3050
Mn-complex of DO2A-benzothiazole chelate as a new hepatobiliary MRI contrast agentSoyeon Kim1, Hee-Kyung Kim2, Eun-Young Jeon3, Md. Kamrul Islam1, Garam Choi1, Au Reum Baek1, Bo Kyung Sung1, Tae-Jeong Kim3, and Yongmin Chang1,2,4
1Medical & Biological Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Molecular Medicine & BK21 Plus KNU Biomedical Convergence Program, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 3Institute of Biomedical Engineering Research, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Republic of, 4Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University
Synopsis
The purpose of the present work is to design and synthesize a new bifunctional complex for use in Mn(II)-based liver-targeting MR imaging. Its r1 relaxivity in human serum albumin (HSA) solution is 3.21 mM-1s-1, similar to MRI CA such as MnDPDP®. In vivo MR image after injection of Mn-DO2A-BTA by tail vein showed that its excretion is made via kidney and also bile duct, confirming hepatobiliary uptake.
Introduction
Most clinical contrast agents are based on Gd(III) complexes of polyamino polycarboxylic acids. However, in view of the recent discovery that Gd(III) could possibly be involved in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF), much emphasis is now being put on alternative approaches based on non-lanthanide metals, in particular manganese, for MR imaging. Although there is no direct relation has been found between Mn and NSF so far, the potential neurotoxicity of free Mn ions is still remaining as major safety concern when used as contrast agent. Indeed, MnDPDP (Mangofodipir; TeslascanTM), which was FDA approved as T1 MR contrast agent for liver imaging, showed strong dechelation in plasma after intravenous (IV) injection. Therefore, there have been several efforts to design stable Mn(II) complexes for MR imaging. Herein, we report the design and the synthesis of a new highly stable Mn(II)-based complexes (Mn-DO2A-BTA) for use as a new class of hepatobiliary MRI CA.Materials and Methods
All reagents were purchased from commercial sources and used as received. DO2A (= 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,7-diacetic acid) and BTA derivative were synthesized in our lab according to literature method1. T1 measurements were carried out using an inversion recovery method with a variable inversion time (TI) at 1.5 T (64MHz, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). For T2 measurements, the CPMG (Carr-Purcell-Meiboon-Gill) pulse sequence was adapted for multiple spin-echo measurements. T1 and T2 relaxation times were obtained from the non-linear least squares fit of the mean pixel values for the multiple spin-echo measurements at each TI value and echo time. Relaxivities (r1 and r2) were then calculated as an inverse of relaxation time per mM. MR images of anaesthetized mice were obtained pre- and post- MnL (0.1 mmol Mn/kg) injection by tail vein with a 1.5 T MR unit (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) with home-made small animal RF coil. The imaging parameters for SE (Spin echo) were as follows: repetition time (TR) = 300 ms; echo time (TE) = 12 ms; 8 mm field of view (FOV); 192×128 matrix size; 1.2 mm slice thickness; number of acquisition (NEX) = 8. HEK-293 (human embryonic kidney) cells were pated 1 x 104 in 96-well plate. The DMEM serum depletion media for 24 h. Then the live cell count was assayed using CCK-8 (Dojindo, Sunnyvale, CA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.Results and Discussion
Scheme 1 shows the synthesis of manganese based DO2A-benzothiazole conjugated complex (Mn-DO2A-BTA). After each step, the synthesized complexes confirmed by 1H NMR or high resolution mass spectroscopy. The synthesized complex (3.2 mM-1s-1) shows good relaxivity in HSA solution compared with MnDPDP® (3.6 mM-1s-1)2. HSA binding test (m-titration, Figure 1) shows that the corresponding binding constant Ka provide the evidence for the noncovalent lipophilic interaction between the chelate Mn-DO2A-BTA. In vivo MR images of Mn-DO2A-BTA are represented by T1-weighted MR images of 8-week-old male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice after bolus injection of Mn-DO2A-BTA through tail vein (Figure 2). It shows strong signal enhancement in liver, kidney, gallbladder, heart and aorta. These results show that MnL is able to act as not only liver targeting agent but also blood pool agent. The cytotoxicity of Mn-DO2A-BTA was tested by empoying HEK-293, a normal cell line. Figure 3 shows the Mn-DO2A-BTA has negligible cytotoxicity.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Kim H.-K., Chang Y., Kim T.-J., et al. Gadolinium Complex of DO3A-benzothiazole Aniline (BTA) Conjugate as a Theranostic Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2013; 56: 8104-8111.
2. Eric M. G., Peter C., et al. A Manganese Alternative to Gadolinium for MRI Contrast. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015; 137: 15548-15557.
Figures
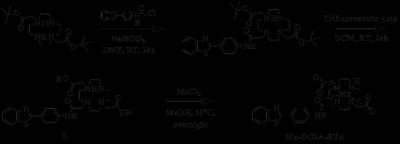
Sheme 1. The synthesis of Mn-DO2A-BTA
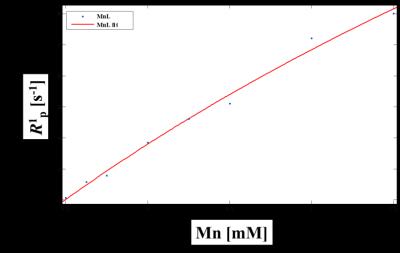
Figure 1. Proton longitudinal paramagnetic relaxation rates
of Mn-DO2A-BTA as a function of [Mn] in water solution of HSA (0.67mM) at 64MHz
and 293K.
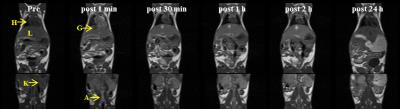
Figure 2. In
vivo MR coronal images of mice obtained with Mn-DO2A-BTA
(0.1 mmol/kg): H, heart; L, liver;
G, gall bladder; K, kidney; A, abdominal aorta.
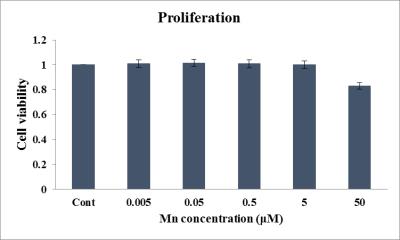
Figure 3. Proliferation of HEK-293 cell after treatment with
various concentrations of Mn-DO2A-BTA.