2810
The Use of Flip Angle Modulation in Zero TE ASL MRA for Improved Angiogram Quality1MR Research China, GE Healthcare, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 2Radiology Department, Peking University People's Hospital
Synopsis
Time resolved MRA is valuable in study of cerebrovascular disorders. ASL based MRA permits visualization of blood flow without injection of contrast agent. Continuous labeling combined with zero TE readout features maximal labeling efficiency and high angiogram fidelity. However, the constant small flip angle excitation scheme limits its applicability in time resolved visualization. This work performed variable flip angle modulation to improve the quality of angiography in zTE-ASL MRA.
Purpose
Time resolved MRA could provide valuable of about the hemodynamics of blood flow pattern, and has been widely used in the study of cerebrovascular disorders [1]. Time resolved MRA used to be only feasible with the contrast enhanced MRA, however not only CE MRA requires the administration of contrast its temporal resolution is determined by the acquisition strategy. Arterial spin labeling (ASL) based dynamic angiography permits time resolved visualization of angiogram with endogenous blood bolus as contrast, and the temporal resolution may be adjusted in the labeling delay time. Among different labeling strategies, continuous ASL strategy features the maximal efficiency, combined with the zero echo time acquisition strategy, high quality angiogram has been demonstrated [2]. However, the SNR of zTE acquisition is limited by the intrinsically small flip angle (FA) used. Repeated excitation train with short intervals may further reduce the overall signal fidelity. This study aims explore the feasibility of variable flip angle (VFA) excitation in ASL MRA to improve the quality of resulting angiogram.Method
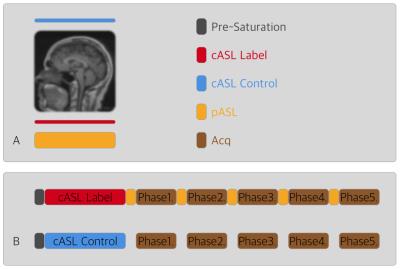
The pulse sequence diagram is illustrated in Fig.1. In zTE dynamic angiography, continuous labeling (cASL) was immediately followed by segmented zTE readouts interleaved with pulsed RF for improved signal level [3], so that supply of inverted blood is ensured during the readout train. Quadrature phase pre-saturation pulse was also implemented to eliminate any residue labeled blood. Conventionally, the zTE readout train uses a constant flip angle strategy that the FA stays the same (3 to 5 degree). In VFA modulation, the FA was changed following quadratic function: flip angle gradually increased with flip angle curve obeys quadratic function. In this way, the inversion difference is consumed less in earlier phases and the inversion based contrast is saved for later phases. The VFA strategy was implemented on a 3.0T whole body system (GE MR 750w, Milwaukee, Wisconsin) equipped with a 24 channel head coil. The imaging parameters were listed as follows. FOV 16cm, isotropic resolution 1.2 mm, continuous labeling duration 500 ms, pulsed tagging duration 50 ms, spokes per readout segment 100. Five phases were acquired with a temporal resolution of 197 ms. The inversion thickness of pASL was set to 75 mm. In constant flip angle prescription, the excitation flip angle was fixed to 3 degree. In VFA prescription, the flip angle was changed from 2 degree to 5 degree gradually. Simulation with the same pulse sequence were performed with artery blood parameters set to: T1/T2 1650/100ms, velocity 40cm/s. A healthy volunteer was recruited for the comparison between the two strategies, consent form was obtained. The angiogram quality with and without FA modulation was compared qualitatively.Result
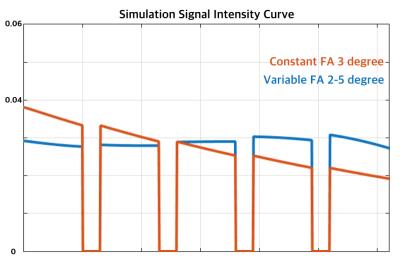
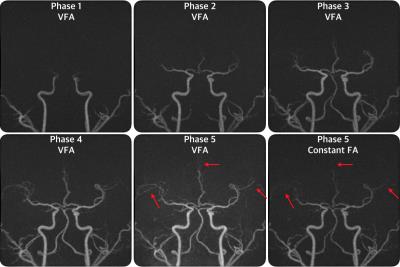
Fig.2 demonstrates the simulation result of signal intensity curve along multi-phase readout. For the last two phases, angiogram with FA modulation has increased signal intensity. The multi-phase zTE MRA results using both constant and variable flip angle strategy are shown in Fig.3. Fig.3a-e are the five phases with variable flip angle modulation. Fig.3f is the last phase of constant flip angle group. It can be seen that the angiogram with VFA shows improved quality compared to constant flip angle excitation (Fig.3e, f). The vessel intensity of feeding end in VFA was brighter in later phases. Distal vessels, indicated by red arrows, could only be seen in VFA exam.Discussion and Conclusion
In this study, a variable flip angle strategy was proposed to improve the signal level in zTE based ASL MRA. With smaller excitation angle, the inversion based contrast was consumed less in earlier phases. Increasing the flip angle in later phases improves the angiogram quality. The flip angle variation may be further explored for optimal pattern.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Y.Iryo, etc., Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Evaluation with 3T 4D MRA using ASL, Radiology, 2014
[2] I.Koktzoglou, etc., Arterial Spin Labeled Carotid MRA: A Phantom Study Examining the Impact of Technical and Hemodynamic Factors, MRM, 2015
[3] L.Yan, etc., Time-Resolved Noncontrast Enhanced 4D Dynamic MRA Using Multibolus TrueFISP-Based Spin Tagging with Alternating Radiogrequency (TrueSTAR), MRM, 2014
Figures