3012
GABA editing with reduced sensitivity to B1 inhomogeneity and improved detectability at 7T using MEGA-LASER1Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States
Synopsis
GABA spectroscopy is performed at 7T in vitro and in vivo using MEGA-PRESS and MEGA-LASER sequences. MEGA-LASER is shown to be much less sensitive to B1 inhomogeneity, and having higher signal intensity than MEGA-PRESS. Relative inter- and intra-sequence variabilities with respect to B1 inhomogeneity and regional variation are reported. Higher signal intensity in MEGA-LASER is attributed to reduced chemical shift displacement artifact and less signal loss resulting from spatial effects in phase evolution of J-coupled GABA.
Purpose
In
vivo MR spectroscopy (MRS)
of Gamma amino butyric acid (GABA), a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, has
gained popularity in last decade. While spectral editing using MEGA-PRESS
sequence is perhaps the most popular method in GABA MRS, strong chemical shift
displacement error (CSDE) at high field as 7T makes PRESS localization almost
impossible since very high RF amplitude is needed to generate broadband refocusing
pulses to minimize CSDE. Localization by adiabatic refocusing (LASER) method can
mitigate this challenge. MEGA-sLASER (semi LASER) sequence has been used at 7T1, in which 2 pairs
of adiabatic hyperbolic secant (HS) refocusing pulses are used, but it is still
susceptible to B1 inhomogeneity due to the non-adiabatic 90° excitation pulse, which is very important at high field like
7T. LASER provides full adiabatic excitation but compared to sLASER has higher
specific absorption rate (SAR) and TE. However, using gradient modulated
adiabatic pulses it is possible to reduce the SAR and TE of LASER. We have
performed (i) in vitro MEGA-PRESS and
MEGA-LASER scans to study the relative dependences on B1 inhomogeneity of the 2
sequences, and (ii) in vivo scans in
2 different brain locations with the 2 sequences to explore improvement of GABA
editing with MEGA-LASER at 7T and regional dependence thereof.
Methods
Phantom
and volunteer scans were performed at Siemens 7T Magnetom with SC72 gradient
(Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen) using a 32-channel head coil (Nova
Medical). The LASER component consisted of six GOIA-W(16,4)2 adiabatic refocusing pulses, GOIA
duration: 5 ms, BW = 20 kHz, B1 modulation: WURST-16, G modulation: WURST-4,
VERSE factor: 1 , which required
a B1max adiabatic threshold of 570 Hz. Because of the low power the B1 max was
increased by 10% to compensate more for B1 inhomogeneity. For MEGA-LASER
editing, the settings were edit ON = 1.9 ppm OFF = 1.5 ppm (Henry method to
minimize macromolecule3 in vivo) and 7.5 ppm (in vitro), MEGA BW = 103 (in vivo) /145 Hz (in vitro), TE=80/75ms, TR=5500 ms, voxel size = 20×20×20mm3.
The MEGA-PRESS parameters were matched
to that of MEGA-LASER. A water unsuppressed scan (average=1) followed each
editing scan in in vivo scans. The
editing frequencies in the in vitro
scans of a 10 mM GABA and 10 mM glycine (Gly) phantom were adjusted to account
for frequency shift at room temperature. A gradient recalled echo B1 mapping
sequence was run during the in vitro
scan, and 2 voxels differing in B1 strength by ~45% were scanned. Macromolecule minimized GABA editing scans
were run at visual cortex and motor cortex of one healthy volunteer was scanned
using Institutional Review Board approved protocol. MRUI software was used for
data analysis4, which consisted
of (i) phase correction with respect to residual water of the ON and OFF
spectra, (ii) apodization by a 5 Hz Gaussian filter, (iii) zero filling, (iv)
zero and 1st order phase correction as needed, (v) baseline
correction, (vi) subtraction of the averaged OFF spectra from the averaged ON
spectra to obtain the edited spectrum, and (vii) determination of areas under
3.01 ppm GABA peak in the edited spectra, 3.03 ppm creatine (Cr) peak in the
OFF spectra, 3.57 Gly peak (in vitro)
and water peak in water unsuppressed spectra using AMARES.5
Results and Discussion
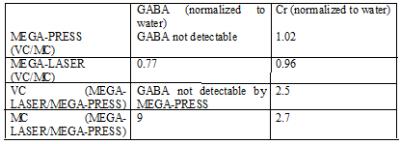
The in vitro results demonstrate that MEGA-PRESS signal intensity is more affected by B1 inhomogeneity (Table 1, Fig. 1). While the effect is seen in both GABA and Gly intensities, GABA is more affected by B1 inhomogeneity, which we speculate is due to more spatial effects (four compartment model) in phase evolution6 in MEGA-PRESS with smaller bandwidth refocusing pulse. In addition, GABA signal in MEGA-LASER is larger than in MEGA-PRESS by a factor of 4.94 and 1.85 in the low and high B1 fields respectively. The in vivo data show considerable improvement of up to nine-fold increase of GABA signal using MEGA-LASER compared to MEGA-PRESS (Table 2, Fig. 2). While more subjects are needed to properly quantify the improvement with MEGA-LASER, combination of in vitro and in vivo results clearly show the significant increase of GABA signal with MEGA-LASER.Conclusion
GABA editing at 7T improves significantly with MEGA-LASER over MEGA-PRESS sequence. The effect of improvement is attributed to reduced CSDE, and less signal loss resulting from spatial effects in phase evolution of J-coupled GABA. In addition, GABA-editing with MEGA-LASER is less affected by B1 inhomogeneity than MEGA-PRESS.Acknowledgements
Cleveland Clinic Research Program Committee, Siemens Medical Solutions (Sineyob Ahn).Figures
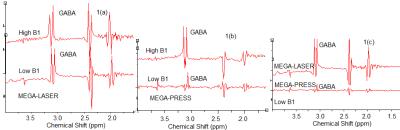
Fig. 1. B1
field change has much less effect on edited GABA intensity in MEGA-LASER (1(a))
than in MEGA-PRESS (1(b)). MEGA-LASER improves GABA intensity in comparison to
MEGA-PRESS in low B1 (1(c)).
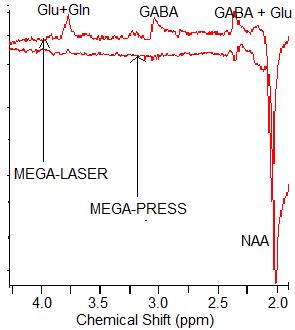
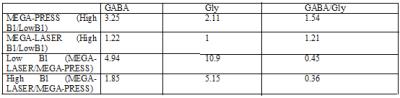
Table 1:
Changes in GABA and Glycine signal intensities between MEGA-LASER and
MEGA-PRESS in vitro scans. GABA
intensity varies more with B1 change, but the overall change is less with
MEGA-LASER.