3062
One-pot microwave synthesis of fluorinated silicon nanoparticles for dual 19F-MRI and fluorescence imaging1Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance in Biological Systems, State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
In this study, we have designed a one-pot microwave strategy for facile and rapid synthesis of blue-emitting 19F-SiNPs. The as prepared 19F-SiNPs significantly exhibited ultral small sizes, excellent water solubility and strong fluorescence. Besides, The chemically and magnetically equivalent trifluoromethyl groups grafted on the prepared nanoparticles displayed a single NMR signal, which offered advantages to maximize the generated magnetic resonance signal. In summary, such resultant 19F-SiNPs are particularly suitable for real-time 19F-MRI and fluorescence dual modality imaging.
Introduction
As a noninvasive molecular imaging modality, optical imaging provides high sensitivity and specificity but poor tissue penetration depth. On the contrary, MRI has high spatial resolution in deep tissue, but it suffers the drawbacks of low sensitivity [1]. The combination of MRI and optical imaging, which takes advantages of both modalities, has received widespread attention in biological and medical application. Compared to conventional 1H-MRI, 19F-MRI displays an intense sensitivity (0.83 relative to 1H) and negligible background signal [2]. Herein, we developed a one-pot microwave assisted synthesis of fluorinated silicon nanoparticles (19F-SiNPs) for dual 19F-MRI and fluorescence imaging. As expected, the 19F-SiNPs exhibited strong fluorescence, high 19F-MRI sensitivity, favorable biocompatibility and excellent aqueous solubility.Methods
The 19F-SiNPs was prepared by using (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane as coupling reagents, trisodium citrate dihydrate as reducing reagents and perfluoro-tert-butyl alcohol as fluorine resources, and reacted under microwave irradiation. The as prepared 19F-SiNPs exhibit intense blue-color fluorescence under UV irradiation, which were suitable for real time cellular imaging. Besides, the chemically and magnetically equivalent trifluoromethyl groups grafted on the prepared nanoparticles displayed a single NMR signal.Results and Discussion
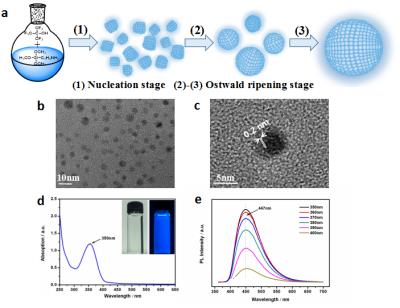
The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image shows that the prepared 19F-SiNPs displayed as spherical particles without obvious aggregation (Fig. 1b), and the lattice planes in the HRTEM image revealed the crystallinity of the resultant 19F-SiNPs[3] (Fig. 1c) . The normalized UV and PL spectra of the 19F-SiNPs indicated that the 19F-SiNPs possess good optical properties with distinct absorption peaks and symmetrical PL peaks (Fig. 1d, e).
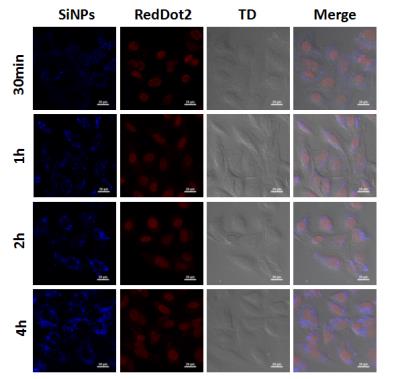
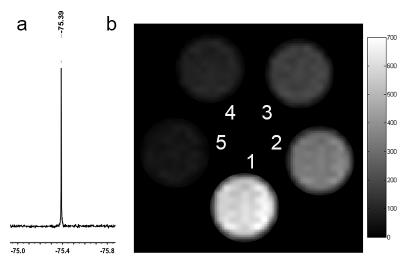
After incubating with human lung cancer cells, the 19F-SiNPs could be swallowed into cells in the very short time, and gradually accumulated in the cytoplasm in the continues several hours (Fig. 2). The fluorine moieties grafted on silicon nanoparticles were confirmed by 19F-NMR spectrum with a single peak (Fig. 3a), which offered advantages to maximize the generated magnetic resonance signal. The preliminary 19F-MRI results indicated that stronger signals were observed dependent on the increased nanoprobe concentration (Fig. 3b).
Conclusion
In summary, we have designed a one-pot microwave strategy for facile and rapid synthesis of 19F-SiNPs. The as prepared 19F-SiNPs significantly exhibited excellent water solubility, strong fluorescence and high 19F-MRI sensitivity, well suitable for 19F-MRI and fluorescence imaging in cell level.Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81227902, 81625011, 21305156, 21575157, 21605158) and National Program for Support of Eminent Professionals (National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals).References
[1] Angelovski G; What We Can Really Do with Bioresponsive MRI Contrast Agents. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. , 2016, 55, 7038-46.
[2] Ruiz-Cabello, J.;Barnett, B. P.; Bottomley, P. A.; Bulte, J. W. M.; Fluorine (19F) MRS and MRI in biomedicine. NMR Biomed., 2011, 24, 114–129.
[3] Zhong Y L, Peng F, Bao F, Wang S Y, Ji X Y, Yang L, Su Y Y, Lee S T, He Y. Large-Scale Aqueous Synthesis of Fluorescent and Biocompatible Silicon Nanoparticles and Their Use as Highly Photostable Biological Probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2013, 135, 8350–8356.
Figures