3057
Multifunctional magnetic nanocomposites for T1/T2 Dual-Mode MRI and pH-responsive drug delivery1Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance in Biological Systems, State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
In this abstract, multifunctional Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD nanocomposites were designed and synthesized to load water soluble Mn-porphyrin and anticancer drug doxorubicin, which could realize both pH-responsive drug release and T1/T2 dual-mode MRI capability. In vitro cell fluorescent imagings showed that c(RGDyk)-modified nanocomposites can effectively target A549 cells. Furthermore, in vitro T1-weighted and T2-weighted MR images of A549 cells were observed. For in vivo MRI, T1 and T2 relaxation was significantly accelerated in the tumor after i.v. injection of nanocomposites. These evidences showed that the nanocomposites could be used as pH-responsive T1/T2 dual-mode contrast agent, and have the potential for the tumor-targeted MRI and drug delivery.
Introduction
In the recent years, T1/T2 dual-mode contrast agents have been gained constant attention, because the complementary and self-confirmed diagnostic information from the two modes might validate reconstruction and visualization of the data in an accurate and reliable manner [1]. Stimuli-response imaging strategy offers a way to light or quench the detection signal in an exceptional environment, which further increases the accuracy by reducing the background noise [2]. Herein, multifunctional Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD nanocomposites (NCs) were designed and synthesized to load water soluble Mn-porphyrin and anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX), which could realize both pH-responsive drug release and T1/T2 dual-mode MRI capability.Methods
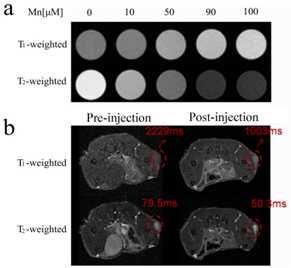
The multifunctional magnetic nanocomposites are composed of Fe3O4 nanoparticle as core, SiO2 as middle layer, PAA as shell, and cRGD as the targeting group (Figure 1a, b). Water soluble Mn-porphyrin was chosen as the T1-contrast agent and the Fe3O4 core acted as the T2-contrast agent. The PAA coated mSiO2 layer can be used as a pH-responsive vehicle for loading T1-contrast agent and anticancer drug. The nanocomposites exhibited a stimuli-response T1/T2 MRI enhancement (Figure 1c) and pH-responsive drug release behavior.Results and Discussion
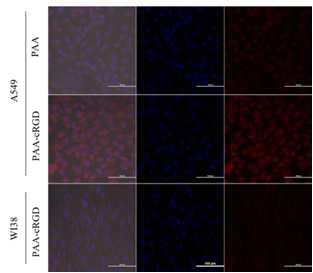
Tumor targeting ability of the DOX-loaded Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD NCs was investigated by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) following the incubation of cells with the nanocomposites for 1h. The red fluorescence (attributed to DOX) in A549 cells incubated with Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD NCs was distinguishably higher than that of NCs without modified with c(RGDyk), and the fluorescence in A549 cells was much higher than WI-38 cells (Figure 2). In vitro T1-weighted and T2-weighted MR images of A549 cells were observed after incubated with Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD NCs for 1h. The 1/T1 and 1/T2 were increased with the increase of the NCs concentration (Figure 3a). T1 and T2 relaxation was significantly accelerated in the tumor after i.v. injection of Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD NCs. The decrease percentage of T1 and T2 was 55% and 37% respectively after 3h injection of the NCs. These evidences showed that the synthesized Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD nanocomposites exhibited highly sensitive MR contrast effects.Conclusion
New multifunctional magnetic nanocomposites Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-cRGD were prepared, which could be used as pH-responsive T1/T2 dual-mode contrast agent, and have the potential for the tumor-targeted MRI and drug delivery.Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81227902, 8162501, 21305156, 21575157, 21605158) and National Program for Support of Eminent Professionals (National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals).References
[1] Choi J-S, Lee J-H, Shin T-H, et al. Self-confirming “AND” logic nanoparticles for fault-free MRI. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2010, 132, 11015-11017.
[2] Chen Y, Yin Q, Ji XF, et al. Manganese oxide-based multifunctionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive MRI, ultrasonography and circumvention of MDR in cancer cells. Biomaterials, 2012, 33, 7126-7137.
Figures