3065
A new highly stable macrocyclic gadolinium complex as a liver targeting MRI contrast agent1BK21 Plus KNU Biomedical Convergence Program, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 2Medical &Biological Engineering, Kyungpook National University, 3Biomedical Engineering Research Instite, Kyungpook National University, 4Radiology, Kyungpook National University
Synopsis
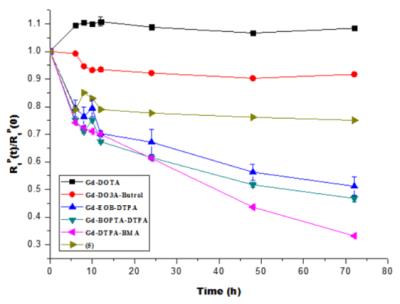
Gd-EOB-DO3A is prepared according to the general synthetic methods, and characterized by spectroscopic analysis. The relaxivities are r1 = 8.07, r2 = 8.57 mM-1s-1. From in vivo T1-weighted MR images, we observe good liver-specific enhancement that can be compared with commercial liver targeting agents, and confirm the biliary excretion via gallbladder. Also the kinetic stability of the gadolinium complex was determined with time-dependent longitudinal relaxation rate (R1,p(t)/R1,p(0)) and the relaxation was maintained above 70% against to initial value during the measurement.
Introduction
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has an important role in the detection of various liver diseases. Several hepatobiliary MRI contrast agents (CAs) like Primovist©, Multihance©, and Mn-DPDP (Teslacan©) have been successfully used with good liver enhancement. However, Acyclic MRI CAs are gadolinium complexes that have low kinetic stability causing various problems in the human body like nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF), deposition of gadolinium ions in a brain.(1) On the other hand, it is well known that macrocyclic MR CAs have higher kinetic stability than those of acyclic types. In this study, we designed and synthesized a gadolinium based macrocyclic MRI CA, Gd-DO3A-EOB for kinetically improved stability and liver targeting property.Materials and Methods
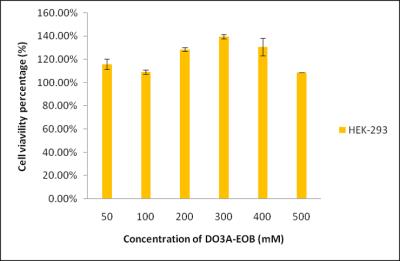
All reagents were purchased from commercial sources and used as received. Characterization of the synthesized compounds have been determined by analytical spectroscopic methods.(2) T1 measurements were carried out using an inversion recovery method with variable inversion times (TI) at1.5 T (64 MHz). For T2 measurements, the CPMG (Carr-Purcell-Meiboon-Gill) pulse sequence was adapted for multiple spin-echo measurements. T1, T2 relaxation times were obtained from the nonlinear least-squares fit of the mean pixel values at variable TI and TE, respectively. The relaxivities (r1 and r2) were then calculated as a slope of linear fit of relaxation rate along with concentrations. The in vivo MR experiments was performed in accordance with the rules of the animal research committee of Kyungpook National University (KNU). In these studies, the mice (26 ~ 27 g) were anesthetized by 1.5% isoflurane in oxygen. MR images were acquired before and after intravascular injection of each MR contrast agents (Gd-DO3A-EOB, Primovist©, Multihance©; dose: 0.1 mmol Gd/kg). The images were acquired with a 1.5 T (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) equipped with a homemade small animal volume coil. Also image parameters of coronal images for spin-echo are as follows: Repetition time (TR) = 300 msec; echo time (TE) = 13 msec; 11 mm field of view (FOV); 192 128 matrix size; 1.2 mm slice thickness; number of acquisition (NEX) = 8; scan time of each image = 2 min 37 sec.(3) The kinetic inertness was measured by evaluating the time-dependent longitudinal relaxation rate (R1,p(t)/R1,p(0)) of a buffered solution (PBS, pH 7.4) containing 2.5 mmol/L gadolinium complex in presence of equimolar ZnCl2. In vitro cell toxicity of this compound was assessed with normal human kidney cell line (HEK-293) at various concentrations.Result and Discussion
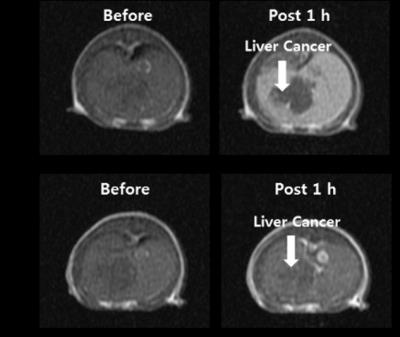
Scheme 1 shows the synthesis of Gd-EOB-DO3A. Relaxivities of Gd-EOB-DO3A (r1 = 8.1, r2 = 8.6 mM-1s-1) are much higher than those of primovist© (r1 = 4.7, r2 = 5.1 mM-1s-1) and Multihance© (r1 = 4.0, r2 = 4.3 mM-1s-1). Gd-EOB-DO3A shows high kinetic stability in chemically competitive environment, retaining the longitudinal relaxation rate (R1,p(t)/R1,p(0)) above 70% , than other acyclic liver targeting agents (Figure 1). In addition, Gd-DO3A-EOB does not show particular cell toxicity with normal kidney cell, HEK-293 (Figure 2). In vivo MRI experiment, Gd-DO3A-EOB shows specifically good liver enhancement immediately after tail vein injection. Also it is excreted via gallbladder, confirming hepatobiliary uptake as seen in Figure 3. Figure 4 shows the axial T1-weighted MR images of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model nude mice which were obtained by tail vein injection with Gd-EOB-DO3A and Gd-DOTA for comparative purpose. The difference in Gd-EOB-DO3A uptake between normal hepatocytes and tumor cells demonstrates significant difference in MR signal enhancement (Figure 4a). In case of non-specific extracellular agent, Gd-DOTA, the MR images shows undistinguishable contrast enhancement between normal liver tissue and tumor regions. (Figure 4b). Therefore, Gd-EOB-DO3A demonstrated the significant clinical potential to detect liver tumor and differentiate the margin between normal liver cell and HCC.Conclusion
We have synthesized Gd-DO3A-EOB as a highly stable liver targeting MRI CA. The results shows that it might be useful as diagnostic agent in field of liver disease with good hepatobiliary property and kinetic inertness. Therefore, it can be concluded that in every respect, a new macrocyclic Gd-EOB-DO3A may put an entry into a new family of practical liver-specific MRI CAs with more merits than their linear counterparts.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
(1) Nevzat Karabulut, Diagn. Interv. Radiol., 2015, 21, 269-270
(2) Nikolaos Eleftheriadis, Frank J. Dekker, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2015, 94, 265-275
(3) Hee-Kyung Kim, Tae-Joeng Kim, Youngmin Chang, J. Med. Chem., 2013, 56, 8104-8111
Figures