. Characterizing focal hepatic lesions by free-breathing intravoxel incoherent motion MRI at 3.0 T. Acta Radiologica, 2014; 55(10):1166-1173.
4. Doblas S, Wagner M, Leitao H S, et al. Determination of malignancy and characterization of hepatic tumor type with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion-derived measurements. Investigative Radiology, 2013; 48(10):722-728.
Figures