3030
Hyperpolarized [6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine as a Novel Probe to Interrogate Arginase Activity1Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, NY, United States
Synopsis
Across most cancer types, increased macrophage infiltration is associated with a worsening prognosis. This is because tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) exhibit a variety of pro-tumor effects ranging from vascular recruitment, cell proliferation, extravasation, and immune suppression. A marker of TAMs is arginase-1 expression, which converts arginine to urea and ornithine. It is thought that arginase expression reduces the amount of arginine available to local T-cells, leading to T-cell receptor dysfunction. In this abstract, we outline the synthesis and characterization of novel compound [6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine as a hyperpolarized 13C MRS probe to interrogate arginase activity, with the potential for in vivo translation.
Purpose
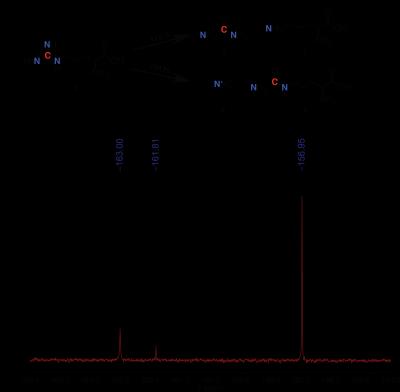
In normal physiology, macrophages can be classified as pro-inflammatory M1 or anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages1. These two cell types can be differentiated by the manner in which they metabolize arginine; M1 macrophages favor iNOS mediated nitric oxide production while M2 macrophages overexpress Arginase-1 (Arg-1), which converts arginine to urea and ornithine1 (Figure 1A). Macrophages are one of the most common normal cells in the tumor microenvironment, and they overexpress Arg-1 and support immunosuppression like their M2 counterparts2. Thus, increased tumor associated macrophage (TAM) infiltration in tumors is correlated with a worse prognosis in most tumors3. Arg-1 overexpression in the tumor microenvironment has been linked to T-cell dysfunction due to arginine insufficiency4, and Arg-1 mediated ornithine/polyamine production supports cell proliferation5. Furthermore, reprogramming TAMs to an M1-like phenotype can improve therapeutic efficacy6. Therefore, a method to interrogate Arg-1 activity within a tumor could potentially serve as a surrogate readout of TAM infiltration, and this information could prove useful in therapy selection, monitoring therapeutic efficacy, and determining prognosis. By tracking the fate of arginine’s carbon-6 via 13C MRS, it is possible to monitor its conversion to urea (via Arg-1) or citrulline (via iNOS), as demonstrated in the NMR spectrum in Figure 1B. Below, we detail the synthesis and characterization of [6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine-HCl, a novel hyperpolarized 13C probe to measure Arg-1 and iNOS enzyme activity with the potential for in vivo translation.Methods
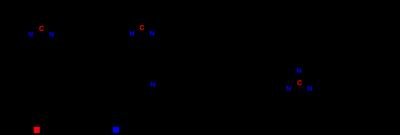
[6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine-HCl was synthesized using the multi-step synthetic scheme detailed in Figure 2, adapted from Qu et al. and Hailton et al7,8. In vitro Arg-1 enzyme activity was measured using murine Raw 264.8 macrophages. These cells were differentiated into M1 and M2 lineages via a protocol detailed by Liu et al9. Arginase activity was measured using an Arginase activity kit (Sigma) on cell lysate, and activity values were normalized to total protein content measured by a BCA assay (Thermo Fisher). To confirm the reduction of quadrupolar relaxation at the guanidino-carbon by 15N enrichment, 13C NMR spectra for unlabeled and [6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine were obtained in a 14.1T magnet. The full width half max (FWHM) of the guanidino-carbon peak was measured, and the FWHM of the carbon-1 peak was used as an internal standard. For hyperpolarized T1 measurements, [6-13C]-Arginine-HCl or [6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine-HCl was mixed with 1 equiv. HCl and dissolved to a final concentration of 1.3 M in 2:3 H2O:glycerol with 15 mM OX063 radical. The sample was polarized for at least 1 hour in a SpinSolve polarizer. The T1 for the arginine guanidino-carbon was calculated via acquisition of dynamic single-scan 13C NMR spectra with a 30° flip angle and 3s repetition time starting approximately 30s after dissolution using a Magritek 1T NMR, and peak integral vs. time was fit to an exponential decay formula correcting for hyperpolarization loss from the flip angle. This was performed twice and the calculated T1 values were averaged.Results
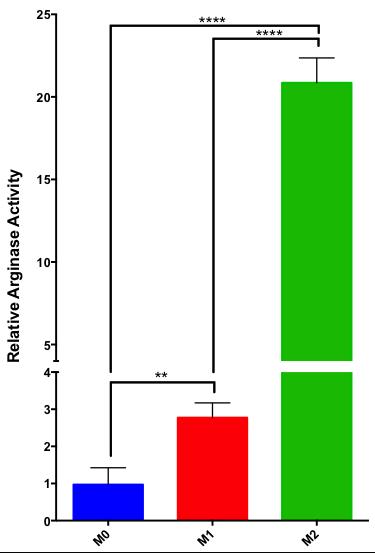
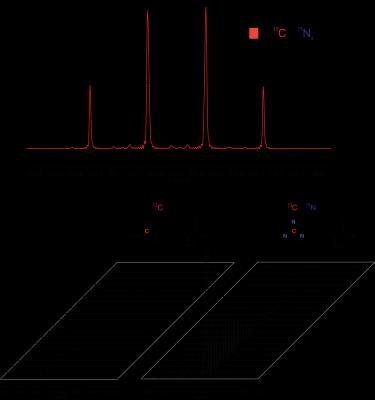
[6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine-HCl was synthesized with an 8.5% overall yield. M2-differentiated murine macrophages exhibit approximately 7-fold increased arginase activity compared to M1-macrophages, and a 20-fold increase compared to undifferentiated Raw 264.8 macrophages (Figure 3). The FWHM of the guanidino-carbon peak for natural abundance and [6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine was measured to be 1.4 Hz and 1.0 Hz, respectively (Figure 4A), and the FWHM of carbon-1 was 0.9 Hz for both compounds. The T1 of the guanidino-carbon of hyperpolarized [6-13C]-Arginine could not be measured due to quadrupolar relaxation, and the T1 of the guanidino-carbon of hyperpolarized [6-13C,6-15N3]Arginine was calculated to be 20.4 ± 0.4s (Figure 4B).Discussion
The arginase activity assay data demonstrates the establishment of an in vitro model for low and high arginase-expressing cells. Future experiments on M2 differentiated cells, which are similar to TAMs, can provide insight into Michaelis-Menten enzyme kinetics of TAM arginase and arginine transporter activity, which can be used to guide future in vivo experiments. The FWHMGuanidino:FWHMCarbon-1 ratio decreases by 29% in the labeled compound, confirming that 15N labeling of arginine reduces quadrupolar relaxation at the guanidino-position. The dynamic HP 13C NMR data reveals the importance of 15N labeling of guanidino-nitrogens towards mitigating quadrupolar relaxation and extending hyperpolarized signal lifetime. This is essential towards future in vivo MRS applications that typically use low field magnets, and quadrupolar relaxation is increased in lower fields.Discussion
Arginase activity can serve as a surrogate for TAM infiltration within tumors, which is a negative prognostic indicator for most tumors. We have outlined the synthesis and polarization of [6-13C,6-15N3]-Arginine which minimizes quadrupolar relaxation at the guanidino-carbon to extend it’s T1, which allows for future in vivo studies that would not be possible without 15N enrichment at the 6-position.Acknowledgements
Grants: NIH P30, Ludwig
Memorial Sloan Kettering's Center for Molecular Imaging and Nanotechnology
References
1. Rath, M., Muller, I., Kropf, P., Closs, E. I. & Munder, M. Metabolism via Arginase or Nitric Oxide Synthase: Two Competing Arginine Pathways in Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 5, 1–10 (2014).
2. Noy, R. & Pollard, J. W. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: From Mechanisms to Therapy. Immunity 41, 49–61 (2014).
3. Ruffell, B. & Coussens, L. M. Macrophages and therapeutic resistance in cancer. Cancer Cell 27, 462–472 (2015).
4. Geiger, R. et al. L-Arginine Modulates T Cell Metabolism and Enhances Survival and Anti-tumor Activity Article L-Arginine Modulates T Cell Metabolism and Enhances Survival and Anti-tumor Activity. Cell 167, 829–836.e13 (2016).
5. Chang, C., Liao, J. C., Kuo, L. & Cytotoxicity, O. T. Macrophage Arginase Promotes Tumor Cell Growth and Suppresses Nitric Oxide-mediated Tumor Cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 61, 1100–1106 (2001).
6. Klug, F. et al. Low-Dose Irradiation Programs Macrophage Differentiation to an iNOS+/M1 Phenotype that Orchestrates Effective T Cell Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 24, 589–602 (2013).
7. Qu, W. et al. Facile synthesis [5-(13)C-4-(2)H(2)]-L-glutamine for hyperpolarized MRS imaging of cancer cell metabolism. Acad. Radiol. 18, 932–9 (2011).
8. Hamilton, D. J. & Sutherland, A. A flexible approach for the synthesis of selectively labelled l-arginine. Tetrahedron Lett. 45, 5739–5741 (2004).
9. Liu, C.-Y. et al. M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells, partially through TLR4/IL-10 signaling pathway. Lab. Investig. 93, 844–54 (2013).
Figures