2772
MR Imaging of Vasa Vasorum During Lipid-Lowering Therapy to Carotid Unstable Plaque: A Prospective Study in Chinese Patients1Bethune international peace hospital, Shi jiazhuang, People's Republic of China, 2Chinese PLA general hospital
Synopsis
Carotid plaque vasa vasorum angiogenesis from adventitia may be influenced by inflammation, could promote intraplaque hemorrhage and decrease the thickness of fibrous cap, finally, the cap is prone to rupture. Drug therapy and assessment to the vulnerable plaque, in vivo, would be of major clinical interest. To investigate whether lipid therapy leads to changes in vasa vasorum characteristics of carotid unstable plaque in chinese patients, as measured by using dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI. Focus on inflammation to monitor the early beneficial therapy using vasa vasorum MR imaging, biomarker in vivo.
Introduction
Markers of inflammation by the dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI may be fastest response of the beneficial therapy in vivo. However, the correlation in the unstable plaque, overlaid thin fibrous caps or with intraplaque hemorrhage(IPH), has not been well studied.Objectives
To evaluate whether the intensive lipid therapy could reduce the vasa vasorum perfusion and improve plaque composition with IPH by MRI. And to evaluate whether the intensive lipid therapy could reduce the intraplaque vasa vasorum perfusion in the carotid plaque overlaid thin fibrous caps by the DCE-MRI.Method
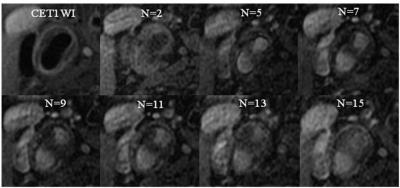
Study Population: Between March 2009 and March 2012, the prospective study, Rosuvastatin Evaluation of Atherosclerotic Chinese Patients (REACH Study, NCT 00885872), recruited 32 subjects with advanced lesions(≥3 mm thickness without >50% calcification), matched MRI scans and acceptable image quality. All subjects received rosuvastatin 5~20 mg/d to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels to < 80 mg/dl over the 24-month follow-up period. MR Imaging Protocol: Carotid high-resolution(HR) MRI and DCE-MRI were underwent at baseline and 3, 12 , 24 months at a 3.0T whole body scanner (GE) with a 4-channel phased-array carotid surface coil. A standardized protocol was used to acquire T1-weighted, T2-weighted black-blood images and 3D-TOF bright-blood angiographic images. DCE-MRI using double inversion recovery technique was performed on six selected axial slices chosen from T1-weighted image set at 15 times separated by a repetition interval of 16 seconds. The acquisition of the forth time was coincident with the initiation of the intravenous injection of 0.2 mmol/kg gadolinium-based contrast agent at a rate of 2 ml/sec through a power injector. After the DCE-MRI scanning, the T1-weighted sequence was repeated to achieve the contrast-enhanced images. Data analysis: Plaque composition was analyzed using CASCADE(IBMarker Company). Thin fibrous cap appears as the absence of hypointense juxtaluminal band in time-of-flight images without a region of hyperintensity in plaque adjacent to the lumen. The DCE-MR imaging analysis was performed using the population arterial input function and Patlak model 3 to calculate kinetic parameters Vp and Ktrans for each pixel based on its temporal changes in intensity on the ≥3 mm thick slice. The analysis of perfusion was performed with blinding to the composition.Results
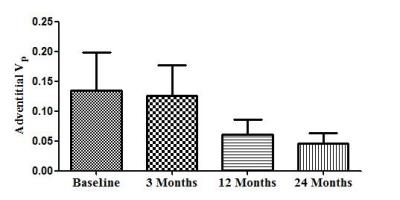
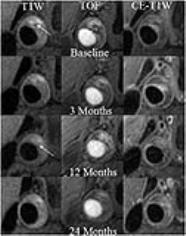
Among the 32 subjects, there were 2 cases shows IPH. After 12 and 24 months of treatment, there was a obvious reduction was found in mean adventitial Vp (0.134 ± 0.090[standard deviation] to 0.061 ± 0.036, 0.046±0.024. Fig. 1), but no statistically significant trend between baseline and 3 months(0.126 ± 0.073. Fig. 1). The HRMRI indicated that there was no significant improvement in composition of IPH during 24-month treatment (Fig. 2). HRMRI example of irreversible IPH and time points.
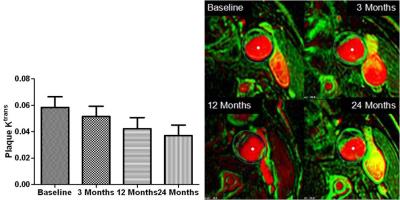
In total, 6 cases had thin fibrous caps without intraplaque hemorrhage. After 12 and 24 months of treatment, there was a obvious reduction was found in mean plaque Ktrans (0.0486 ± 0.0289[standard deviation] to 0.0422 ± 0.0166, 0.0370 ± 0.0179. Fig. 3), no statistically significant trend between baseline and 3 months(0.0486 ± 0.0149). The thinning of fibrous caps might be gradually thickening within the first one year after treatment(Fig. 4).
Discussion and Conclusions
In conclusion, evaluation of effects of lipid-lowering therapy on atherosclerotic plaques with IPH should be focused on inflammatory activity rather than composition and plaque burden. IPH may be irreversible content within the first one year after treatment.
Evaluation of effects of lipid-lowering therapy on atherosclerotic plaque with thinning fibrous caps should be focused on inflammatory activity rather than plaque burden.
Lipid-lowering therapy might reduce vasa vasorum perfusion, suppress plaque inflammation, as well as stabilize vulnerable plaque with IPH or thin caps of this study. Imaging markers of inflammation by the DCE-MRI may monitor the early response of the beneficial therapy to carotid unstable plaque. Kinetic parameters of DCE-MRI has the most possibility to become the biomarker in vivo, noninvasively.
Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
1. Libby P. Nature. 2002;420:868.
2. Kolodgie FD, et al. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:2316.
3. Liu L, et al. Stroke. 2011;42:3651.
4. Kerwin WS,et al. MRM. 2008;59:507
5. Gaens ME,et al. Radiology. 2012;266:271.
6. Zhao XQ, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;4:977.
Figures