2727
Myocardial fibrosis is a predictor of adverse outcomes in thalassemia intermedia patients1Fondazione G. Monasterio CNR-Regione Toscana, Pisa, Italy, 2"ARNAS" Civico, Di Cristina Benfratelli, Palermo, Italy, 3Presidio Ospedaliero “Giovanni Paolo II”, Lamezia Terme, Italy, 4Presidio Ospedaliero "Giovanni Paolo II" - Distretto AG2 di Sciacca, Sciacca, Italy, 5Azienda Ospedaliera Civile - O.M.P.A. Ragusa, Ragusa, Italy
Synopsis
Myocardial fibrosis detected by LGE has been confirmed as an independent predictor of CV complications in thalassemia intermedia patients. Our finding is consistent with a growing evidence that LGE has a strong prognostic impact in thalassemic patients, warranting a close clinical and instrumental follow-up.
Purpose
Myocardial fibrosis detected by late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) is currently used to predict adverse cardiovascular events in different cardiomyopathies.1 However, its clinical implications in thalassemia intermedia (TI) have not been studied.
The aim of this study was to assess the distribution and the predictive value of myocardial fibrosis for future events in TI.
Methods
We considered 218 white TI patients (37.82±11.00 years, 113 females) consecutively enrolled in the Myocardial Iron Overload in Thalassemia (MIOT) network2 and free of cardiac complications concomitant to CMR. LGE images were acquired to detect myocardial fibrosis and the extent of LGE areas was quantified using a semiautomatic, previously validated software.3Results
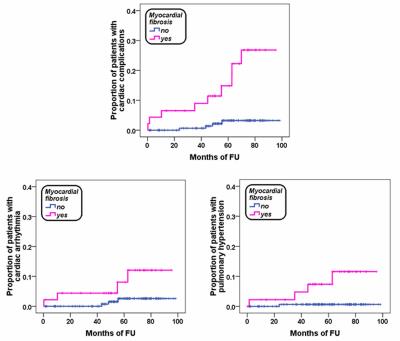
Myocardial fibrosis was detected in 46 patients (21.1%). LGE followed a subendocardial ischemic pattern typical of coronary artery disease in two patients. One patient showed both an ischemic and non ischemic pattern. Thirty-two patients had a single focus while 14 had at least two foci. The mean number of LGE segments per patient was 2.70±1.52. LGE involved the septal region in 76.1% of patients. The extent of LGE areas was 2.09±1.77% of the total left myocardial mass. Twenthy-two (47.8%) patients showed fibrosis in the infero- or anteroseptal junction, 18 (39.1%) had a non ischemic no-junctional pattern (intra or subepicardial) and 6 (13.0) had both a junctional and no-junctional pattern.
Mean follow-up was 56.76±23.17 months. We recorded 13 cardiac complications: 1 heart failure, 7 arrhythmias and 5 pulmonary hypertension (PH). Myocardial fibrosis was a significant prognosticator for arrhythmias, PH and cardiac complications globally considered (see Table). Number of segments with LGE and extent of myocardial fibrosis were comparable in patients who developed cardiac complications versus the patients who did not.
Conclusion
In TI patients, myocardial fibrosis is a predictor of adverse outcome.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Assomull RG, Prasad SK, Lyne J, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance, fibrosis, and prognosis in dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(10):1977-1985.
2. Meloni A, Ramazzotti A, Positano V, et al. Evaluation of a web-based network for reproducible T2* MRI assessment of iron overload in thalassemia. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78(8):503-512.
3. Positano V, Pingitore A, Giorgetti A, et al. A fast and effective method to assess myocardial necrosis by means of contrast magnetic resonance imaging. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2005;7(2):487-494.