2793
Does TWIST with iterative reconstruction improve diagnostics of AVM of the hand?1Institute of Radiology, University Hospital Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany, 2Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
Synopsis
Highly accelerated TWIST MRA with standard and iterative reconstruction was compared to a standard TWIST technique in 11 patients with AVM of the hand and/or fingers. Qualitative and quantitative analysis revealed significant advantages for the accelerated protocol with iterative reconstruction: Separation of arterial and venous phase as well as delineation of central and peripheral arterial feeders were significantly improved due to higher temporal resolution compared with our standard protocol while maintaining high spatial resolution.
Purpose
TWIST MRA with its ability for high spatial and temporal resolution is an important non-invasive tool to visualize the extent, angioarchitecture, and hemodynamics of vascular malformations for treatment planning. Imaging of arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) of the hand remains a major challenge even with TWIST MRA that yields sufficient spatial but not temporal resolution. Iterative reconstruction has shown the potential to improve temporal resolution and/or delineation of small vessels 1, 2. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess the value of iterative reconstruction in TWIST for AVM of the hand in comparison to our standard TWIST protocol.Methods
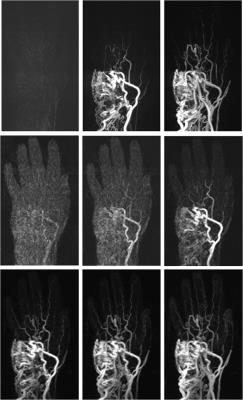
11 patients with AVM of the hand and/or fingers underwent MRI for interventional treatment planning or follow-up. All patients (9 women, 2 men, age: 27-78 years, mean: 43 years) were examined at 3T (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) using a 16-channel hand/wrist coil. 2 TWIST acquisitions were applied to all patients: our routine protocol with an acceleration (PAT) factor of 3 (“TWIST_3”), a voxel size of 0.77mmx0.70mmx0.83mm, and a 3D data set reconstructed each 5.57s, and “TWIST_12”, a protocol with improved temporal resolution (a 3D data set reconstructed each 1.44s), PAT 12, voxel size (0.72mm)3. All MRAs were acquired with a low dose of Gadovist (20-50% of a single dose). TWIST_12 was reconstructed with the standard view sharing technique and with a prototype iterative reconstruction 1. Furthermore, iterative reconstruction was performed with 4 different regularization factors 0.001, 0.002, 0.004, 0.008.
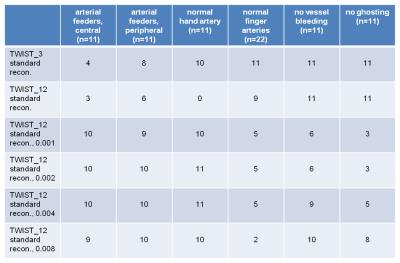
A small ROI (area: 0.02cm2) was placed within a major hand artery, and mean signal intensity was divided by standard deviation in this ROI to calculate an apparent “vessel SNR”. Delay of venous versus arterial phase was determined by measuring the peak signal intensity in major arteries (the common digital arteries or the radial/ulnar artery – depending on the extent of the AVM) and the adjacent dominant outflow vein. Visual evaluation was performed by an experienced interventional radiologist: Identification and delineation of arterial feeders (yes or no) were evaluated directly adjacent to the nidus (central) and in more distant regions (peripheral). Delineation of not affected arteries was judged in an unaffected finger and in the hand (preferably: deep palmar arch) on a 4-point scale (uniform, nearly uniform, partial, or no delineation). Furthermore, bleeding (involving the radial or ulnar artery) and ghosting artifacts were judged on a 3-point scale (not present; present, but not relevant; diagnostically relevant). Statistics were calculated with the sign-test: results with p<0.05 were regarded significant.
Results
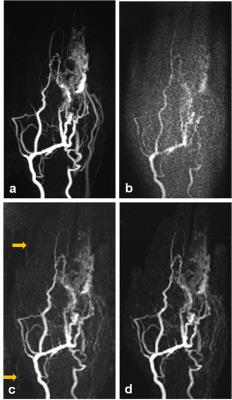
On average, vessel SNR in major hand arteries was improved by a factor of 2.71 using iterative reconstruction. Calculation time was about 8min 30s for 50 volumes with a 320x320 matrix size and performed directly at the scanner utilizing its GPU. In 4 patients, the temporal resolution of our standard TWIST protocol was not sufficient to discriminate major arteries and dominant outflow veins while this discrimination was possible with TWIST_12 in all patients. Central delineation of arterial feeders was significantly improved by iterative reconstruction in TWIST_12 and in comparison to TWIST_3 (Figs. 1-3); the difference for peripheral delineation was not statistically significant. Delineation of hand arteries was significantly improved by iterative reconstruction, but no diagnostic advantage was seen compared to TWIST_3. Iterative reconstruction did not improve delineation of normal finger arteries. Severe bleeding was seen in 3, severe ghosting in 4 patients using iterative reconstruction with a regularization factor of 0.001; increasing the regularization factor helped to reduce those disadvantages. Larger regularization factors, however, resulted in blurring of small vessels with inferior delineation of normal finger arteries.Discussion
Differentiation of arteries and veins as well as identification and delineation of arterial feeders – the most important tasks of pre-therapeutical MR in AVM – were significantly improved using a TWIST protocol with increased temporal resolution and iterative reconstruction. This protocol proved to be a robust tool to image AVM of the hand and/or fingers with a low dose of gadolinium contrast agent (down to 20% of a single dose) even without dedicated timing or application of a preceding test-bolus. Iterative reconstruction was able to compensate for the SNR reduction caused by a high acceleration factor. Delineation of normal vessels was similar to our optimized standard TWIST protocol which uses a nearly identical voxel size. Applying a regularization factor of 0.004 or 0.002 yielded the best results for the current algorithm.Conclusion
TWIST with increased temporal resolution and iterative reconstruction is superior in differentiating arterial versus venous phase and in delineating arterial feeders and, therefore, resulted in improved diagnostics of AVM of the hand and/or fingers.Acknowledgements
noneReferences
1. Stalder AF, Schmidt M, Quick HH, et al.: Highly undersampled contrast-enhanced MRA with iterative reconstruction: integration in a clinical setting. Magn Reson Med 2015; 74: 1652-1660. 2. Wetzl J, Forman C, Wintersperger BJ, et al. High-resolution dynamic CE-MRA of the thorax enabled by iterative TWIST reconstruction. Magn Reson Med 2016 (epub ahead of print).Figures