Sherman SM Lo1, WL Poon1, KW Tang1, and TL Poon2
1Department of Radiology & Imaging, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Kowloon, Hong Kong, 2Department of Neurosurgery, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Synopsis
Globus pallidus internus (GPi) and Subthalamic
nucleus (STN) are the two main target for deep brain stimulation (DBS) in
treatment for patients with advanced Parkinson's disease (PD) not respond to
medical therapies. MRI brain imaging is used for selection of patients for DBS
and localize the target nucleus. This study confirms that GPi/STN-DBS may be placed
with high accuracy by using a correct and optimal MRI-guided sequences. Correct
deep brain stimulation electodes placement can provides a safe and effective
treatment for severe Parkinson’s disease not responsive to medical therapies.
Background & Purpose
Globus pallidus internus (GPi) and Subthalamic nucleus (STN) are the two
main target for deep brain stimulation (DBS) in treatment for patients with
advanced Parkinson's disease (PD) not respond to medical therapies. MRI brain
imaging is used for selection of patients for DBS and localize the target
nucleus. This study presents the clinical outcomes of patients with PD treated
with GPi/STN DBS using special MRI-guided sequences deep brain nuclei localization
with intra-op microelectrode recording.Materials and Methods
A cohort of 35 patients (17 male; mean age 55) who
underwent GPi/STN DBS were recruited and followed-up clinically for a minimum
period of 1 years. All patients underwent pre-op 3T MRI (Siemens Skyra) study,
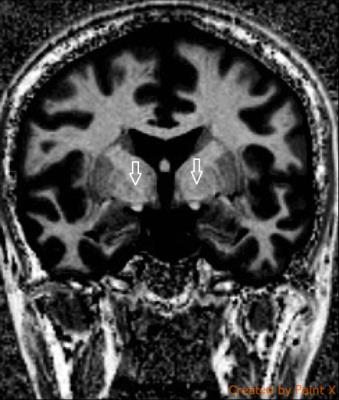
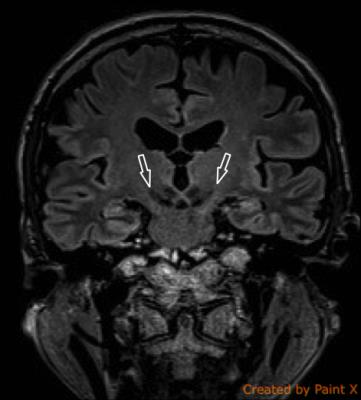
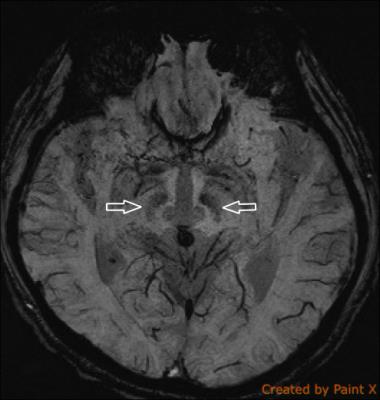
deep brain nuclei were localized using Magnetization-Prepared 2 Rapid
Acquisition Gradient Echo (MP2RAGE) sequence, susceptibility weighted imaging
sequence, and 3D T2 weighted fast spin echo sequence (SPACE).
Preoperative and postoperative motor status was
evaluated using Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale part III
clinical-scored monitored motor evaluation (UPDRS-III), in on- and
off-medication/on-stimulation conditions.
Preoperative and postoperative assessments
further included self-evaluation of activities of daily living (UPDRS-II),
neuropsychological and speech assessments. Active contacts localisation was
calculated and compared with clinical outcomes.
Results and Discussion
All pre-op MR imaging deep brain nuclei
stereotactic data obtained excellent precision with verification of intra-op
microelectrode monitoring.
MRI guided GPi/STN DBS significantly improved
1st year off-medication UPDRS-II & III scores, compared with baseline
(preoperative UPDRS II 21.9 +/-10.9. UPDRS III 53.3 +/-15.9; postoperative UPDRS
II 13.2 +/- 7.8, UPDRS III 25.5 +/- 8.6; p<0.05). Dyskinesia scale
(preoperative dyskinesia scale 76 +/- 12.1; postoperative dyskinesia scale 41.9
+/-12.0; p<0.05), motor fluctuations and demands in dopaminergic medication
remained significantly reduced. Only one complication, perioperative
subarachnoid hemorrhage, encountered out of 35 patients.
In this study, we used new MRI sequence
(MP2RAGE) and other MRI sequences for accurate localization of Gpi/STN and achieved
correct placement of deep brain stimulation electrodes. This can be used as a
sole navigation technique without the use of physiologic monitoring, such as
microelectrode recording.
Conclusions
Our data confirm that GPi/STN-DBS may be placed with high accuracy by
using a correct and optimal MRI-guided sequences. Correct deep brain
stimulation electodes placement can provides a safe and effective treatment for
severe Parkinson’s disease not responsive to medical therapies.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.